1. Peters JM, Ansari MQ. Multiparameter flow cytometry in the diagnosis and management of acute leukemia. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2011; 135:44–54. PMID:
21204710.

2. Béné MC. Biphenotypic, bilineal, ambiguous or mixed lineage: strange leukemias! Haematologica. 2009; 94:891–893. PMID:
19570749.

3. Wolach O, Stone RM. How I treat mixed-phenotype acute leukemia. Blood. 2015; 125:2477–2485. PMID:
25605373.

4. Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, et al. The 2008 revision of the WHO classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: rationale and important changes. Blood. 2009; 114:937–951. PMID:
19357394.
5. Zhao XF, Gojo I, York T, Ning Y, Baer MR. Diagnosis of biphenotypic acute leukemia: a paradigmatic approach. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2009; 3:75–86. PMID:
19918331.
6. Weinberg OK, Seetharam M, Ren L, Alizadeh A, Arber DA. Mixed phenotype acute leukemia: A study of 61 cases using World Health Organization and European Group for the Immunological Classification of Leukaemias criteria. Am J Clin Pathol. 2014; 142:803–808. PMID:
25389334.
7. Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian R, et al. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood. 2016; 127:2391–2405. PMID:
27069254.

8. Béné MC, Porwit A. Acute leukemias of ambiguous lineage. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2012; 29:12–18. PMID:
22372202.

9. Killick S, Matutes E, Powles RL, et al. Outcome of biphenotypic acute leukemia. Haematologica. 1999; 84:699–706. PMID:
10457405.
10. Matutes E, Pickl WF, Van't Veer M, et al. Mixed-phenotype acute leukemia: clinical and laboratory features and outcome in 100 patients defined according to the WHO 2008 classification. Blood. 2011; 117:3163–3171. PMID:
21228332.

11. van den Ancker W, Terwijn M, Westers TM, et al. Acute leukemias of ambiguous lineage: diagnostic consequences of the WHO2008 classification. Leukemia. 2010; 24:1392–1396. PMID:
20485373.

12. Cheson BD, Bennett JM, Kopecky KJ, et al. Revised recommendations of the International Working Group for Diagnosis, Standardization of Response Criteria, Treatment Outcomes, and Reporting Standards for Therapeutic Trials in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2003; 21:4642–4649. PMID:
14673054.

13. Vignetti M, Orsini E, Petti MC, et al. Probability of long-term disease-free survival for acute myeloid leukemia patients after first relapse: A single-centre experience. Ann Oncol. 1996; 7:933–938. PMID:
9006744.

14. Buyse M, Michiels S, Squifflet P, et al. Leukemia-free survival as a surrogate end point for overall survival in the evaluation of maintenance therapy for patients with acute myeloid leukemia in complete remission. Haematologica. 2011; 96:1106–1112. PMID:
21546500.

15. Craig FE, Foon KA. Flow cytometric immunophenotyping for hematologic neoplasms. Blood. 2008; 111:3941–3967. PMID:
18198345.

16. Chiaretti S, Zini G, Bassan R. Diagnosis and subclassification of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2014; 6:e2014073. PMID:
25408859.

17. Deininger M, Lehmann T, Krahl R, Hennig E, Müller C, Niederwieser D. No evidence for persistence of BCR-ABL-positive cells in patients in molecular remission after conventional allogenic transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2000; 96:779–780. PMID:
10950517.
18. Heesch S, Neumann M, Schwartz S, et al. Acute leukemias of ambiguous lineage in adults: molecular and clinical characterization. Ann Hematol. 2013; 92:747–758. PMID:
23412561.

19. Xu XQ, Wang JM, Lü SQ, et al. Clinical and biological characteristics of adult biphenotypic acute leukemia in comparison with that of acute myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a case series of a Chinese population. Haematologica. 2009; 94:919–927. PMID:
19454497.

20. Yan L, Ping N, Zhu M, et al. Clinical, immunophenotypic, cytogenetic, and molecular genetic features in 117 adult patients with mixed-phenotype acute leukemia defined by WHO-2008 classification. Haematologica. 2012; 97:1708–1712. PMID:
22581002.

21. Shi R, Munker R. Survival of patients with mixed phenotype acute leukemias: A large population-based study. Leuk Res. 2015; 39:606–616. PMID:
25858895.

22. Zhang Y, Wu D, Sun A, et al. Clinical characteristics, biological profile, and outcome of biphenotypic acute leukemia: a case series. Acta Haematol. 2011; 125:210–218. PMID:
21266800.

23. Liu QF, Fan ZP, Wu MQ, et al. Allo-HSCT for acute leukemia of ambiguous lineage in adults: the comparison between standard conditioning and intensified conditioning regimens. Ann Hematol. 2013; 92:679–687. PMID:
23274355.

24. Lee JH, Min YH, Chung CW, et al. Prognostic implications of the immunophenotype in biphenotypic acute leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2008; 49:700–709. PMID:
18398737.

25. Kawajiri C, Tanaka H, Hashimoto S, et al. Successful treatment of Philadelphia chromosome-positive mixed phenotype acute leukemia by appropriate alternation of second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors according to BCR-ABL1 mutation status. Int J Hematol. 2014; 99:513–518. PMID:
24532437.

26. Shimizu H, Saitoh T, Machida S, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for adult patients with mixed phenotype acute leukemia: results of a matched-pair analysis. Eur J Haematol. 2015; 95:455–460. PMID:
25605541.

27. Al-Seraihy AS, Owaidah TM, Ayas M, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcome of children with biphenotypic acute leukemia. Haematologica. 2009; 94:1682–1690. PMID:
19713227.

28. He G, Wu D, Sun A, et al. B-Lymphoid and myeloid lineages biphenotypic acute leukemia with t(8;21)(q22;q22). Int J Hematol. 2008; 87:132–136. PMID:
18288568.

29. de Leeuw DC, van den Ancker W, Denkers F, et al. MicroRNA profiling can classify acute leukemias of ambiguous lineage as either acute myeloid leukemia or acute lymphoid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 2013; 19:2187–2196. PMID:
23444217.

30. Manola KN. Cytogenetic abnormalities in acute leukaemia of ambiguous lineage: an overview. Br J Haematol. 2013; 163:24–39. PMID:
23888868.

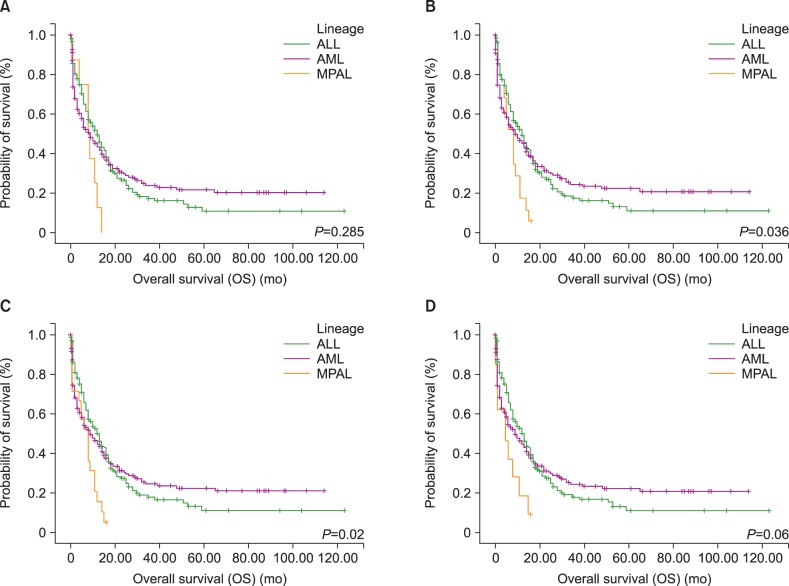
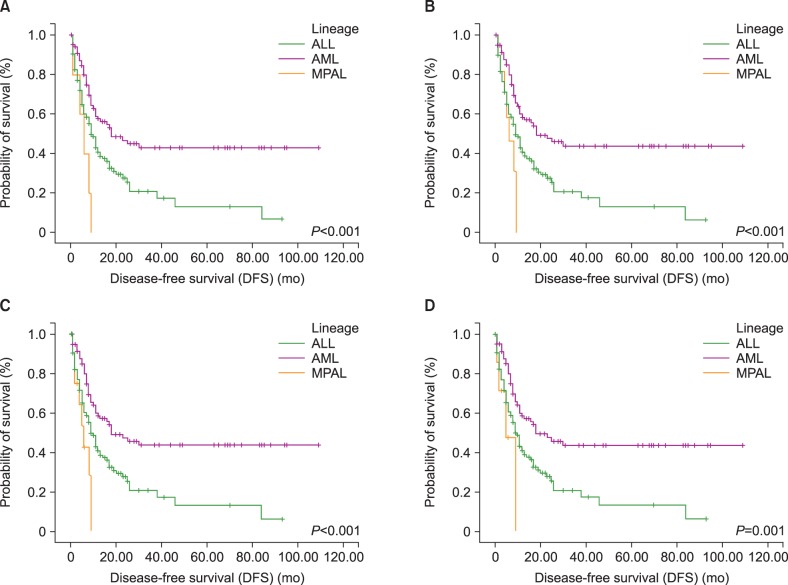
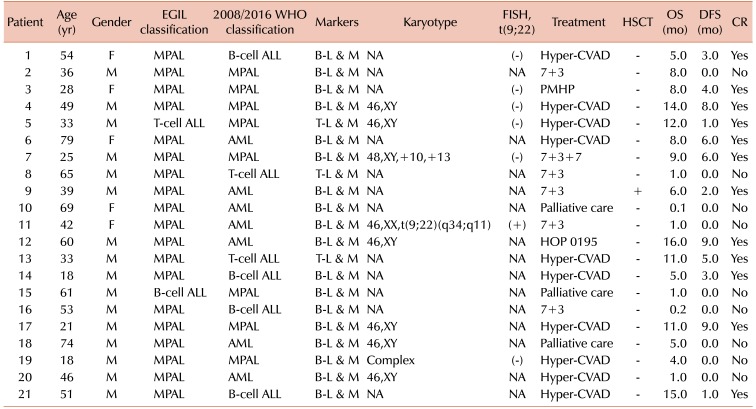
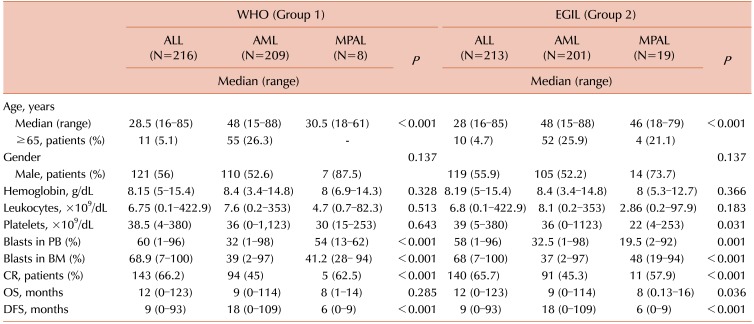




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download