A 74-year-old woman with multiple myeloma (MM) presented with fever and diffuse abdominal pain. She had received 2 cycles of chemotherapy with thalidomide-cyclophosphamide-dexamethasone for relapsed MM after previous chemotherapy with bortezomib-melphalan-prednisolone and lenalidomide-dexamethasone.
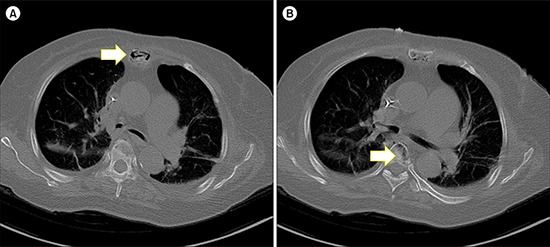
She developed septic shock, and Escherichia coli was observed in her blood culture. She gradually improved with antibiotics (meropenem). Chest computed tomography (CT) showed incidental intraosseous gas in her sternum (A) and T6 vertebra (B), which was absent on CT images taken 3 months prior. Following the diagnosis of emphysematous osteomyelitis due to E. coli, antibiotics and supportive care were continued. The patient recovered and was discharged 20 days later.
Intraosseous gas is a sign of emphysematous osteomyelitis caused by gas-forming organisms. Important differential diagnoses include degenerative diseases, trauma (including iatrogenic), or less commonly, neoplasm. However, when a patient with MM presents with bone lesions and concomitant intraosseous gas, the lesion could be misinterpreted as a destructive manifestation of MM without suspicion of infection.
These CT findings call attention to various bony manifestations of MM. Our findings also raise concern about osteomyelitis and/or emphysematous osteomyelitis, especially in a patient with confirmed bacteremia and bony manifestations.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download