INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study design
Treatment and evaluation
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Patient characteristics
Table 1
Clinical and laboratory characteristics of the patients.
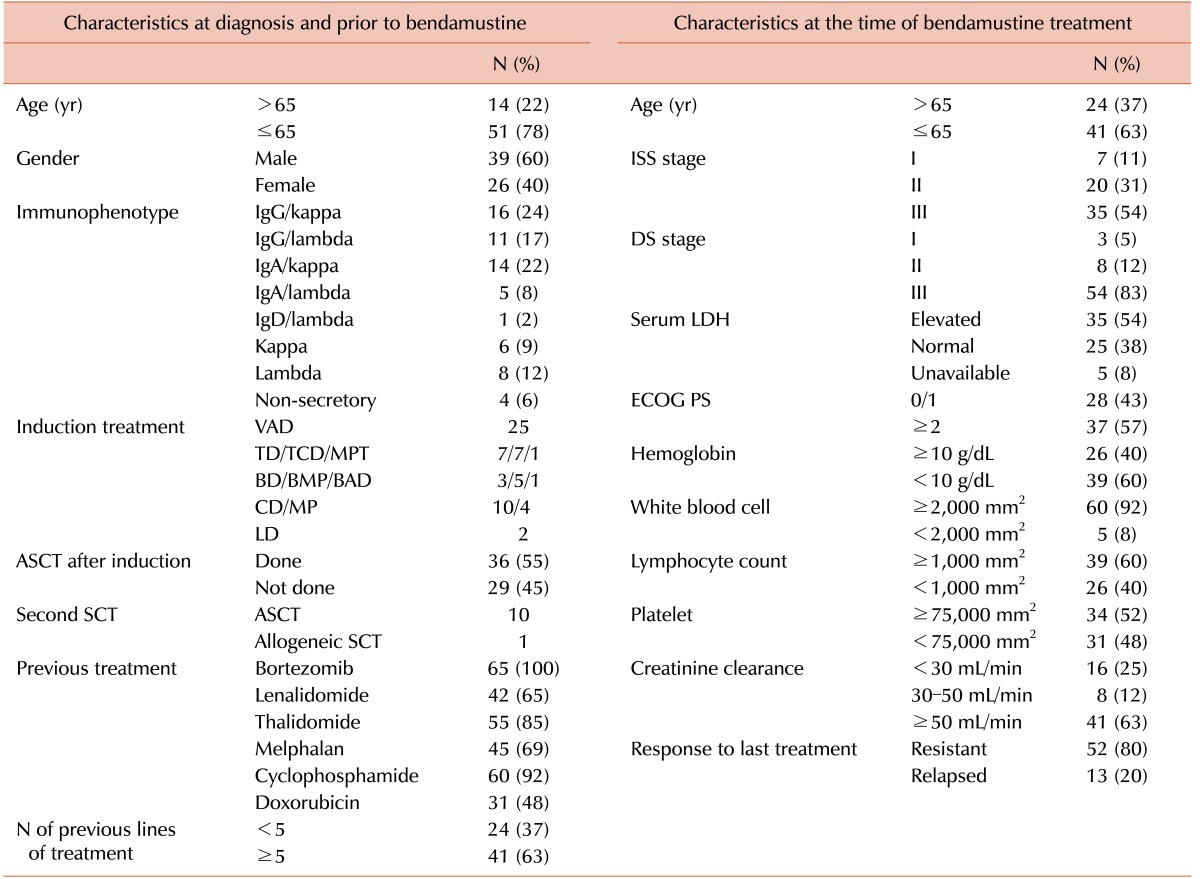
Abbreviations: ASCT, autologous stem cell transplantation; BAD, bortezomib, doxorubicin, dexamethasone; BD, bortezomib, dexamethasone; BMP, bortezomib, melphalan, prednisolone; CD, cyclophosphamide, dexamethasone; DS, Durie-Salmon; ECOG, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; ISS, International Staging System; LD, lenalidomide, dexamethasone; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; MP, melphalan, prednisolone; MPT, melphalan, prednisolone, thalidomide; PS, performance status; TD, thalidomide, dexamethasone; TCD, thalidomide, cyclophosphamide, dexamethasone; SCT, stem cell transplantation; VAD, vincristine, doxorubicin, dexamethasone.
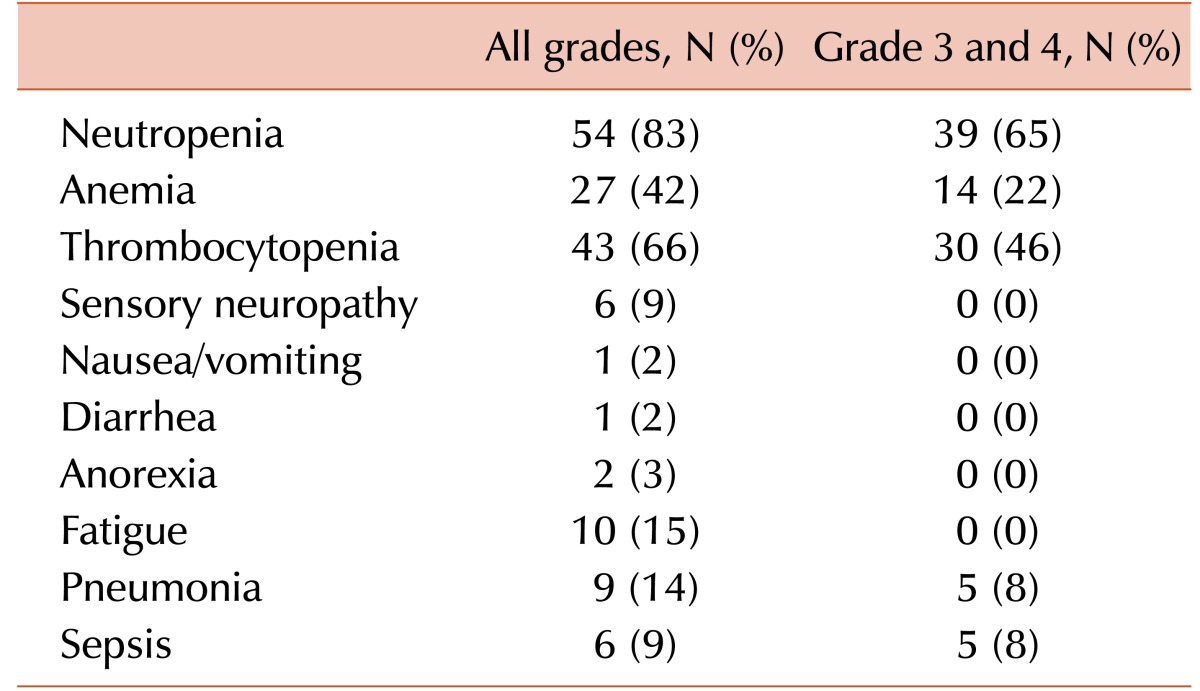
Response and toxicity
Survival outcome
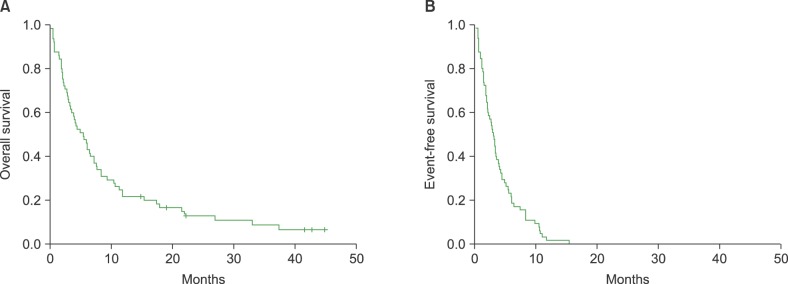 | Fig. 1(A, B) Median overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) after bendamustine treatment was 5.5 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 3.5–7.5 mo) and 3.1 months (95% CI, 2.4–3.8 mo), respectively. |
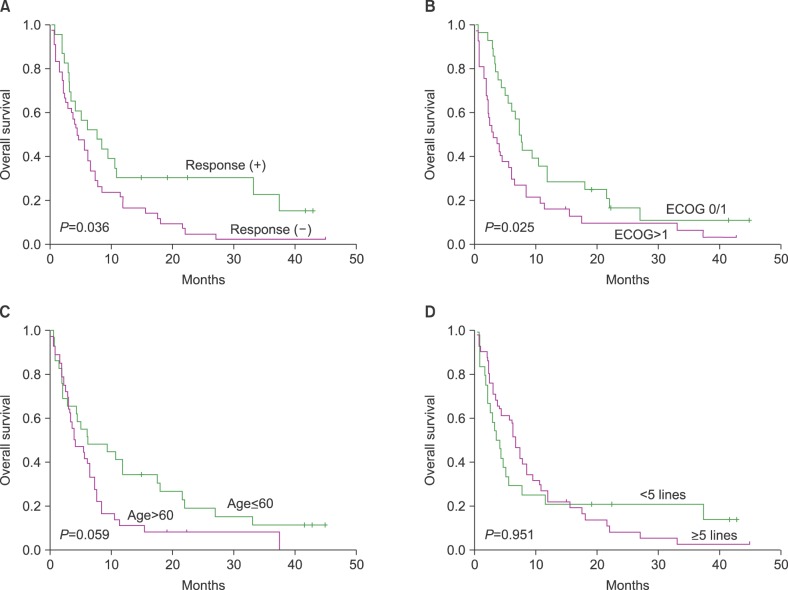 | Fig. 2(A) The OS of patients who responded to bendamustine was significantly better than that of patients who did not. (B) Performance status at the time of bendamustine treatment was significantly associated with OS. (C) Patients ≤60 years old at the time of bendamustine treatment showed a trend towards better OS. (D) The median number of lines prior to bendamustine treatment was not associated with OS. |
DISCUSSION
Table 3
Comparisons between multicenter studies of bendamustine treatment for relapsed or refractory myeloma.
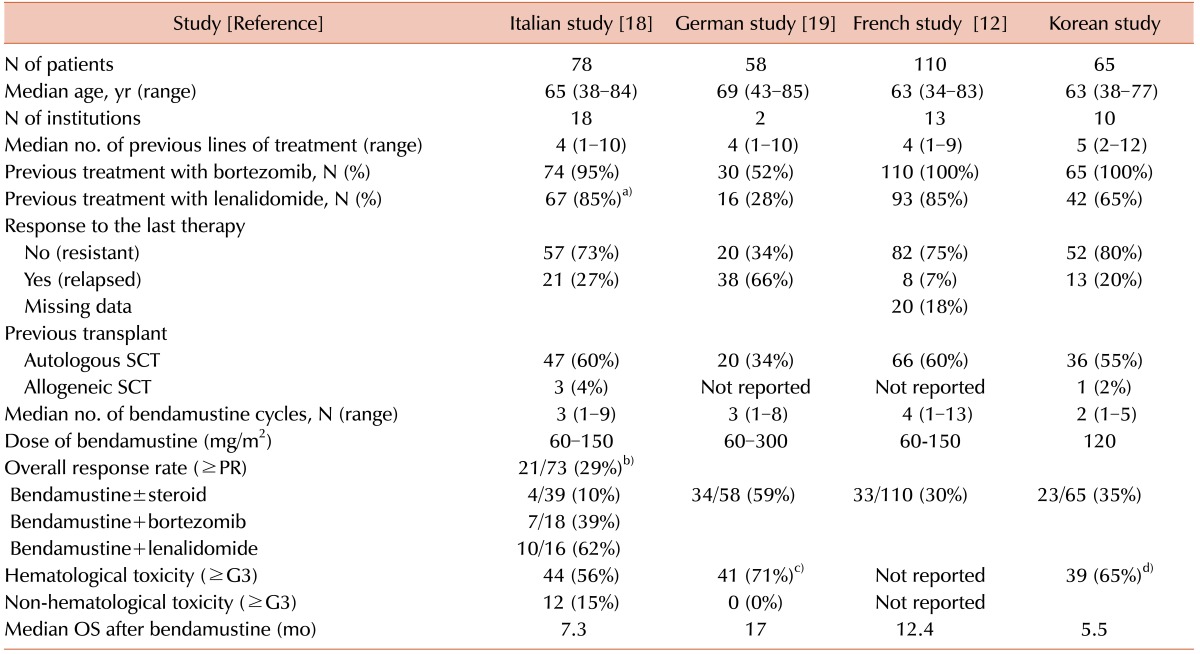
a)This study just described the percentage of patients exposed to immunomodulatory drugs. b)The ORR of the study included the response rates of different regimens. c)The hematologic toxicity was based on grade 3/4 anemia. d)The hematologic toxicity was based on grade 3/4 neutropenia.
Abbreviations: G, grade; OS, overall survival; PR, partial response; SCT, stem cell transplantation.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download