INTRODUCTION
PATIENTS AND METHODS
Cytogenetic study
Azacitidine treatment
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Patients
Table 1
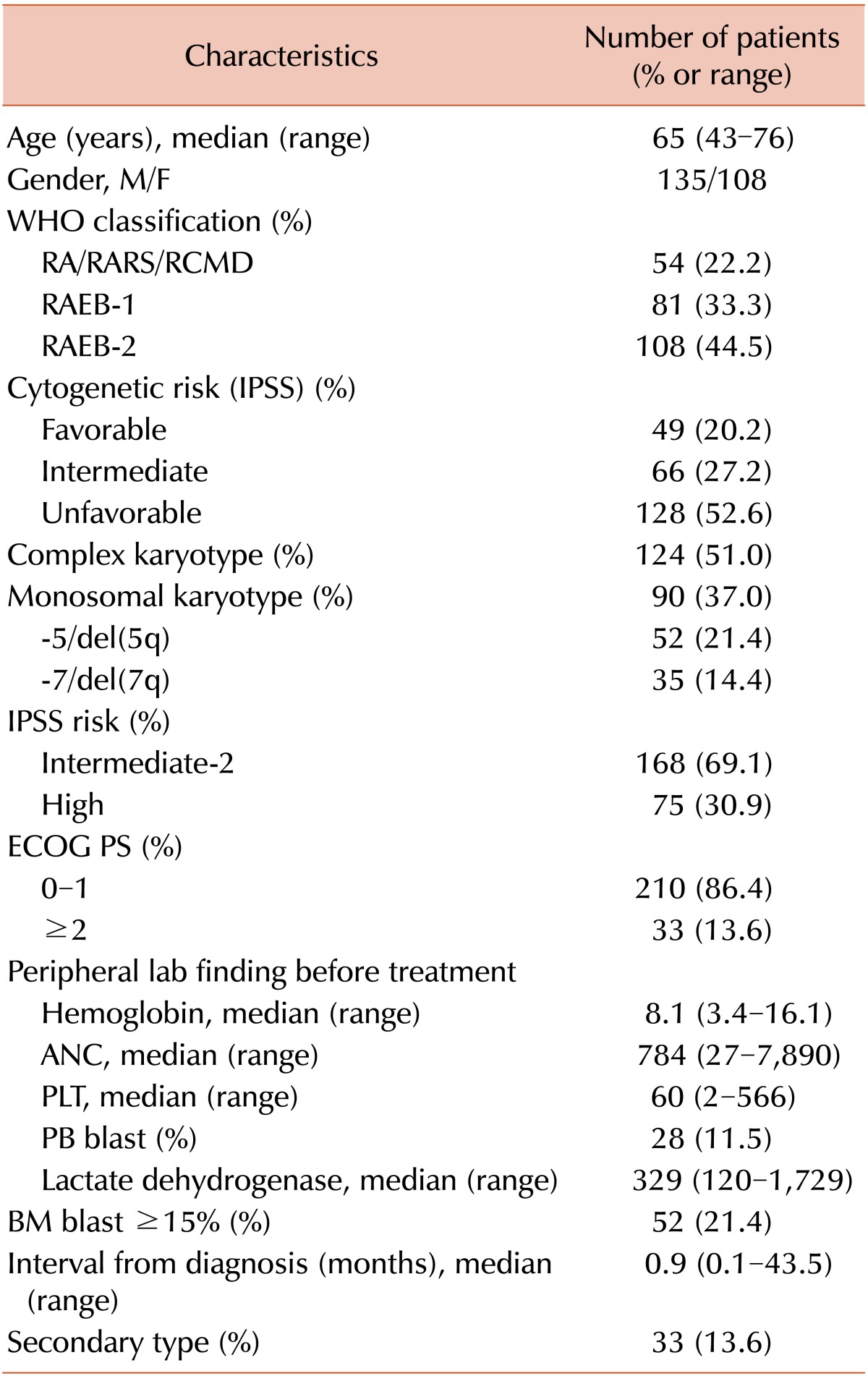
Abbreviations: RA, refractory anemia; RAEB, refractory anemia with excess blasts; RARS, refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts; RCMD, refractory cytopenia with multilineage dysplasia; IPSS, International Prognostic Scoring System; ECOG PS, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status; ANC, absolute neutrophil count; PLT, platelet; PB, peripheral blood; BM, bone marrow; M/F, male/female; WHO, World Health Organization.
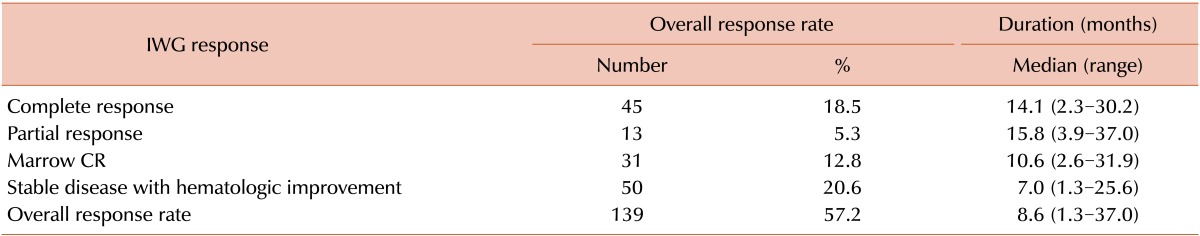
Overall response rate and prognostic factors
Table 3
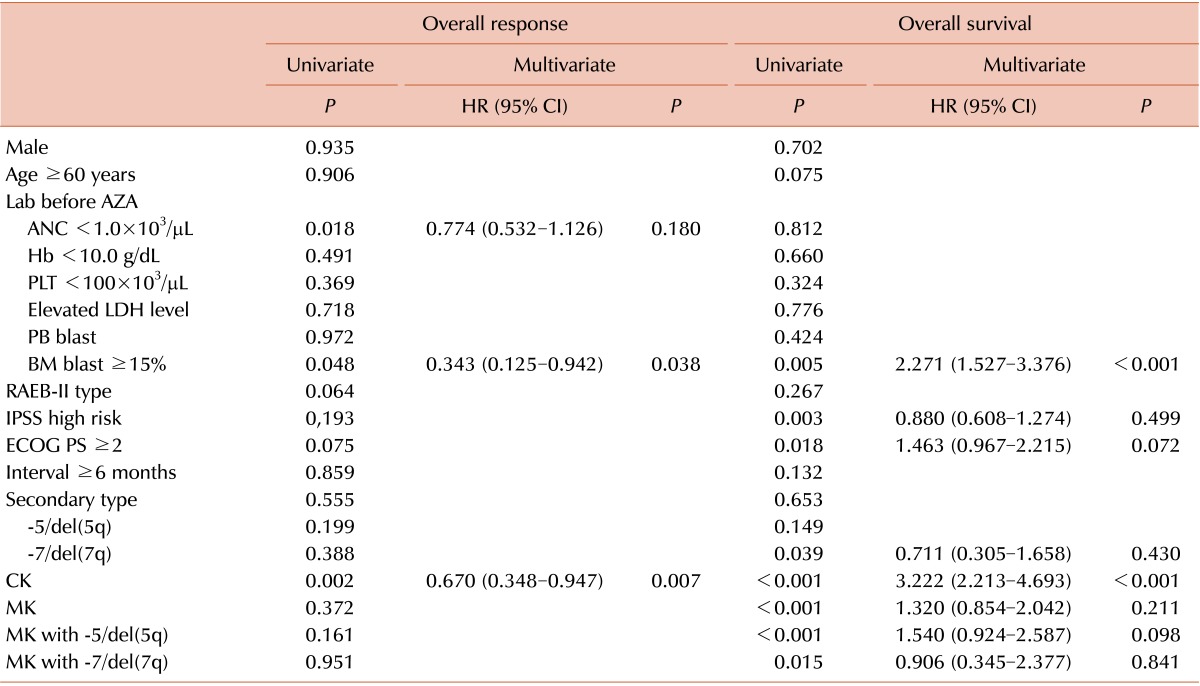
Abbreviations: AZA, azacitidin; ANC, absolute neutrophil count; Hb, hemoglobin; PLT, platelet; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; PB, peripheral blood; BM, bone marrow; RAEB, refractory anemia with excess blasts; IPSS, International Prognostic Scoring System; ECOG PS, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status; CK, complex karyotype; MK, monosomal karyotype; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval.
Overall survival and prognostic factors
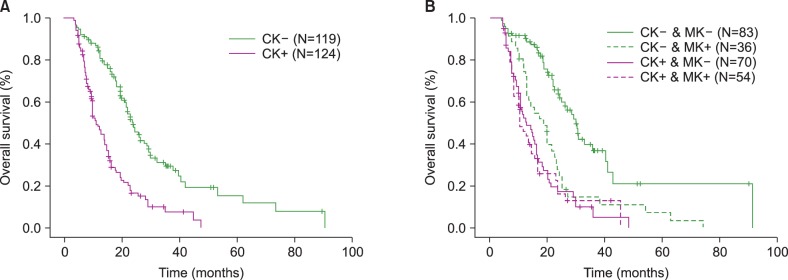 | Fig. 1Comparisons of overall survival (OS) in patients treated with azacitidine according to the presence of a complex karyotype (CK); chromosomal abnormalities [CA] ≥3 (A) and OS according to the presence of a CK (CA≥3) combined with the monosomal karyotype (MK) (B). OS in the group without CK was significantly lower compared to the group with CK in a median follow-up time of 24.2 months (OS, 21.8% in the group with CK, 37.8% in the group without CK, P <0.001) (A). The MK negative status in the group without CK was higher than the other 3 groups (OS of MK +/- in the group without CK, 18.7% vs. 44.8%; MK +/- in the group with CK, 22.2% vs. 21.4%; P <0.001) (B). However, the differences in OS among the other 3 groups were not significant. |
Impact of monosomal karyotype on survival in patients with/without complex karyotype
Table 4
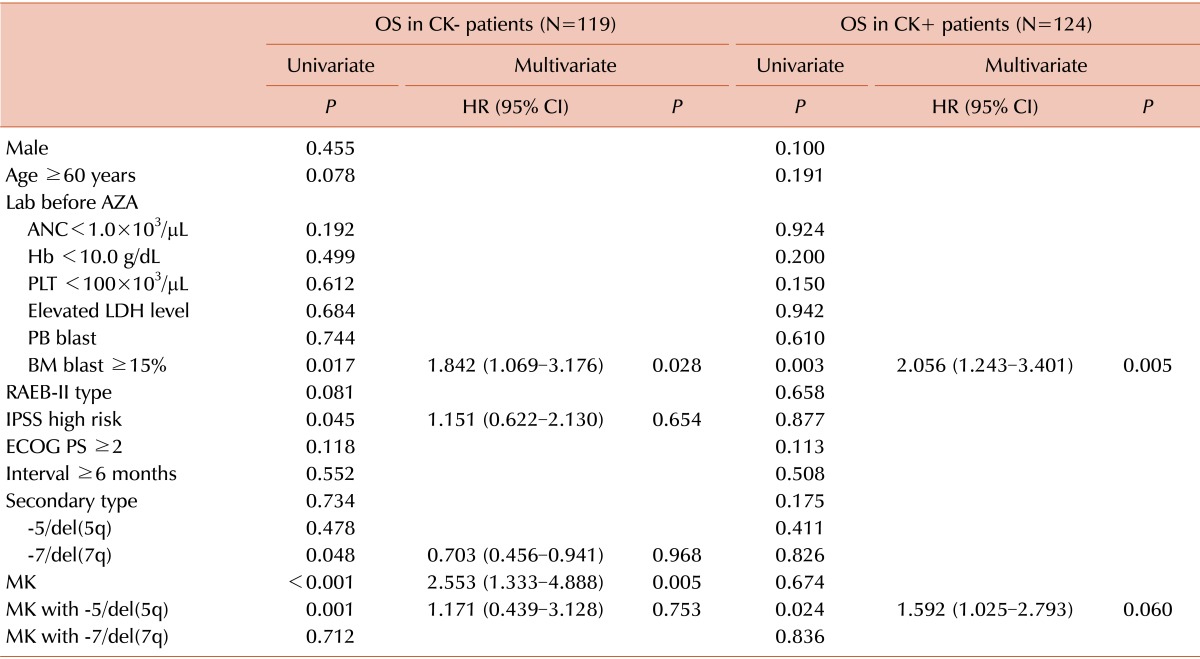
Abbreviations: AZA, azacitidine; ANC, absolute neutrophil count; Hb, hemoglobin; PLT, platelet; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; PB, peripheral blood; BM, bone marrow; RAEB, refractory anemia with excess blast; IPSS, International Prognostic Scoring System; ECOG PS, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status; CK, complex karyotype; MK, monosomal karyotype; OS, overall survival; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval.
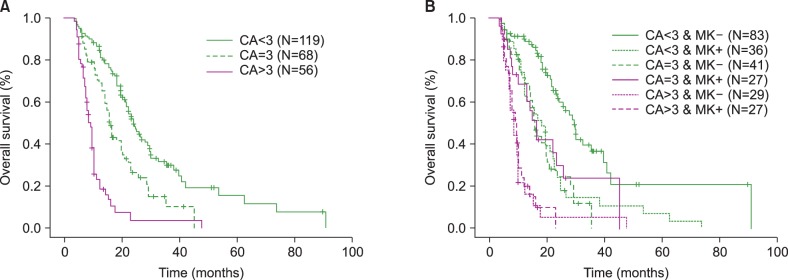 | Fig. 2Comparisons of overall survival (OS) in patients treated with azacitidine according to the numbers of chromosome abnormalities (CAs); CA <3, CA=3, and CA>3 (A) and OS according to the numbers of CAs combined with the presence or absence of a monosomal karyotype (MK) (B). OS in the group with CA<3 was significantly higher than the other 2 groups (OS, 14.5% in the CA>3 group, 27.9% in the CA=3 group, 37.8% in the CA<3 group; CA<3 vs. CA=3, P=0.001). OS in the CA>3 group was lower than the other 2 groups (CA>3 vs. CA=3, P=0.001) (A). According to the presence or absence of MK combined with the number of CAs, OS was highest in the non-MK group with CA<3 compared to the other 5 groups (OS, 23.3% vs. 50.6% in the CA<3 groups with/without MK, 33.3% vs. 24.4% in the CA=3 groups with/without MK, 11.1% vs. 17.2% in the CA>3 groups with/without MK, P <0.001) (B). |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download