1. Coleman RE. Optimising treatment of bone metastases by Aredia(TM) and Zometa(TM). Breast Cancer. 2000; 7:361–369. PMID:
11114866.
2. Berenson JR, Hillner BE, Kyle RA, Anderson K, Lipton A, Yee GC, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guidelines: the role of bisphosphonates in multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol. 2002; 20:3719–3736. PMID:
12202673.

3. Bone HG, Hosking D, Devogelaer JP, Tucci JR, Emkey RD, Tonino RP, et al. Ten years' experience with alendronate for osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:1189–1199. PMID:
15028823.

4. Park HM, Lee ES, Kim SM. The use of osteoporosis medications in Korea in 2008. J Bone Metab. 2009; 16:87–93.
5. Miller PD. The kidney and bisphosphonates. Bone. 2011; 49:77–81. PMID:
21232648.

6. Lin JH. Bisphosphonates: a review of their pharmacokinetic properties. Bone. 1996; 18:75–85. PMID:
8833200.

8. Marx RE. Pamidronate (Aredia) and zoledronate (Zometa) induced avascular necrosis of the jaws: a growing epidemic. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003; 61:1115–1117. PMID:
12966493.

9. Ruggiero SL, Dodson TB, Assael LA, Landesberg R, Marx RE, Mehrotra B. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons position paper on bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws: 2009 update. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009; 67(5 Suppl):2–12.
10. Silva PG, Ferreira Junior AE, Teófilo CR, Barbosa MC, Lima Júnior RC, Sousa FB, et al. Effect of different doses of zoledronic acid in establishing of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis. Arch Oral Biol. 2015; 60:1237–1245. PMID:
26093347.

11. Manzano-Moreno FJ, Ramos-Torrecillas J, De Luna-Bertos E, Ruiz C, García-Martínez O. High doses of bisphosphonates reduce osteoblast-like cell proliferation by arresting the cell cycle and inducing apoptosis. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2015; 43:396–401. PMID:
25614214.

12. National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002; 39(2 Suppl 1):S1–S266. PMID:
11904577.
13. Levey AS, Eckardt KU, Tsukamoto Y, Levin A, Coresh J, Rossert J, et al. Definition and classification of chronic kidney disease: a position statement from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. 2005; 67:2089–2100. PMID:
15882252.

14. Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang YL, Castro AF 3rd, Feldman HI, et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med. 2009; 150:604–612. PMID:
19414839.

15. Park JC, Rhee SH, Kim YH, Kang MS, Son YH, Kim HG, et al. The effectiveness of the surgical approach and drug-holiday on the treatment of bisphosphonate related osteonecrosis of the jaw patient. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015; 44(Suppl 1):e275.

16. Nickolas TL, Leonard MB, Shane E. Chronic kidney disease and bone fracture: a growing concern. Kidney Int. 2008; 74:721–731. PMID:
18563052.

17. Coresh J, Astor BC, Greene T, Eknoyan G, Levey AS. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and decreased kidney function in the adult US population: Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003; 41:1–12. PMID:
12500213.

18. Khosla S, Burr D, Cauley J, Dempster DW, Ebeling PR, Felsenberg D, et al. Bisphosphonate-associated osteonecrosis of the jaw: report of a task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Miner Res. 2007; 22:1479–1491. PMID:
17663640.

19. Ruggiero SL, Dodson TB, Fantasia J, Goodday R, Aghaloo T, Mehrotra B, et al. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons position paper on medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: 2014 update. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014; 72:1938–1956. PMID:
25234529.
20. O'Hare AM, Choi AI, Bertenthal D, Bacchetti P, Garg AX, Kaufman JS, et al. Age affects outcomes in chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007; 18:2758–2765. PMID:
17855638.
21. Gifre L, Peris P, Monegal A, Martínez-Ferrer A, Hernández MV, Guañabens N. Effect of bisphosphonates on renal function in patients with osteoporosis. Eur Geriatr Med. 2013; 4:380–383.

22. Lee JK, Kim KW, Choi JY, Moon SY, Kim SG, Kim CH, et al. Bisphosphonates-related osteonecrosis of the jaw in Korea: a preliminary report. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013; 39:9–13. PMID:
24471011.

24. Mavrokokki T, Cheng A, Stein B, Goss A. Nature and frequency of bisphosphonate-associated osteonecrosis of the jaws in Australia. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007; 65:415–423. PMID:
17307586.

25. Damm DD, Jones DM. Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws: a potential alternative to drug holidays. Gen Dent. 2013; 61:33–38.
26. Marx RE, Cillo JE Jr, Ulloa JJ. Oral bisphosphonate-induced osteonecrosis: risk factors, prediction of risk using serum CTX testing, prevention, and treatment. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007; 65:2397–2410. PMID:
18022461.

27. Song JW, Kim KH, Song JM, Chun BD, Kim YD, Kim UK, et al. Clinical study of correlation between C-terminal cross-linking telopeptide of type I collagen and risk assessment, severity of disease, healing after early surgical intervention in patients with bisphophonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011; 37:1–8.

28. Grbic JT, Black DM, Lyles KW, Reid DM, Orwoll E, McClung M, et al. The incidence of osteonecrosis of the jaw in patients receiving 5 milligrams of zoledronic acid: data from the health outcomes and reduced incidence with zoledronic acid once yearly clinical trials program. J Am Dent Assoc. 2010; 141:1365–1370. PMID:
21037195.
29. Park W, Kim NK, Kim MY, Rhee YM, Kim HJ. Osteonecrosis of the jaw induced by oral administration of bisphosphonates in Asian population: five cases. Osteoporos Int. 2010; 21:527–533. PMID:
19484166.

30. Bamias A, Kastritis E, Bamia C, Moulopoulos LA, Melakopoulos I, Bozas G, et al. Osteonecrosis of the jaw in cancer after treatment with bisphosphonates: incidence and risk factors. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23:8580–8587. PMID:
16314620.

31. Hoff A, Toth B, Altundag K, Guarneri V, Adamus A, Nooka A, et al. Osteonecrosis of the jaw in patients receiving intravenous bisphosphonate therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:8528.

32. Baqain ZH, Sawair FA, Tamimi Z, Bsoul N, Al Edwan G, Almasad JK, et al. Osteonecrosis of jaws related to intravenous bisphosphonates: the experience of a Jordanian teaching hospital. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2010; 92:489–494. PMID:
20522306.

33. Vahtsevanos K, Kyrgidis A, Verrou E, Katodritou E, Triaridis S, Andreadis CG, et al. Longitudinal cohort study of risk factors in cancer patients of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:5356–5362. PMID:
19805682.

34. Markowitz GS, Appel GB, Fine PL, Fenves AZ, Loon NR, Jagannath S, et al. Collapsing focal segmental glomerulosclerosis following treatment with high-dose pamidronate. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001; 12:1164–1172. PMID:
11373339.

35. Markowitz GS, Fine PL, Stack JI, Kunis CL, Radhakrishnan J, Palecki W, et al. Toxic acute tubular necrosis following treatment with zoledronate (Zometa). Kidney Int. 2003; 64:281–289. PMID:
12787420.

36. Suresh E, Pazianas M, Abrahamsen B. Safety issues with bisphosphonate therapy for osteoporosis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014; 53:19–31. PMID:
23838024.

37. Levey AS, Coresh J, Balk E, Kausz AT, Levin A, Steffes MW, et al. National Kidney Foundation practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Ann Intern Med. 2003; 139:137–147. PMID:
12859163.

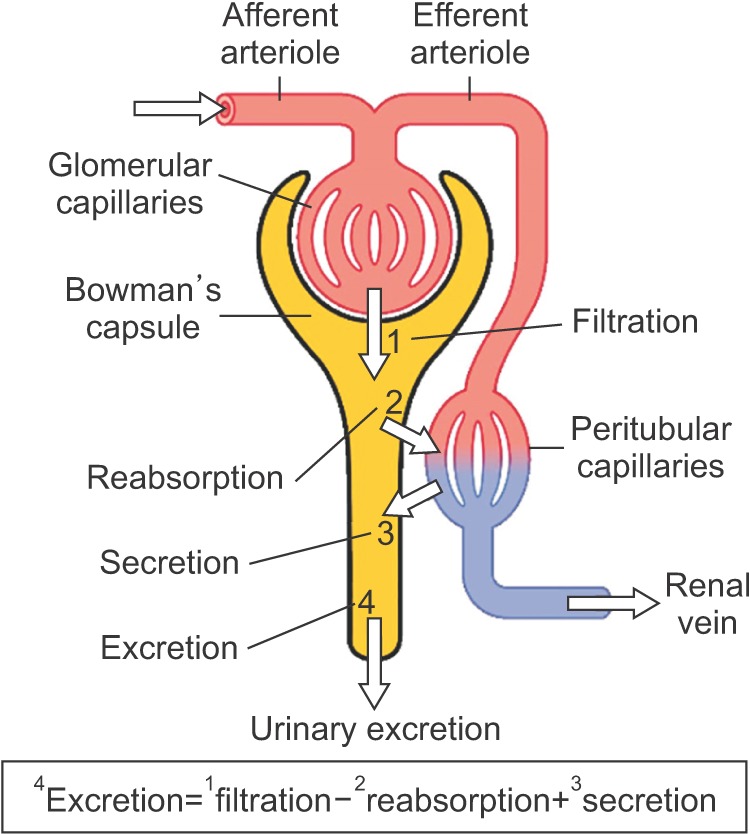
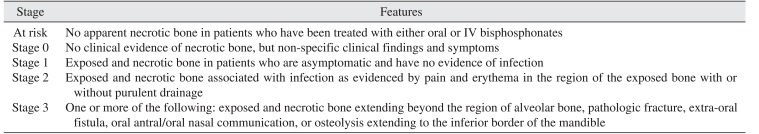
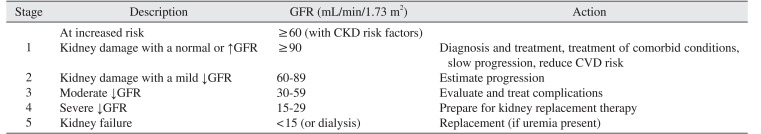
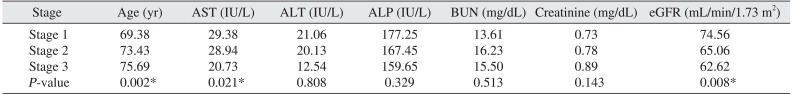




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download