IV. Discussion
Most common malignant fibrous-osseous lesions are osteosarcoma and Ewing's sarcoma
6-
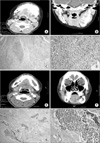
8 . Osteosarcoma is a malignant tumor caused by the malignant transformation of mesenchymal cells which have capacity to generate osteoid tissue or immature woven bone. The etiology of this tumor is obscure. Moreover, osteosarcoma in the maxillofacial area occupy only 10% of total osteosarcoma. The mean ages of onset in maxillofacial area ranges from the 10s to the 20s, a little later than those of the other body parts and the survival rate is higher. In this study, the age distribution was 10s to the 60s, mostly among over 30s. At least 5 of the 8 (63%) treated cases survived. In cases of osteosarcoma in long bones, a male is prone to the onset than a female; in the head and neck, however, the sex ratio is similar. Similar results were deducted in our study. Many other scholars reported a similar onset ratio of osteosarcoma in the maxilla and mandible but this study recorded a ratio of 8 : 1, with higher onset on the mandible. Continuous pain, swelling, and paresthesia have been reported as general symptoms and clinical findings. In our study, facial swelling was a chief complaint, with serous tooth mobility in the lesion. For all patients with osteo sarcoma of the jaws, computed tomography (CT) scan and whole body bone scan were performed. A positrom emission tomography-CT scan was utilized when metastasis was doubtful. A CT scan of the head and neck revealed a typical sunburst, sunray appearance caused by the formation of osteophytes in the bone surface of lesion. Such symptom was observed among 60% of the patients. The periodontal ligament space widening with tooth mobility in panoramic radiographs were observed among 40% of the patients.
The treatment of osteosarcoma primarily based on wide excision with surgical margin of 3 cm. However surgical margins are often not feasible in head and neck osteosarcoma. In 7 of 8 patients with osteosarcoma except Ewing's sarcoma, excision was performed, and 2 of 7 patients (28%) recurred. Other treatments in parallel with the surgery for patients with osteosarcoma have been introduced. In case of osteosarcoma in the long bones, chemotherapy with various combination of drugs are used. Chemotherapy in the long bones is performed pre and postoperatively, and survival rates have improved from 20% to as high as 60-70% since the beginning of the 1980s in the past. In osteosarcoma in the head and neck, however, the advantage of neoadjuvant chemotherapy is still unclear. Some hypothesis exist for this phenomenon. Micrometastasis of osteosarcoma in the long bones under a microscope reaches 80%, whereas that of osteosarcoma in the head and neck records an 18% distant metastasis rate. Second, the histological malignancy of osteosarcoma in long bone reaches 85%, whereas the one in the head and neck is 56-79%. Third, the response of osteosarcoma in the head and neck to neoadjuvant chemotherapy is below 25%. Among our clinical cases, 5 cases with surgery were osteoblastic type, and 2 cases were chondroblastic type. Adjuvant chemotherapy was performed in 2 cases with a large lesion. Due to the lack of cases, it was difficult to judge the treatment effects (survival rate and recurrence rate) of adjuvant chemotherapy. According to the operators, there are some literatures on radiation therapy after the surgery in the cases of high grade and infeasible surgical margin. In these cases, there were not any radiation after surgery. For 2 years of follow up, 5 of 8 cases survived.
Continuous observations on osteosarcoma and Ewing's sarcoma are very important and should be checked every two months after surgery. Furthermore, distant metastasis should be checked through chest and abdominal CT scans every 3 months for 2 years, and bone scan using radioactive isotope should be done every 6 months for 2 years; after 2 years, clinical examination and chest CT scan should be done every year.
Unlike the prognosis of malignant fibrous-osseous lesions on the jaws, that of benign fibrous-osseous lesions is generally good; such benign fibrous-osseous lesions can be completely healed with accurate diagnosis and treatment. Benign fibrous-osseous lesions clinically have various bone disorder and similar histopathological features. Such lesions are common in the head and neck region, especially in the jaws. Among these lesions, osseous dysplasia is classified as a single disease, but juvenile active ossifying fibroma and aggressive, active psammomatoid ossifying/cementifying fibroma are still debatable
9-
12. The various classification systems of fibrous-osseous lesions on the jaws have been introduced, but Waldron's classification
13 reported in 1985 is still used. This clinical study on benign fibrous-osseous lesions classified the lesions more simply according to Waldron's modified classification
14 as fibrous dysplasia, ossifying fibroma, periapical cemental dysplasia and osteoblastoma, and cementoblastoma and considered each disease's clinical aspect and radiological and histological findings.
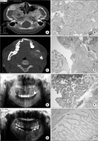
Fibrous dysplasia is benign, a slowly growing disease with normal bone being replaced by fibrous tissue with varying calcification. The etiology is unclear yet. Houston's summarized report
15 on the presented pathophysiology included 1) transformed activity of boneforming mesenchyme, 2) expression of hyperphosphatamia-induced chronic hyperparathyroidism, 3) expression of complex metabolic disorders, 4) metabolic disorders of calcium and phosphorus, 5) nonspecific reaction of bone to trauma, 6) increased secretion of estrogen, 7) congenital mesenchymal disorder, 8) form of lipoid granulomatosis, and 9) transformation of von Recklinghausen's neurofibromatosis. Nonetheless, fibrous dysplasia is accepted to be neither familial nor here ditary disease. Recently, pathologists regard it as non-neoplastic developmental disorder of bone
16,
17. Fibrous dys plasia is classified as monostotic and polyostotic. Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia may show metabolic disorder (i.e., Albright's syndrome). Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia may also be classified into the case related to endocrine abnormalities and the case without endocrine abnormalities. Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia is rarer than monostotic fibrous dysplasia, making up 30% of total fibrous dysplasia with about 20% afflicting the mandible
18,
19. In this study, one case was proven to be Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia. The diseases in such case occurred simultaneously in various regions of facial bone. In whole body bone scan using radioactive isotope, There were lesions in the cervical region, thoracic vertebrae, lumbar region, unilateral scapula, and femur region as well as facial bone. The patient with such polyostotic fibrous dysplasia was a woman in her twenties, and there was no other functional disorders in the endocrine system. Four of 5 cases of fibrous dysplasia were diagnosed as monostotic fibrous dysplasia. The onset age of the patients was generally 30s. The duration of disease was from 3 years to 10 years. According to the literature, the symptoms reported in fibrous dysplasia varied depending on the morbidity. The most dominant symptom in monostotic fibrous dysplasia in maxillofacial region is facial asymmetry caused by slow-growing mass. The main clinical symptom of patients in this study was facial asymmetry or buccal swelling, which, sometimes in the case of a small lesion, was also discovered in a routine dental exam by chance. Various radiological findings on fibrous dysplasia were reported. Radiologically, the features were classified into 3 categories such as pagetoid type, sclerotic type, and cystlike type. In this study, the features could be mostly pagetoid type in the radiography, showing ground-glass radiopacity. The lesion affected mandible (2 cases) and maxilla and adjacent bone regions (3 cases) with one case of afflicting the maxilla, zygoma, and sphenoid bones. Therefore, to find out the morbidity of such lesions, various radiographic examinations and bone scans are performed such as conventional CT and 3-dimensional CT as well as panoramic radiograph. The common histological finding on such lesions is that normal bone is replaced by cellular fibers including various minerals. At this time, there is no significant difference between the monostotic and the polyostotic type, but there is a difference primarily in the total change of fibrous dysplasia and the appearance of osteoid feature. Fibroblasts may be arranged in various forms from helical arrangement to fine fibrous stroma; a fibrous tissue contains well-differentiated cells and solid collagen matrix. Fib stroma contains irregularly arranged bony trabeculae in immature bone which is called "Chinese character trabeculae" due to the similarity with the Chinese script
17. In these cases, such immature, irregular bony trabeculae distinctively contained in fibrous stroma were observed as the finding of a lump having similar form as Chinese characters, and such bony trabecular form in microscopy were considered to have diagnostic value. An indication of surgical treatment depends on an aspect of each symptom. For the lesion without symptom, surgical treatment may not be an indication. Fibrous dysplasia is generally small and slow-growing. As the lesion becomes bigger, there may be serious facial deformity and general facial abnormalities. In this study, the patients were mostly in their 30s. And there was a case of a 15-year-old girl afflicted by the disease. She came to the hospital with chief complaint of facial asymmetry since the mandible, maxilla, and zygoma were affected. Bony recontouring was performed to correct the facial deformity even though she was young. There are many surgical methods available for fibrous dysplasia. Some clinicians strongly assert that all injured bone tissues should be removed. These are based on the following theories: 1) operational therapy with incomplete excision of the lesions may accelerate the growth of the remaining lesions, 2) continuous growth of the lesions occurs in 20% of the cases, and 3) patient's burden of the remaining lesions. On the other hand, other surgeons raised doubts on the complete excision of the lesions by presenting problems in aesthetic defect after surgery or complicated reconstructive surgery. They maintained that conservative surgery including partial excision or osseous resection has a high rate of recurrence (23%), but additional treatments are not required. Consequently, most of the patients can be fully healed through the bone regeneration process
20. In this study, the examination period after the surgery was about 3 years. Since facial asymmetry in the maxilla was recognized in 2 years after surgery in one case with polyostotic fibrous dysplasia, the lesion was additionally resected. Two years later, satisfactory progress was noted.
Ossifying fibroma and cementifying fibroma are regarded as a single lesion in fibrous-osseous entity. There is only a difference in histological findings on bone between calcified element and cementum; all the other features are interchangeable with each other. Ossifying fibroma is observed mostly in the lower molar and premolar regions but are sometimes detected in the anterior maxilla and mandible as well. The lesions are slow-growing and asymptomatic
21. In 6 cases of this clinical study, 2 of them were in 10s, 1 in 20s, 2 in their 40s and 1 in 50s. Most of the patients except for one were female. Lesion was in the mandibular body. Patients' chief complaints were facial swelling and pain. Our cases mostly showed the aspect of bony enlargement in buccal and lingual cortical bone and the mixed aspect of radiolucency with clear sclerotic bone margin with radiopacity. In the CT scan, most of the lesions showed spherical contour, and the margins were radiolucent. The histological findings on these clinical cases revealed little clear difference of lesions from adjacent normal bone tissue as the aspect of immature bony trabeculae spread into a fibrous stroma and a mixed aspect of substance showing cementumlike calcification with bony trabeculae in cases with advanced ossification. As treatment for the clinical 6 cases, limited excision of the lesion was mostly performed; no recurrence was observed. But, In one case, since wide ossifying fibroma was in the mandibular body, complaints of facial asymmetry and pain followed. Partial bone resection of the mandibular body was performed, and iliac bone grafting was carried out immediately.
Juvenile ossifying fibroma is a type of ossifying fibroma afflicting children; it has a different aspect from the one occurring among adults
10. The lesion occurring in the orbital region should be separated from the one originating in the periodontal ligament. In this clinical study, one case- an adult woman in her 40s- had ossified lesion with a type of calcification similar to the one observed in juvenile ossifying fibroma. For juvenile ossifying fibroma, conservative surgical treatment is recommended, because patients with conservative surgery showed similar result with wide surgery.
Florid osseous dysplasia is a chronic, progressive disease. There are clear clinical, radiological, and histological findings on it, and the lesion is observed in each quadrant of facial bone. Florid osseous dysplasia mainly occurs in the mandibular premolar and molar region, and some patients complain of pain, tenderness, and swelling. Florid osseous dysplasia occur in both dentulous and edentulous patients. Moreover, the disease generally affects both sides of the mandibular ramus. Each of such lesions has a different size, and they can be radiologically classified into the early, middle, and late stages in terms of progress
22. Unlike general fibrous-osseous lesions, it has its distinct clinical symptom, and it may be observed in the maxilla. In this clinical study, one patient, a male in his/her 60s, came to the hospital with complaint of pain on both posterior mandible. The lesion showed the mixed radiopacity and radiolucency. At first examination, the diagnosis was fibrous dysplasia. Unlike other fibrous-osseous lesions, the patient complained of continuous pain and the lesion was removed and healed uneventfully without recurrence. The histological findings finally confirmed it as florid osseous dysplasia.
Periapical cemental dysplasia, focal cemento-osseous dysplasia is generally asymptomatic, mainly occurring on the lower part of the posterior mandible unlike cementoma that occurs on the lower anterior, Radiologically, it shows radiolucency in the early stage but a mixed aspect with radiopacity in the middle stage and radiopacity with spherical shape in the late mature stage
23. In these cases, the lesion affected the entire posterior mandible, and there was no difference in age and sex. Excision was done and the finally diagnosed as periapical cemental dysplasia with fibrous stroma containing immature bony trabeculae.
Osteoblastoma mainly occurs in long bone and rarely occurs maxillofacial lesions. Cementoblastoma similar to osteoblastoma occurs mainly among males rather than females. The initial symptoms are swelling and pain, and most of the patients are reported in their 10s, and facial bone lesion seems to be related to a permanent tooth and to be fused with tooth; predilection sites are the mandibular premolar and molar area
24-
27. Osteoblastoma seemed to be one of a bone destructive disease and most of the lesions have osteolytic borders together with the expansion of the cortical bone plate. One case was observed in our study. A 21-year-old female had lesions in the posterior mandible and came to the hospital with chief complaints of pain and swelling persisting for several months. The small spherical mandibular body lesions were mixed with radiolucency and radiopacity in the panoramic radiography, and the MRI findings revealed multiple septa in the lesions with bone expansion on the buccal side. The histological findings on osteoblastoma showed that the lesions are similar to fibrous-osseous lesions, but may be mistaken for osteosarcoma due to increased cell activity. Despite a lump with calcified tissue, the characteristic findings revealed that it is a stroma with high cell differentiation and was found to be attached to the affected teeth. In our case, since the result of two biopsies before the surgery cast doubt on osteosarcoma, wide excision was performed. Iliac bone graft was done after the surgery, with the patient showing no evidence of recurrence for 2 year follow-up check. However, permanent specimen showed an interconnected form of bony trabeculae in the fibrovascular stroma, and osteoid which was diagnosed as osteoblastoma surrounded with osteoblast cells. The treatment method is to excise the relevant bone and tooth with margins by regarding it as a locally aggressive benign tumor
26,
27.
Fibrous-osseous lesions have similar features each other
9,
13,
16. However, such similarity induces difficulties in differential diagnosis. It is crucial to isolate malignant lesions with benign ones. Genetic examination is tried to diagnose and pro gnose the fibrous-osseous disease in advance, but clinical application is yet difficult. The clinical, histological, and radiological findings proven in this clinical study could be helpful as a reference indicator during treatment.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download