Dear Editor,
Persistent infection with human papillomavirus (HPV) is the main cause of cervical cancer. Screening of cervical specimens for high-risk human papillomaviruses (HR-HPV) has become a routine part of patient care in most countries. The Roche cobas 4800 system (Roche Molecular Systems Inc., Pleasanton, CA, USA), a fully automated system that uses in vitro qualitative real-time PCR technology, displays high sensitivity and specificity for HR-HPV detection [1]. However, a small proportion of invalid results may occur in specimens showing mucopurulent discharge because of pipetting errors, clot formation, or failed amplification, which could cause a delay in the results and lead to additional waiting time for patients and extra work hours for staff, although most cases are resolved by vortexing the specimens and retesting. To the best of our knowledge, no researcher has tried to overcome this problem by pretreating specimens with an appropriate concentration of Sputasol (Oxoid Ltd., Basingstoke, United Kingdom); Sputasol (dithiothreitol 1.4%) has been used to aid culturing and DNA extraction from sputum specimens in some laboratories [2]. Here, we propose a standard method to improve HR-HPV detection without affecting the performance of the cobas 4800 HPV system.
The cobas 4800 HPV system comprises a cobas x480 instrument (for specimen preparation) and a cobas z480 analyzer (for real-time PCR). The cobas 4800 HPV test is available on the cobas 4800 system that can detect 14 HR-HPV types (16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 66, and 68). The cobas 4800 system software automatically displays reportable results as negative, positive, or invalid.
Prior to the study, written consent was obtained from all of the patients enrolled and institutional review board approval was also obtained. Twenty cervical specimens, which might have failed the test or been reported invalid because of visible quantities of cervical mucus, were prepared for the study. Each specimen was aliquoted into three 13-mL round-based secondary tubes for three different tests. The first set of tubes served as the control group, and remained untreated (test 1). The second set of tubes was vortexed for 1 min before testing (test 2). The third set of tubes was pretreated with an appropriate concentration of Sputasol (dithiothreitol 0.54%) and then vortexed for 1 min before testing (test 3).
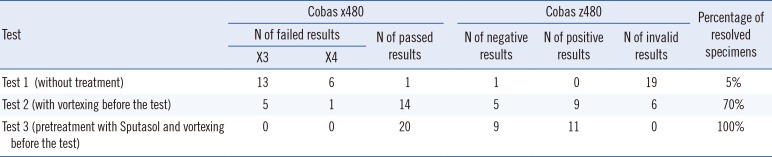
In our study, a problem of excess mucus was deemed resolved if a valid result was obtained from the cobas 4800 system. As shown in Table 1, invalid results were indicated by errors on the cobas x480 instrument (X3 or X4). Our results indicated that the percentages of resolved specimens were 5%, 70%, and 100% for tests 1, 2, and 3, respectively. It was therefore evident that almost no specimens from test 1 were resolved owing to large quantities of mucus. By contrast, 13 of 19 failed specimens were resolved in test 2, indicating that vortexing of the specimens prior to testing increased the success rate of the test. However, the results of test 3 indicated that four HR-HPV-negative results and two HR-HPV-positive results from test 2 were invalid. In test 3, 20 cervical specimens for which clinical data were available, including 9 HR-HPV-negative specimens and 11 HR-HPV-positive specimens, were pretreated with Sputasol (dithiothreitol 0.54%) before being tested by using the cobas 4800 HPV test. In test 3, all specimens were completely resolved (with threshold cycle values of 25.9–38.9). The test results and the related clinical data were consistent with each of the specimens. Sputasol pre-treatment was therefore an effective method for ensuring the reliability of the results of the cobas 4800 HPV test.
The user-friendly cobas 4800 system appeared to be effective for performing the cobas 4800 HPV test [345]. Excess mucus in the specimens can, however, result in pipetting errors and/or clot formation, which can affect the reliability of the test. We pretreated specimens with an appropriate concentration of Sputasol, which increased the reliability of the cobas 4800 HPV test, without compromising the performance.
One limitation of this study was the small specimen size. Another limitation was that valid specimens should have been tested simultaneously along with invalid specimens. However, we believe believe our data are representative and would be scalable. We recommend laboratories consider pretreating cervical specimens with excess mucus with an appropriate concentration of Sputasol, to increase the reliability of the cobas 4800 HPV test.
References
1. Isidean SD, Coutlée F, Franco EL. cobas 4800 HPV Test, a real-time polymerase chain reaction assay for the detection of human papillomavirus in cervical specimens. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2014; 14:5–16. PMID: 24308341.
2. Baxter CG, Jones AM, Webb K, Denning DW. Homogenisation of cystic fibrosis sputum by sonication--an essential step for Aspergillus PCR. J Microbiol Methods. 2011; 85:75–81. PMID: 21277342.
3. Cui M, Chan N, Liu M, Thai K, Malaczynska J, Singh I, et al. Clinical performance of Roche Cobas 4800 HPV Test. J Clin Microbiol. 2014; 52:2210–2211. PMID: 24719443.
4. Tardif KD, Pyne MT, Malmberg E, Lunt TC, Schlaberg R. Cervical cytology specimen stability in surepath preservative and analytical sensitivity for HPV testing with the cobas and hybrid capture 2 tests. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0149611. PMID: 26905067.
5. White C, Keegan H, Pilkington L, Ruttle C, Kerr P, Sharp L, et al. Evaluation of the clinical performance of the cobas 4800 HPV test in patients referred for colposcopy. J Clin Microbiol. 2013; 51:3415–3417. PMID: 23903550.
Table 1
Three tests performed using the cobas 4800 system on a subset of cervical specimens containing large quantities of mucus




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download