Abstract
Objective
Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
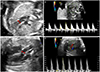 | Fig. 1Ultrasonographic measurement of cardiac output using pulsed-wave Doppler. (A) The pulmonary root diameter (arrow) is used to calculate pulmonary valve area. (B) Pulsed-wave flow profile in the pulmonary root. The angle of insonation for Doppler assessment is minimized so that the flow velocity time integral can be measured directly from the spectral display. (C) The aortic root diameter (arrow) is used to calculate aortic valve area. (D) Pulsed-wave flow profile in the aortic root. |
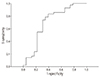 | Fig. 2Receiver-operating characteristics curve for the prediction of pregnancy complication according to cut-off values of left cardiac output. |
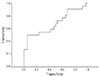 | Fig. 3Receiver-operating characteristics curve for the prediction of pregnancy complication according to cut-off values of right cardiac output to the left cardiac output. |
Table 1
Characteristics between normal group and pregnancy complication group
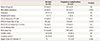
Table 2
A comparison of fetal cardiac function in normal and pregnancy complication group
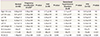
Value are presented as mean±standard deviation; P<0.05 was considered significant.
FGR, fetal growth restriction; PTB, preterm birth; E, peak velocity of the early diastolic transmitral flow; A, peak velocity of the late diastolic transmitral flow; E/A ratio, ratio of peak early vs. late transmitral flow velocity; NS, not significant; TEI, isovolumic contraction time plus isovolumic relaxation time divided by ejection time; SF, shortening fraction; RCO, right cardiac output; LCO, left cardiac output.
a)Several patients experienced more than two complications.
Table 3
Multivariate logistic regression analysis for the prediction of pregnancy complications

Table 4
Multivariate logistic regression analysis of RCO/LCO for the prediction of each pregnancy complication

All outcomes were adjusted for maternal age, body mass index, parity, preterm birth history, gestational age at measuring cardiac output, and estimated fetal weight; P<0.05 was considered significant.
RCO, right cardiac output; LCO, left cardiac output; CI, confidence interval; PTL, preterm labor; PPROM, preterm premature rupture of membranes.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download