Abstract
Objective
Methods
Results
Conclusion
Figures and Tables
 | Fig. 1Porfimer photosensitizer (A: Photofrin, Axcan Pharma Inc., Canada/USA; INMEX Corp., Seoul, Korea) and non-thermal laser device (B: Diomed 630 nm PDT laser, Diomed, Cambridge, UK; LitePharmTech Co., Seoul, Korea). |
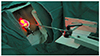 | Fig. 2Photodynamic laser irradiation therapy directly into the lesions (exocervix, endocervix, and the core of cancer tissue). |
 | Fig. 3Schematic figure of the photodynamic therapy irradiation in exocervix. The divided 5 parts (2, 5, 7, 11 o’clock directions and center of the cervix, 1 cm in diameter) were irradiated, each part using 240 J/cm2 with 400 mW for 600 seconds with flat-cut optic fiber. |
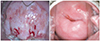 | Fig. 4The pre-photodynamic therapy cervicographic figures of the cervix in a 32-year-old married woman (para 2-0-0-2) with carcinoma in situ histologic lesion showed broad acetowhitening and mosaic lesion with punctuation at 8 to 1 o’clock direction (A). The post-photodynamic therapy cervicographic figures cervicography at 16 months after photodynamic therapy shows nearly normal appearance (B). |
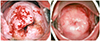 | Fig. 5The pre-combined chemo-photodynamic therapy (CCPDT) cervicographic figures of the cervix in a 30-year-old cohabited woman (para 0-0-0-0) with invasive barrel-shaped endocervical cancer (FIGO [International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics] stage 1B1) showed acetowhitening and slightly bulging lesions with partly bloody increased vessels in all around the exocervix (A). The post-CCPDT cervicographic figures at 62 months after 1st CCPDT shows also normal and beautiful appearance. Pap cytology was negative and human papillomavirus DNA test was negative (B). |
Table 1
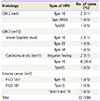
Clinical features in all patients

HPV, human papilloma virus; Pap, Papanicolaou; M, married; HSIL, high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion; CIS, carcinoma in situ; PDT, photodynamic therapy; C, cohabit; ACC, adenocarcinoma; CCPDT, combined chemo-photodynamic therapy; RCC, reactive cellular change; S, single; LSIL, low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion; CIN, cervical intraepithelial neoplasia; SCC, squamous cell carcinoma; ASC-H, atypical squamous cells-exclude high-grade lesions.
Table 3
Results of PDT in patients with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and invasive cervical cancer
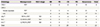
PDT, photodynamic therapy; FIGO, International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics; NR, no response; PR, partial response; CR, complete remission; PD, progressive disease; CIN, cervical intraepithelial neoplasia; CIS, carcinoma in situ; ASC, adenosquamous cell carcinoma; CCPDT, combined chemo-photodynamic therapy; SCC, squamous cell carcinoma.
a)The case of recurrence after complete remission; b)The case of progression after partial remission; c)The case of CCPDT with interstitial type method.
Table 4
Follow-up period after phodynamic therapy

HPV, human papillomavirus; NED, no evidence of disease; PD, progressive disease.
*The case of progressive disease after partial remission in invasive cancer group; **The case of recurrence after complete remission in CIN group. This case also revealed negative Papanicolaou cytology and positive HPV 35 DNA test at 10 months after PDT. Her initial diagnosis was positive HPV 35 DNA test.
a)The case of negative Papanicolaou cytology and a new-type positive HPV 55 DNA test in CIN group at 8 months after PDT. Her initial diagnoses were positive HPV 66 and 70 DNA tests; b),c),d)The cases of negative Papanicolaou cytology and positive HPV DNA test in CIN group.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download