Abstract
Objective
Methods
Results
Conclusion
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Normal quantitative fluorescent polymerase chain reaction results with peak height ratios of allele dosage between 0.8 and 1.4 in more than two short tandem repeats (arrow head) in 46, XY, based on at least two informative markers, except for two short tandem repeat markers on chromosome 18 (D18S391, D18S390) showed uninformative single peaks (arrow). This case was confirmed as 46, XY, normal fetus by long term culture. The XY male sex chromosome constitution is identified by the presence of both the X- and Y- specific products of AMXY (with a normal ratio of 1:1) in addition to the SRY product and the single X-linked HPRT allele. AMXY, amylogenin XY; X, X chromosome; HPRT, hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase; D, DNA; S, Segment; SRY, sex-determining region Y; Y, Y chromosome; ar,area; ht, height; sz, size.

Fig. 2
Positive quantitative fluorescent polymerase chain reaction results with the main short tandem repeat markers in 47, XY, +21: Trisomy 21 is determined by the trisomic triallelic pattern for D21S1414, D21S1411, D21S1435, and D21S1446 (arrow). AMXY, amylogenin XY; X, X chromosome; HPRT, hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase; D, DNA; S, Segment; SRY, sex-determining region Y; Y, Y chromosome; ar,area; ht, height; sz, size.

Fig. 3
Positive quantitative fluorescent polymerase chain reaction results with extra short tandem repeat markers in 47,XY,+21: Trisomy 21 is identified by a trisomic diallelic pattern for D21S1008, D21S1412, and D21S1437 (≤0.6 or ≥1.8) (arrow) and a trisomic triallelic pattern for D21S1411 and D21S1435 (ratio 1:1:1) (arrow head). D, DNA; S, Segment; ar,area; ht, height; sz, size.

Table 2
Indications of chorionic villus sampling with QF-PCR (n=384)
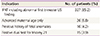
IFNT was diagnosed according to the previous reported criteria of above the 95 percentile level of nuchal translucency [10].
QF-PCR, quantitative fluorescent polymerase chain reaction; IFNT, increased fetal nuchal translucency; US, ultrasonographic.
Table 3
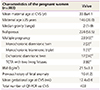
Comparison of results between QF-PCR and long-term culture (n=403)

QF-PCR, quantitative fluorescent polymerase chain reaction.
a)45,X[46]/46,XX3].
b)46,XY,der(4)t(3;4)(q23;q35); 45,XX,der(13;18)(q10;q10); 46,XX,inv(1)(p22p34.1); 46,XY, der(1)t(1;7)(p36.3;p15); 47,XX,+16; 47,XX,+15; 46,XX,t(15;20)(q15;q11.2); 46,XY,?inv(1)(q42q44); 46,XX,?del(18)(p11.2); 46,XX,der(4)t(1;4)(q42;p16),t(6;17)(p21.1;p12); 46,XY,add(7)(q3?3); 46,XX,?del(4)(q32q34); 46,XY,t(3;6)(p13;q25); 46,XY,t(1;6)(q32;q16); 46,XX,?add(17)(p13).
c)47,XY,t(3;22)(q26.3;q12),+18.
d)46,XX,+13,der(13;13)(q10;q10).
Table 4
QF-PCR findings according to indication of CVS

Abnormal QF-PCR results were as follows: evidence of trisomy 21, 18, or 13; Abnormal first trimester US findings: cystic hygroma (71), hydrops fetalis (21), abdominal wall defect (12), hypoplastic or absent nasal bone (12), congenital heart defects (6), acrania (2), bladder outlet obstruction (1), and fetal renal pelvis dilatation (1).
QF-PCR, quantitative fluorescent polymerase chain reaction; CVS, chorionic villus sampling; IFNT, increased fetal nuchal translucency; US, ultrasonographic.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download