1. Beseler CL, Taylor LA, Leeman RF. An item-response theory analysis of dsm-iv alcohol-use disorder criteria and “binge” drinking in undergraduates. J Stud Alcohol Drugs. 2010; 71(3):418–423.

2. Robin RW, Long JC, Rasmussen JK, Albaugh B, Goldman D. Relationship of binge drinking to alcohol dependence, other psychiatric disorders, and behavioral problems in an American Indian tribe. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1998; 22(2):518–523.

3. Knight JR, Wechsler H, Kuo M, Seibring M, Weitzman ER, Schuckit MA. Alcohol abuse and dependence among U.S. college students. J Stud Alcohol. 2002; 63(3):263–270.

4. Kim SG, Kim JS, Pack HJ, Sung HN. Usefulness of heavy drinking and binge drinking for the diagnosis of alcohol use disorder. Korean J Fam Med. 2016; 37(4):214–220.

5. Cherpitel CJ. Analysis of cut points for screening instruments for alcohol problems in the emergency room. J Stud Alcohol. 1995; 56(6):695–700.

6. Shibuya A, Yasunami M, Yoshida A. Genotypes of alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase loci in Japanese alcohol flushers and nonflushers. Hum Genet. 1989; 82(1):14–16.

7. Jung JG, Kim JS, Oh MK. The role of the flushing response in the relationship between alcohol consumption and insulin resistance. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2010; 34(10):1699–1704.

8. Jung JG, Kim JS, Yoon SJ, Oh MK. Relationships among alcohol consumption, facial flushing response, and metabolic syndrome in healthy men. Ann Epidemiol. 2012; 22(7):480–486.

9. Suh HS, Kim JS, Kim SS, Jung JG, Yoon SJ, Ahn JB. Influence of the flushing response in the relationship between alcohol consumption and cardiovascular disease risk. Korean J Fam Med. 2014; 35(6):295–302.

10. Kim EC, Kim JS, Jung JG, Kim SS, Yoon SJ, Ryu JS. Effect of alcohol consumption on risk of hyperhomocysteinemia based on alcohol-related facial flushing response. Korean J Fam Med. 2013; 34(4):250–257.

11. Kim SG, Kim JS, Kim SS, Jung JG, Yun SJ, Kim EC. Relationships between the level of alcohol consumption and abnormality in biomarkers according to facial flushing in Korean male drinkers. Korean J Fam Med. 2013; 34(2):123–130.

12. Jung JG, Kim JS, Kim YS, Oh MK, Yoon SJ. Hypertension associated with alcohol consumption based on the facial flushing reaction to drinking. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2014; 38(4):1020–1025.

13. Kim JS. Guideline of moderate alcohol drinking amount for Koreans. Korean J Fam Pract. 2015; 5:Suppl 1. S117–S119.
15. Bouchery EE, Harwood HJ, Sacks JJ, Simon CJ, Brewer RD. Economic costs of excessive alcohol consumption in the U.S., 2006. Am J Prev Med. 2011; 41(5):516–524.

16. Naimi TS, Brewer RD, Mokdad A, Denny C, Serdula MK, Marks JS. Binge drinking among US adults. JAMA. 2003; 289(1):70–75.

17. Willenbring ML, Massey SH, Gardner MB. Helping patients who drink too much: an evidence-based guide for primary care physicians. Am Fam Physician. 2009; 80(1):44–50.
18. Muller MP, Tomlinson G, Marrie TJ, Tang P, McGeer A, Low DE, et al. Can routine laboratory tests discriminate between severe acute respiratory syndrome and other causes of community-acquired pneumonia? Clin Infect Dis. 2005; 40(8):1079–1086.

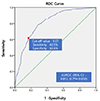
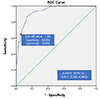
19. Song SW. Using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve to measure sensitivity and specificity. Korean J Fam Med. 2009; 30(11):841–842.

20. Nam TW, Kim JS, Kim SS, Jung JG, Kang DS, Hyeon YH, et al. Utility of single alcohol questions related to binge drinking in identifying problem drinkers. Korean J Fam Med. 2009; 30(10):777–783.

21. McGee S. Simplifying likelihood ratios. J Gen Intern Med. 2002; 17(8):646–649.

22. Henderson MC, Tierney LM, Smetana GW. The patient history: an evidence based approach to differential diagnosis. 2nd ed. New York: McGrawHill;2012. p. 30.
23. Anderson ML, Nokia MS, Govindaraju KP, Shors TJ. Moderate drinking? Alcohol consumption significantly decreases neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Neuroscience. 2012; 224(8):202–209.







 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download