Abstract
Background
The purpose of the study was to compare and contrast ankle range of motion, functional ability, talar-tilt angle and foot injuries between high school ballet majors with and without foot deformities and to provide fundamental data about effective intervention methods for their successful performance and injury prevention.
Methods
Subjects were 18 female high school ballet dancers, eight with foot deformities and ten without foot deformities. For statistical analysis, the independent t-test (SPSS 20.0; SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL, USA) was used and the significant level of P<0.050 was selected.
References
1. Song BR, Jung MS. Dance and politics. The Korean Journal of Dance. 2007; 51(1):181–93.
2. Jung MS, Choi SY, Shim JH, Tark JH. A comparative study of body composition, basic physical strength and cardiopulmonary function between Korean, ballet and modern dancers. The Korean Journal of Dance. 2006; 46(1):209–25.
3. Ryu JY. A Study on Physical Strength and Foot Deformation of Professional Dacers and Ordinary People [dissertation]. Daegu: Catholic University of Daegu;2011. Korean.
4. Kim JS. Kinematic analysis of grand jete in Ballet. The Korean Journal of Dance. 1992; 14(1):112–31.
5. Do JN. A comparative studies on the bone density, physical fitness, and information processing ability among Korea dance, ballet, and general women. The Korean Journal of Dance. 1998; 24(1):81–93.
6. Park JH. Study on flow lines of ballet stance. The Korean Journal of Dance. 2013; 71(5):43–61.
7. Lee KT, Kwak KD, Kim DY, Kim ES, Kim JY, Kim JY, et al. Foot and Ankle Surgery. Seoul: Koonja;2004. p. 1–560.
8. Kim MJ. Analysis of Characteristics between Exercise Ability andFoot Form according to Three Kinds of Dancers [dissertation]. Chungnam: Chungnam National University;1991. Korean.
9. Choi SY. A comparative study on pressure applied to toes while performing ballet movements. The Korean Journal of Dance. 1998; 23(1):399–417.
10. Kim KS. The effect footprint angle on equilibrated state. Korean J Phys Educ. 1977; 15:41–5.
11. Choi SY. A study on the changes of structure and function of ballerinas foot. Korean J Phys Educ. 1991; 30(2):233–8.
12. Lee KT, Kim HC, Jung WK. Foot and ankle disorders in classical ballet dancers. Korean J Sports Med. 1996; 14(2):256–9.
13. Choi SY. A study on the types of foot and ankle injuries in ballet dancers. The Korean Journal of Dance. 1995; 18(1):255–66.
14. Ha KI, Han SH, Chung MY, Yang BK, Kwag JG. The foot deformity of ballerina. Korean J Sports Med. 1993; 11(1):74–8.
15. Kim SK, Choi SY. Study on patterns of an ankle joint injury of ballet majors and Korean dance majors: centering on the students of secondary school. Hanguk Muyong Gwahak Hoeji [Official Journal of Korean Society of Dance Science]. 2003; 7(1):11–21.
16. Kim JM, Shon JH. The necessity of prevention and rehabilitation of dance injuries. The Korean Journal of Dance. 2003; 36(1):201–21.
17. Shin MY. A Study on Injures of Ballet Majoring Students [dissertation]. Seoul: Chung-Ang University;2000. Korean.
18. Lee HJ. A Study on the Analysis and Prevention of Dance Injury according to Dancers' Speciality and Object [dissertation]. Yongin: Yong In University;2007. Korean.
19. Jerosch J, Bischof M. Proprioceptive capabilities of the ankle in stable and unstable joints. Sports Exerc Inj. 1996; 2:167–71.
20. Klement A, Sandholzer H, Frenzen A. [Sports and leisure injuries in summer]. MMW Fortschr Med. 2005; 147(26):26–9. German.
21. Lee HH. Dance Injuries. Seoul: Keumkoang;1992. p. 1–245.
22. Lee SH. A Study on the Causes of Injuries by the Movement of Modern Dance Major [dissertation]. Seoul: Chung-Ang University;2008. Korean.
23. Priscilla M, Margaret S. Science of Dance Training. Champaign, Illinois: Human Kinetics Books;1988. p. 147–92.
24. Lee AD. A Comparison on the Lower Extremity Deformities among Different Types of Dance Majors [dissertation]. Seoul: Ewha Women's University;2004. Korean.
25. Karlsson J, Lansinger O. Laternal instability of the ankle joint. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992; 276:253–61.
26. Hislop H, Avers D, Brown M. Daniels and Worthingham's Muscle Testing. China, Missouri: Elsevier Saunders;2014. p. 1–528.
27. Hoppenfeld S. Physical Examination of the Spine and Extremities. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice Hall International;1976. p. 197–235.
28. Son SY, Park SB, Choi SY. A study on the gait of ballet dancers. Hanguk Muyong Gwahak Hoeji [Official Journal of Korean Society of Dance Science]. 2003; 7(1):39–50.
29. Shon HN. A Study on the Professional Dancers'Feet Transformation [dissertation]. Seoul: Ewha Women's University;1997. Korean.
30. Ko HH. Measurement and evaluation in human performance. Seoul: Yeonsea University;2003. p. 1–503.
31. Korea Institute of Sport Science. Exercise Prescription. Seoul: 21st Publishing;2010. p. 1–306.
32. Lee KT, Bang YS. Dance Medicine and Science. Seoul: Koonja;2009. p. 1–142.
34. Chun SY, Choi OJ. The ankle joint position sense, strength and functional ability of the soccer player with functional ankle instability. Korea J Sports Sci. 2009; 18(3):1119–30.
35. Hyung IH. The Effect of Balance and Muscle Activities on the Stability of Foot [dissertation]. Daegu: Daegu University;2008. Korean.
36. Hyung IH, Bae SS. Effect of lower extremity on the joint therapy and active exercise of ankle and foot complex. J Korean Soc Phys Med. 2008; 3(2):89–96.
37. Bernier JN, Perrin DH. Effect of coordination training on proprioception of the functionally unstable ankle. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 1998; 27(4):264–75.

38. Norkus SA, Floyd RT. The anatomy and mechanisms of syndesmotic ankle sprains. J Athl Train. 2001; 36(1):68–73.
Table 1.
General characteristics of subjectsa
Table 2.
Shapiro-Wilk test
Table 3.
Comparison of ankle range of motion, functional ability and talar tilta
| Variables | FDG (n=8) | NCG (n=10) | t | df | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range of motion | |||||
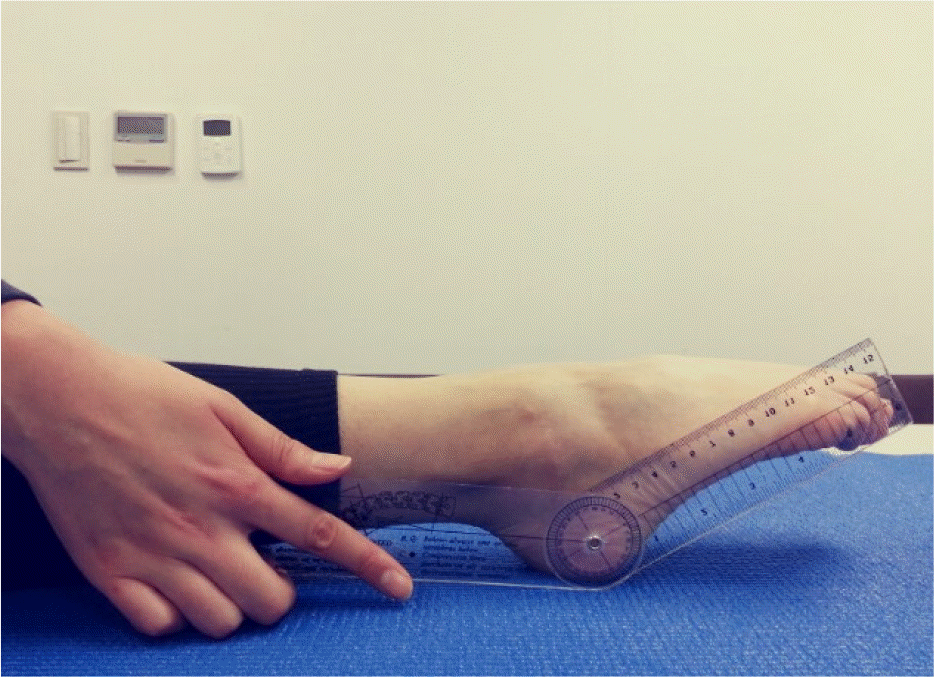
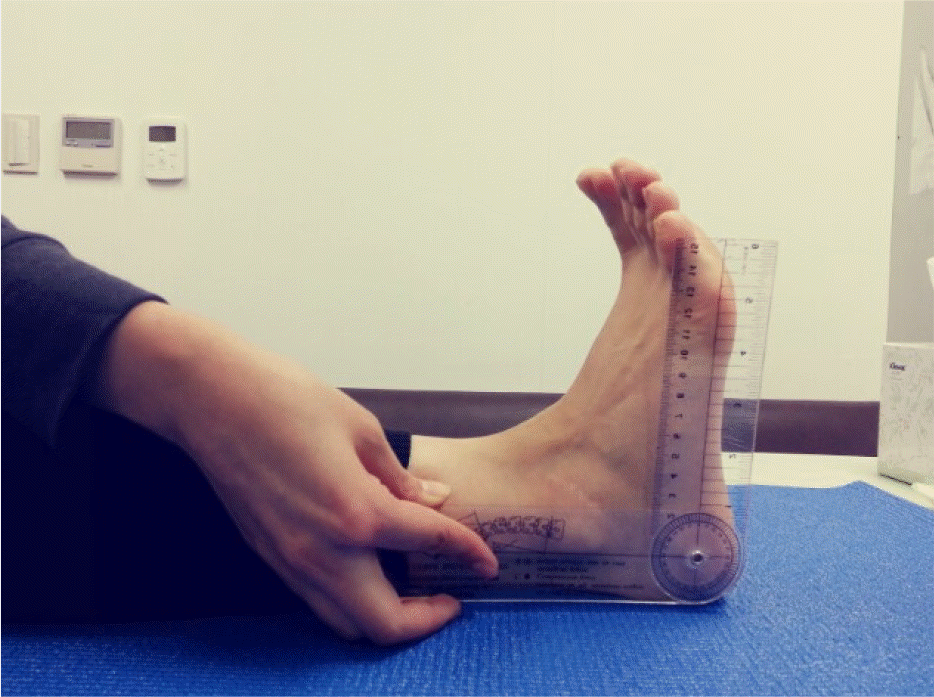
| PF, ○ | 82.75±5.52 | 92.60±8.69 | –2.778 | 16 | 0.013 |
| DF, ○ | 19.37±6.20 | 21.30±8.98 | –0.514 | 16 | 0.614 |
| Functional ability | |||||
| Balance test, s∗ | 32.37±26.75 | 38.50±16.47 | –0.598 | 16 | 0.558 |
| Side step test, times/20 s | 16.12±1.12 | 16.40±1.17 | –0.503 | 16 | 0.622 |
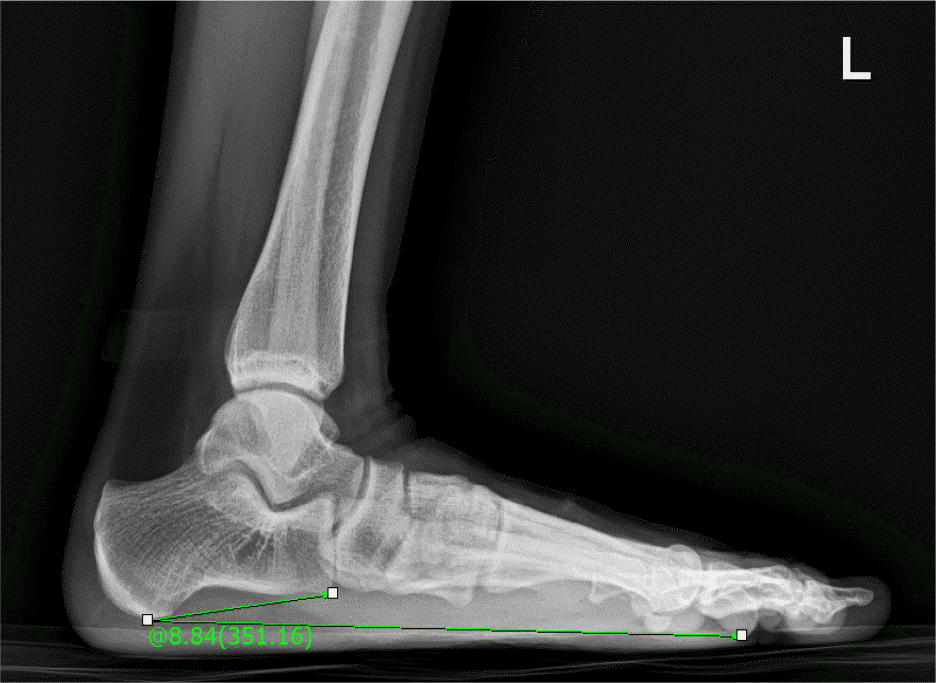
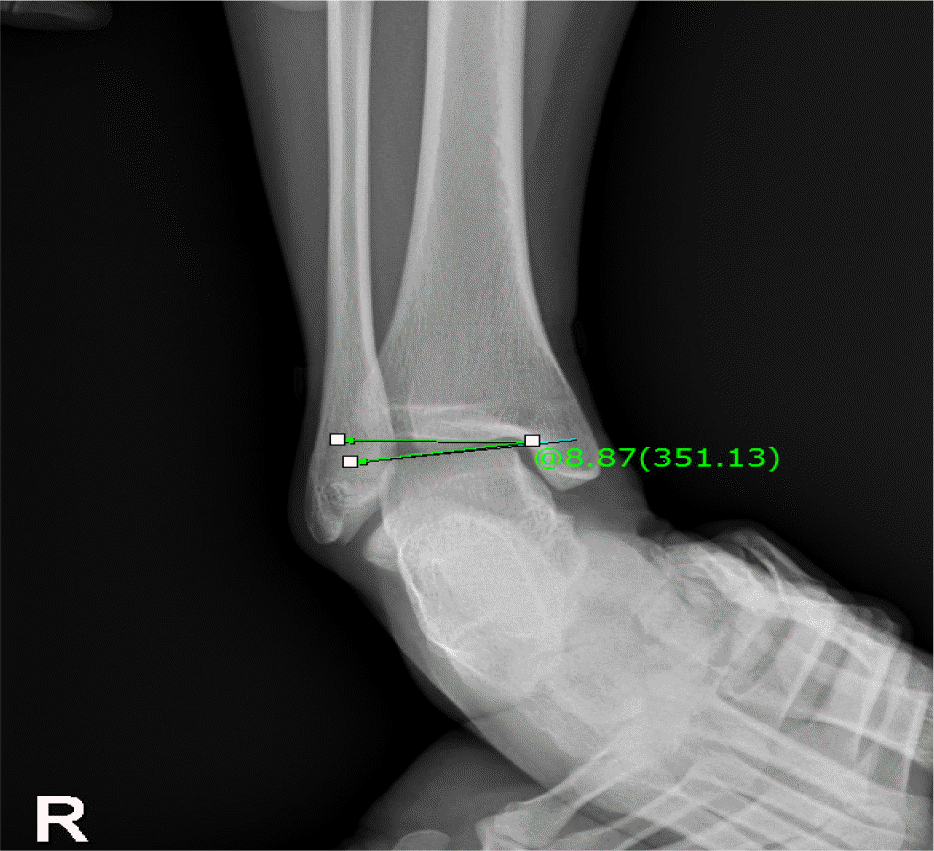
| Talar tilt, ○ | 6.57±2.95 | 3.70±2.42 | 2.266 | 16 | 0.038 |
Table 4.
Comparison of foot injury ratesa
| Variables | FDG (n=8) | NCG (n=10) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical instability | 3 (37.5) | 3 (30.0) |
| Ingrowing toenail | 1 (12.5) | 0 (0) |
| Callus | 10 (100) | 10 (100) |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download