Abstract
Purpose
Sexual function involves a complex interaction of emotions, body image, and intact physical responses. The purpose of this study was to determine the sexual functioning of women who are incontinent and to identify associated factors.
Methods
For this descriptive correlation study, data were collected from 147 women with urinary incontinence. Data were analyzed using t-test, ANOVA, and stepwise multiple regression.
Results
Mean scores were 22.39 (sexual dysfunction ≤26.55) for sexual function, 13.38 (of 63) for depression, and 55.47 (range of score 17~85) for body image. Urinary symptoms and daily life symptoms averaged 36.04 (range of score 20~100) and 16.03 (range of score 8~40). Sexual function had a positive correlation with body image and negative correlation with daily life symptoms. Sexual satisfaction, daily life symptoms, marital satisfaction, and frequency of sexual intercourse were factors affecting sexual function.
Conclusion
Study results indicate that urinary incontinence has a negative impact on various aspects of sexual function. Nurses should be aware of the wider consideration that needs to be made in relation to general and sexual quality of life when caring for clients suffering from urological diseases.
Figures and Tables
Table 1
Sexual Function according to General and Disease related Characteristics of Subjects (N=147)

Table 3
Sexual Function, Depression, Body Image, Urinary Symptoms, and Daily Life Problems of Subjects (N=147)
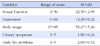
Table 4
Correlation between Sexual Function, Depression, Body Image, Urinary Symptoms, and Daily Life Problems (N=147)

References
1. Abdo CH, Oliveira WM Jr, Moreira ED Jr, Fittipaldi JA. Prevalence of sexual dysfunctions and correlated conditions in a sample of Brazilian women-results of the Brazilian study on sexual behavior (BSSB). Int J Impot Res. 2004; 16:160–166.

2. Aslan G, Koseoglu H, Sadik O, Gimen S, Cihan A, Esen A. Sexual function in women with urinary incontinence. Int J Impot Res. 2005; 17:248–251. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901296.

3. Beck AT. Depression: Causes and treatment. Philadelphia, PA: University of Pennsylvania Press;1961.
4. Bekker MD, Van Driel MF, Pelger RC, Lycklama à Nijeholt GA, Elzevier HW. How do continence nurses address sexual function and a history of sexual abuse in daily pratice? results of a pilot study. J Sex Med. 2010; 8:367–375. http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.1111/j.1743-6109.2010.02044.x.
5. Brown WJ, Miller YD. Too wet to exercise? leaking urine as a barrier to physical activity in women. J Sci Med Sport. 2001; 4:373–378.

6. Chang SB, Kang HS, Kim SN. The sexual satisfaction in married women. J Korean Acad Nurs. 1998; 28:201–209.

7. DeLamater J, Hyde JS, Fong MC. Sexual satisfaction in the seventh decade of life. J Sex Marital Ther. 2008; 34:439–454. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00926230802156251.

8. DuBeau CE, Levy B, Mangione CM, Resnick NM. The impact of urge urinary incontinence on quality of life: Importance of patients' perspective and explanatory style. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1998; 46:683–692. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0022-5347(01)62337-1.

9. Fitts WH. Tennessee self-concept scale. Los Angeles: Western Psychological Services, CA. USA;1964.
10. Hong JY. The efficacy of pelvic floor muscle exercise in patients with genuine stress incontinence. Korean J Urol. 1997; 38:639–643.
11. Jackson S, Donavan J, Brookes S, Eckford S, Swithinback L, Abrams P. The bristol female lower urinary tract symptoms questionnaire: development and psychometric testing. Br J Urol. 1996; 77:805–812.

12. Jeong GH. Body image and depression in post-hysterectomy patients. Seoul: Ewha Womans University;1988. Unpublished master's thesis.
13. Jha S, Radley S, Farkas A, Jones G. The impact of TVT on sexual function. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2009; 20:165–169. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00192-008-0743-3.

14. Kim AK. Body image and depression in women with urinary incontinence. J Korean Acad Adult Nurs. 1998; 10:469–479.
15. Kim HJ, Kim YH, Kim JJ, Kim SM, Jeon MJ. The impact of symptomatic urinary incontinence on female sexual function in middle-to old-aged Korean women. Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 2011; 54:778–783. http://dx.doi.org/10.5468/KJOG.2011.54.12.778.
16. Kim JH, Bae KE, Moon HS, Kang HI. The relationships among body image, depression and sexual function in postmenopausal women. J Korean Acad Adult Nurs. 2005; 17:239–247.
17. Korda JB, Braun M, Engelmann UH. Sexual dysfunction at urinary incontinence. Urologe A. 2007; 46:1058–1065.
18. Lee WS, Choi YS, Lee KW, Lee SJ, Kim MO. Effects on physical symptoms, daily life problems, and sexual life problems of a urinary incontinence management program for women with mixed urinary incontinence. J Korean Clin Nurs Res. 2009; 15:91–102.
19. Lee YH, Song JY. A study of the reliability and the validity of the BDI, SDS, and MMPI-D scales. Korean J Clin Psychol. 1991; 10:98–113.
21. Nygaard I, Turvey C, Burns TL, Crischilles E, Wallace R. Urinary incontinence and depression in middle-aged United States women. Obstet Gynecol. 2003; 101:149–156. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0029-7844(02)02519-X.

22. Oh SJ, Park WH, Park CH, Paick JS, Seo JT, Lee YS, et al. Prevalence of urinary incontinence and incontinence-related quality of life in korean women: A population-based study. J Korean Continence Soc. 2003; 7:73–80.

23. Osgood CE, Suci G, Tannenbaum P. The measurement of meaning. Urbana, IL: University of Illinois Press;1957.
24. Paick JS, Cho MC, Oh SJ, Kim SW, Ku JH. Influence of self-perceived incontinence severity on quality of life and sexual function in women with urinary incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn. 2007; 26:828–835. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/nau.20408.

25. Park YS, Cho IS, Kim YM. A survey of urban middle-aged women's sexual function and sexual distress. Korean J Women Health Nurs. 2007; 13:254–261.

26. Reese PR, Pleil AM, Okano GJ, Kelleher CJ. Multinational study of reliability and validity of the King's Health Questionnaire in parents with overactive bladder. Qual Life Res. 2003; 12:427–442.
27. Rhodes P. The role of the continence adviser: Critique of an emergent nursing specialism. Health Soc Care Community. 1993; 1:35–44. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2524.1993.tb00193.x.
28. Rosen R, Brown C, Heiman J, Leiblum S, Meston C, Shacsigh R, et al. The female sexual function index (FSFI): A multidimensional self-report instrument for the assessment of female sexual function. J Sex Marital Ther. 2000; 26:191–208.
29. Trantafylidis SCA. Impact of urinary incontinence on quality of life. Pelviperineology. 2009; 28:51–53.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download