INTRODUCTION
CASE REPORT
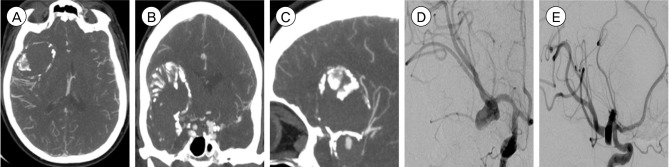 | Fig. 1Computed tomography angiography (CTA) head (A) axial, (B) coronal, and (C) sagittal views demonstrating a giant, partially thrombosed 4.5×3.3 cm right middle cerebral artery (MCA) bifurcation aneurysm with an atherosclerotic, calcified dome. Digital subtraction angiography (DSA), right internal carotid artery (ICA) injection, (D) antero-posterior (AP) and (E) lateral views again demonstrating the giant MCA bifurcation aneurysm. Most of the aneurysm sac does not fill with contrast due to a significant degree of intrasaccular thrombosis. |
 | Fig. 2Initial treatment DSA, (A) AP and (B) lateral views, demonstrating the incompletely deployed PED with a proximally pinched portion and retained transcend microguidewire. The microguidewire was eventually removed but the proximally stenosed portion of the stent could not be dilated and the stent could not be retrieved. (C) CTA head, coronal view, following the initial treatment DSA demonstrating the incompletely deployed PED (arrow) with stenosis of the proximal segment of the stent. (D) Magnetic resonance imaging diffusion weighted imaging, axial view, following the second failed retrieval DSA demonstrating multifocal acute infarcts of the right MCA distribution (DSA: digital subtraction angiography, AP: antero-posterior, PED: pipeline embolization device, CTA: computed tomography angiography, MCA: middle cerebral artery). |
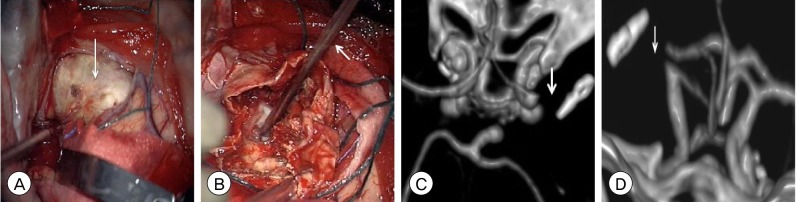 | Fig. 3(A) Intraoperative photograph after dural opening demonstrating the atherosclerotic, calcified dome (arrow) of the giant MCA bifurcation aneurysm. (B) Intraoperative photograph after opening the aneurysm dome and debulking the intrasaccular thrombus demonstrating removal of the incompletely PED (arrow) from the lumen of the MCA M1 segment. Post-operative CTA head 3-dimensional reconstruction, (C) axial and (D) coronal views, demonstrating absence of the right MCA at its origin from the ICA bifurcation (arrow). After aneurysm resection, the detached posterior division of the MCA M2 segment was unable to be reanastamosed to proximal the M1 segment (MCA: middle cerebral artery, PED: pipeline embolization device, CTA: computed tomography angiography, ICA: internal carotid artery). |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download