Abstract
Purpose
Materials and Methods
Results
Conclusions
Figures and Tables
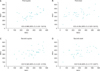 | Fig. 1Scatter plot and intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) between maximum voided volume (MVV) of frequency volume chart (FVC) and maximum cystometric capacity (MCC) of filling cystometry in each posture and filling cystometry time. (A) First supine, (B) first erect, (C) second supine, and (D) second erect. |
Table 1
Baseline demographics

Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or number (%).
SS, supine to supine; EE, erect to erect; SE, supine to erect; ES, erect to supine; BMI, body mass index; IPSS, International Prostate Symptom Score; IPSS-T, total IPSS score; IPSS-V, IPSS voiding subscore; IPSS-S, IPSS storage subscore; OABSS, overactive bladder symptom score; OAB, overactive bladder; PSA, prostate-specific antigen; FVC, frequency volume chart; MVV, maximum voided volume.
a:One-way analysis of variance.
Table 2
Change of filling cystometric parameters by repetition of filling cystometry in the same group

Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or number (%).
SS, supine to supine; EE, erect to erect; SE, supine to erect; ES, erect to supine; CMG, cystometrogram; FSF, first sensation of filling; FDV, first desire to void; SDV, strong desire to void; MCC, maximum cystometric capacity; DO, detrusor overactivity.
a:McNemar test.
Table 3
Comparison of clinical and urodynamic parameters in each posture of the first filling cystometry
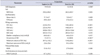
Values are presented as number (%) or mean±standard deviation.
OAB, overactive bladder; FVC, frequency volume chart; MVV, maximum voided volume; Qmax, maximal flow rate; PVR, post-voided residual; FSF, first sensation of filling; FDV, first desire to void; SDV, strong desire to void; MCC, maximum cystometric capacity; DO, detrusor overactivity; BOOI, bladder outlet obstruction index; MUCP, maximum urethral closure pressure.
a:Chi-square test.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download