Abstract
Purpose
Materials and Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
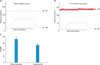 | Fig. 1Representative records of data and intracavernosal pressure/ blood pressure (ICP/BP) from electric field stimulation at 12 weeks after cavernous nerve injury (CNI). Representative time course of changes in ICP for sham operation group rats (A), cavernous nerve (CN) crushing injury group rats (B), and summary of all in vivo data (C). In vivo experiments were performed 12 weeks after CNI in rats. *p-value<0.05, response significantly different compared with sham operation group. |
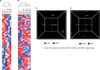 | Fig. 2Different gene expression patterns between normal and diabetes- or cavernous nerve injury (CNI)-induced erectile dysfunction (ED) penile tissues. (A) Unsupervised hierarchical clustering of gene expression profile distinguishes the CNI-induced ED model from (B) the diabetes-induced ED model. (C, D) Principal component analysis (PCA) plots for the CNI-induced and diabetes-induced model data. The sum of % variance is shown for each PCA plot. The diabetic-induced ED (DIED) data is taken from GSE2457 [10]. SON, sham operation normal tissue; NCT, normal cavernous tissue. |
 | Fig. 3Enrichment plot of ANATOMICAL_STRUCTURE_DEVELOPMENT gene signatures. The square box indicates the leading edge subset and the heat map presents 39 genes of the leading edge subset. SON, sham operation normal tissue; CNI_ED, cavernous nerve injury-induced erectile dysfunction; FDR, false discovery rate is the estimated probability that a gene set with a given NES represents a false positive finding; ES, enrichment score; NES, normalized enrichment score. |
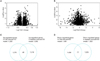 | Fig. 4Differentially expressed genes in cavernous nerve injury (CNI)- and diabetes-induced erectile dysfunction (ED) models identified by analysis of microarrays (SAM) analysis. Volcano plots depicted the magnitude of fold change and significance of p-value of the genes identified by SAM in CNI- (A) or diabetes-induced ED (B) models. The x-axis represents log2 fold change and the y-axis log10 p-value. (C) Forty-six genes were commonly up-regulated, and (D) 77 genes were commonly down-regulated in CNI- and diabetes-induced ED models. The diabetic-induced ED data is taken from GSE2457 [10]. |
Table 1
Summary of data set information and the result of supervised classification analysis

Table 2
The list of 7 gene signatures significantly down-regulated in cavernous nerve injury-induced erectile dysfunction model (GSE31247)
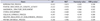
The values of enrichment score (ES), normalized enrichment score (NES), nominal p-value, and false discovery rate (FDR) q-value were rounded off to 3 decimal places. The table is sorted smallest to largest by NES.
a:The ES indicates the degree to which a gene set is overrepresented at the entired ranked gene list. b:The NES was calculated by normalizing the enrichment score (ES) to account for the size of each gene signature. c:FDR q-value: FDR is to control the proportion of false positives corresponding to each NES. FDR was represented as q-value, which is the analog of p-value that has been corrected for multiple hypothesis testing.
Table 3
The list of 33 gene signatures significantly up- or down-regulated in diabetes-induced erectile dysfunction model (GSE2457)

The values of enrichment score (ES), normalized enrichment score (NES), nominal p-value, and false discovery rate (FDR) q-value were rounded off to 3 decimal places. The table is sorted smallest to largest by NES.
a:The ES indicates the degree to which a gene set is overrepresented at the entired ranked gene list. b:The NES was calculated by normalizing the ES to account for the size of each gene signature. c:FDR q-value: FDR is to control the proportion of false positives corresponding to each NES. FDR was represented as q-value, which is the analog of p-value that has been corrected for multiple hypothesis testing.
Table 4
The list of 39 LES genes in ANATOMICAL_STRUCTURE_DEVELOPMENT gene signature
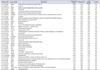
The values of Rank metric score, running enrichment score (ES), fold change and p-value were rounded off to 2 decimal places. The table is sorted smallest to largest by running ES.
a:Score used to position the gene in the ranked list. b:The enrichment score at this point in the ranked list of genes. c:Fold change and q-value were calculated from significance analysis of microarrays analysis.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download