Abstract
The concentration of glucose in the vitreous humor serves as an important diagnostic marker for diabetic mellitus in post-mortem examinations, as the vitreous humor can be easily collected and the glucose test using vitreous humor is not significantly affected by cell autolysis and hemolysis. For a quick and effective glucose test, we suggest a dipstick test of the vitreous humor during autopsy. The results were evaluated and compared with other methods for significance testing. In this study, vitreous humor was analyzed from 257 autopsy cases. Qualitative concordance rate of the dipstick test for glucose and the hexokinase test was 98.7%, positive prediction rate was 89.6%, and negative prediction rate was 100%. However, there was no significant correlation between the dipstick glucose test and the hexokinase test. We conclude that the dipstick glucose test is effective and useful for post-mortem glucose screening testing and for additional post-mortem diabetes testing. Recently, the importance of post-mortem glucose testing has increased with the increase in deaths from diabetes complications. The use of the dipstick glucose test in autopsy practice can improve forensic medicine in Korea.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Boulagnon C., Garnotel R., Fornes P, et al. Post-mortem biochemistry of vitreous humor and glucose metabolism: an update. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2011. 49:1265–70.

2.Belsey SL., Flanagan RJ. Postmortem biochemistry: current applications. J Forensic Leg Med. 2016. 41:49–57.

3.Keltanen T., Sajantila A., Valonen T, et al. HbA1c method evaluation for postmortem samples. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2015. 11:35–9.

Go to : 
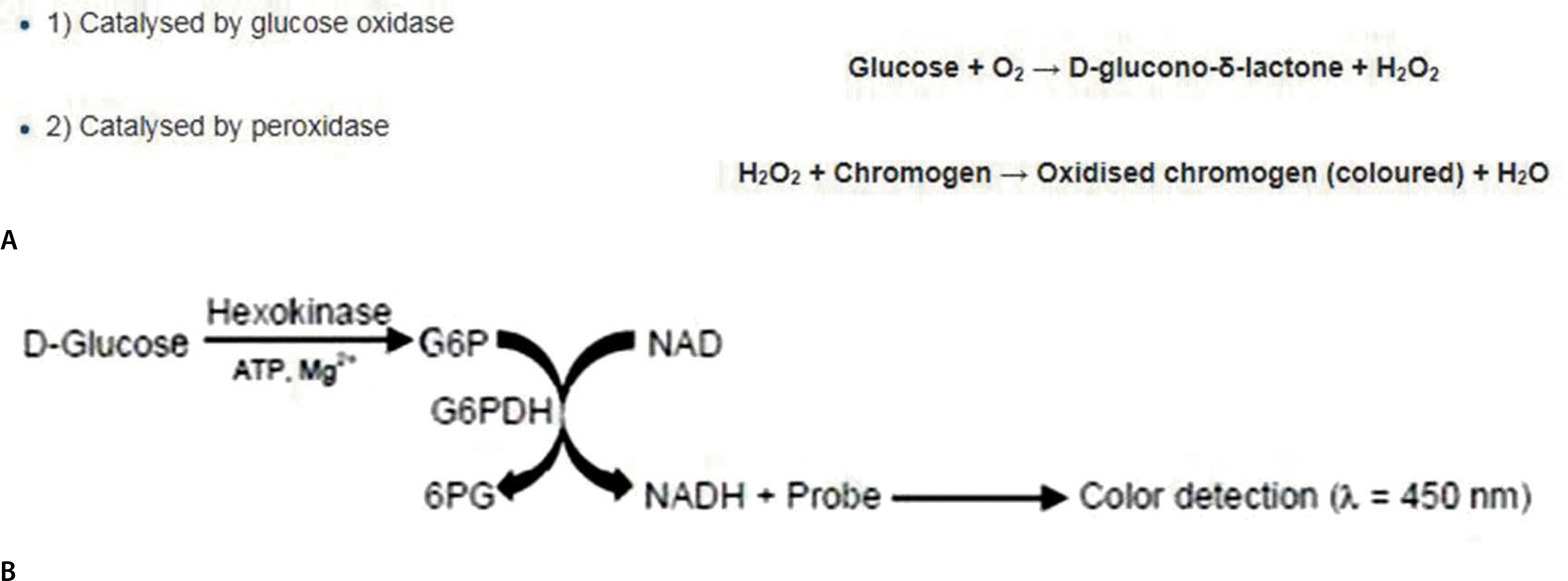 | Fig. 1.(A) Principle of glucose detection of the dipstick glucose test. (B) Principle of glucose detection of the hexokinase test. |
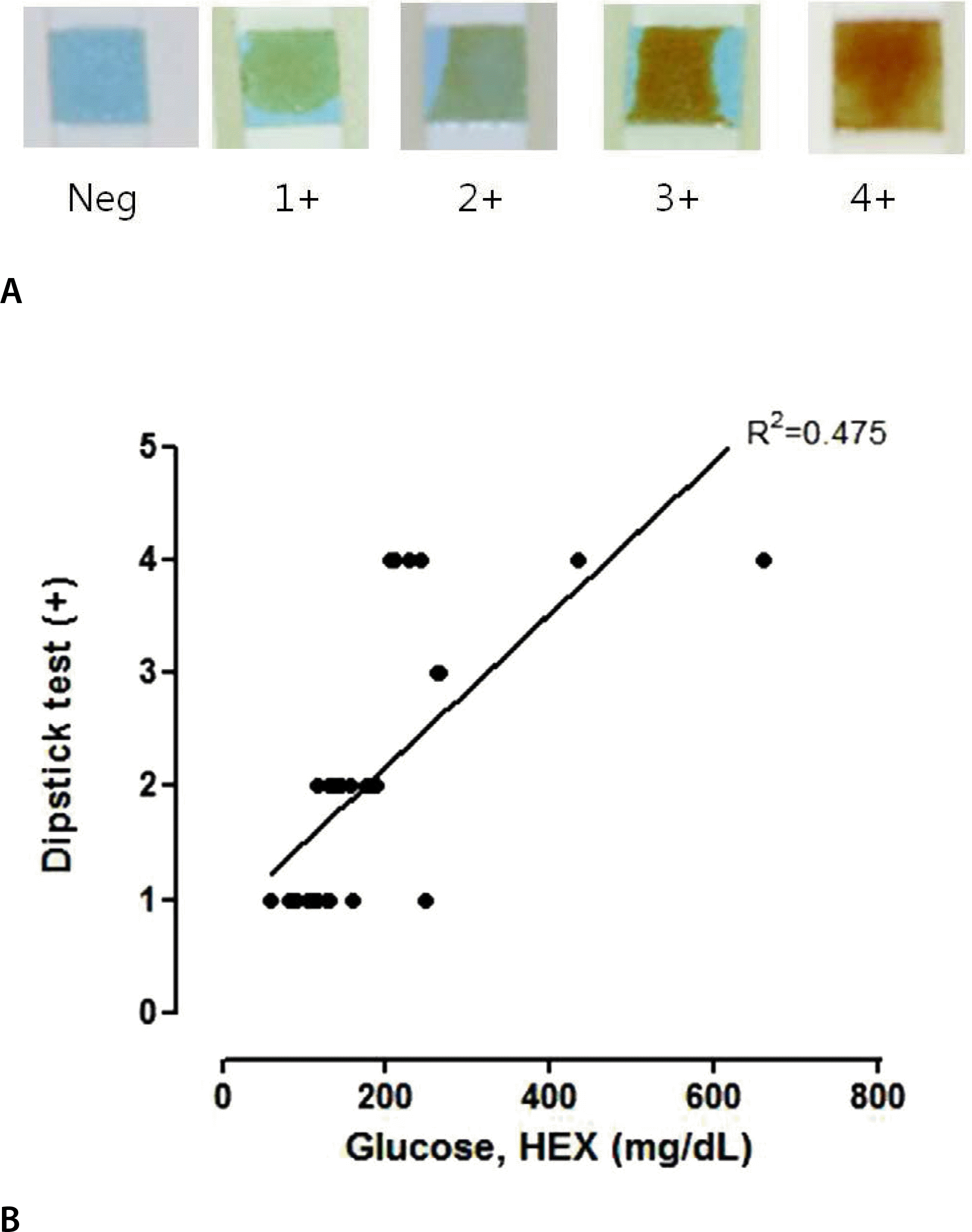 | Fig. 2.(A) Figure shows quantitative change in the dipstick glucose test result to determine vitreous glucose concentration. As the concentration of glucose increases, the strip color changes to darker brown. Classifications are negative, 1+, 2+, 3+ and 4+, dependent on dose. (B) Graph shows linear correlation of the dipstick glucose test and the hexokinase test (HEX) results of the vitreous humor. X-axis is the HEX results (mg/dL). Y-axis is the dipstick test results (n+). |
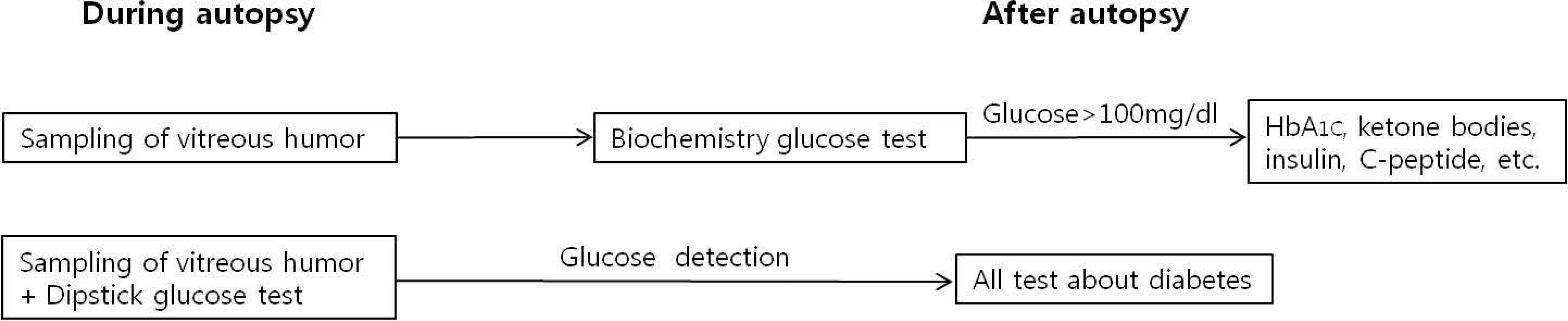 | Fig. 3.Schematic model showing the efficiency of the dipstick glucose test for determining vitreous glucose concentration during autopsy. |
Table 1.
Qualitative concordance rate of the dipstick glucose test and the HEX of vitreous humor
| Dipstick glucose test | Glucose, HEX ≥100 mg/dL | Glucose, HEX <100 mg/dL | Total (n=257) | Concordance ratea) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | 26 | 3 | 29 | 98.7b) |
| Negative | 0 | 215 | 215 | |
| Trace (+/-) | 2 | 11 | 13 |
Table 2.
Autopsy cases with positive results for the dipstick glucose test of vitreous humor
| Case No. | Natural/Unnatural | Cause of death | Dipstick test | Glucose (mg/dL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01a) | Natural | Pneumonia and diabetic complications | 4+ | 659 |
| 02 | Unnatural | Traumatic subdural hemorrhage | 4+ | 242 |
| 03 | Natural | Sudden cardiac death | 4+ | 209 |
| 04 | Unnatural | Hanging | 4+ | 226 |
| 05 | Natural | Pneumonia and ischemic heart diseases | 4+ | 204 |
| 06 | Natural | Ischemic heart diseases | 3+ | 264 |
| 07 | Natural | Sudden cardiac death | 3+ | 260 |
| 08 | Natural | Ischemic heart diseases | 2+ | 139 |
| 09a) | Natural | Acute diabetic complications (ketoacidosis) | 2+ | 175 |
| 10a) | Natural | Acute diabetic complications and chronic alcoholism | 2+ | 187 |
| 11 | Natural | Sudden cardiac death | 2+ | 141 |
| 12 | Natural | Ischemic heart diseases | 2+ | 185 |
| 13 | Natural | Pulmonary embolism | 2+ | 155 |
| 14a) | Natural | Sudden cardiac death and diabetic complications | 2+ | 143 |
| 15 | Natural | Intracerebral hemorrhage | 2+ | 131 |
| 16a) | Natural | Diabetic complications (ketoacidosis) | 1+ | 158 |
| 17 | Natural | Pneumonia | 1+ | 248 |
| 18a) | Natural | Sudden cardiac death and acute diabetic complications | 1+ | 112 |
| 19 | Natural | Chronic alcoholism | 1+ | 129 |
| 20 | Natural | Sudden cardiac death | 1+ | 105 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download