Abstract
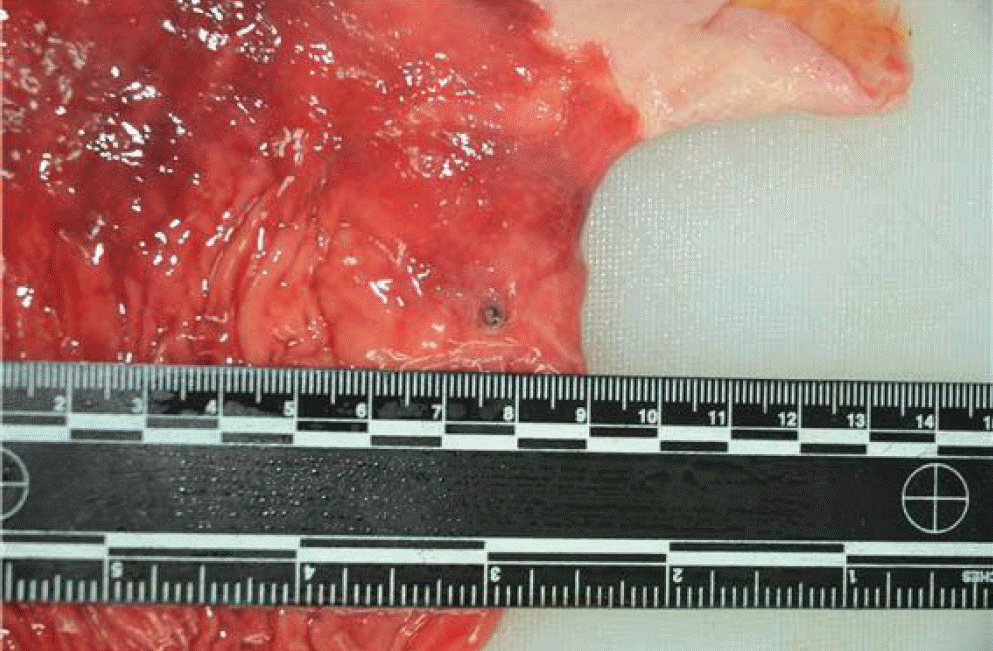
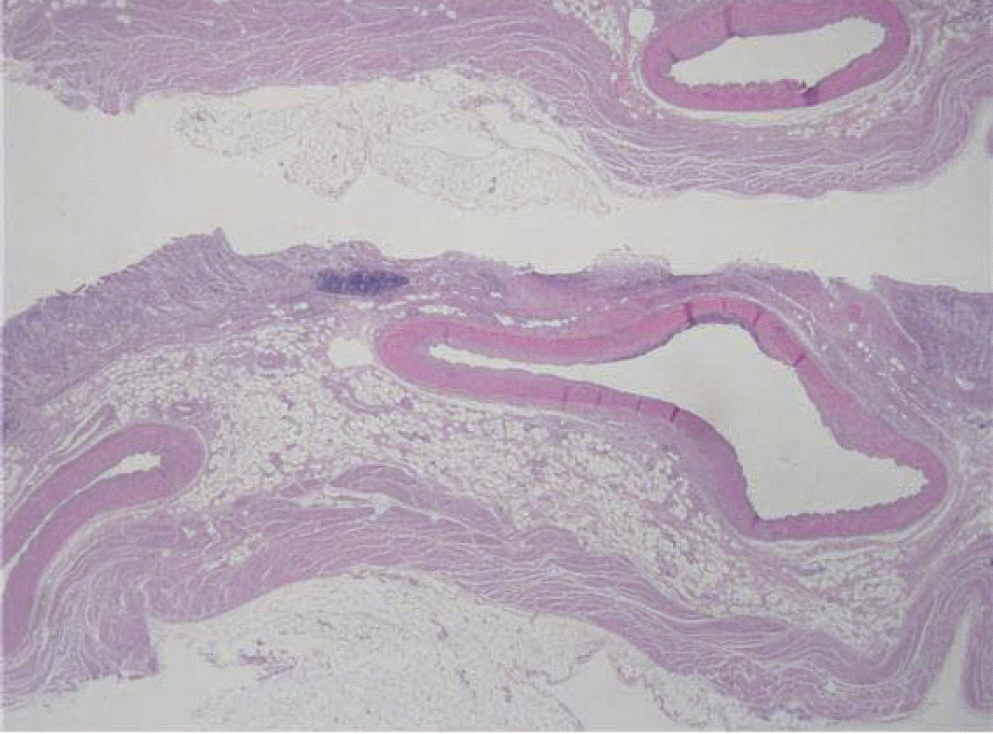
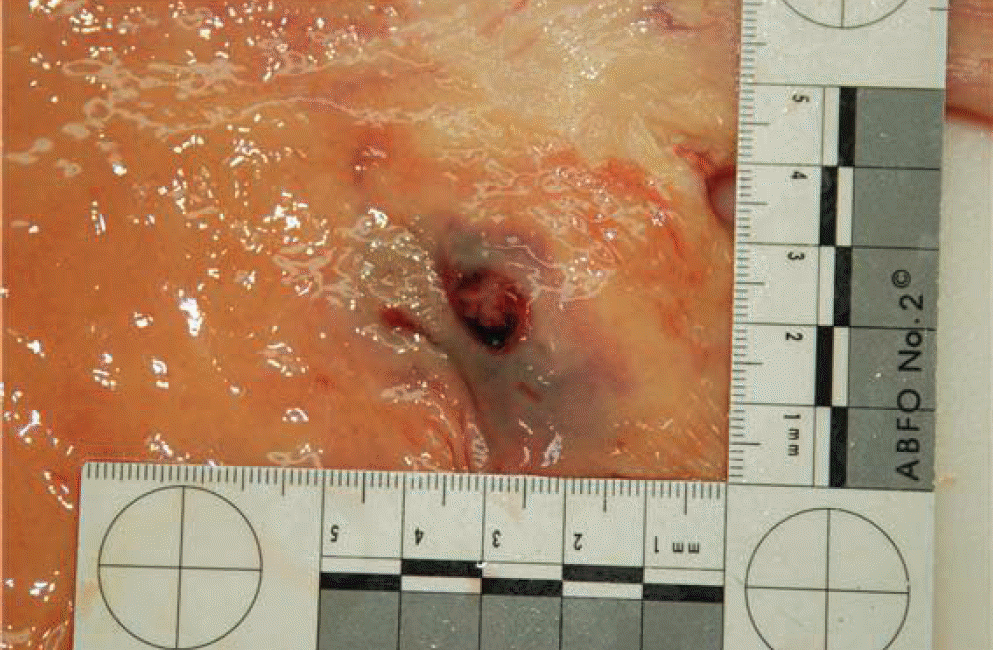
Dieulafoy's lesion is a rare condition that may cause intermittent or massive gastrointestinal bleeding. It is characterized by the exteriorization of an arterial vessel into the lumen of the affected organ, generally the upper digestive tract, through an apparently normal mucosa or a small tear or erosion. We report two patients with Dieulafoy's lesions, one in whom the lesion was misdiagnosed as a submucosal tumor and endoscopic biopsy resulted in fatal bleeding.
Go to : 
References
1. Senger JL, Kanthan R. The evolution of Dieulafoy's lesion since 1897: then and now-a journey through the lens of a pediatric lesion with literature review. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2012; 2012:432517.

2. Baxter M, Aly EH. Dieulafoy's lesion: current trends in diagnosis and management. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2010; 92:548–54.

3. Veldhuyzen Van Zanten SJ, Bartelsman JF, Schipper ME, et al. Recurrent massive hematemesis from Dieulafoy vascular malformations: a review of 101 cases. Gut. 1986; 27:213–22.
4. Lee JR, Kim MS, Kim DJ, et al. Gastric bleeding arisen in a patient with situs inversus totalis and large accessory spleen. J Korean Surg Soc. 2010; 78:258–61.

5. Grace PA, O'Sullivan R, Adam AN, et al. Case report: vascular anomaly in Dieulafoy's disease. Clin Radiol. 1991; 44:201–2.

6. Jeong HW, Kim JY, Kim SJ, et al. A case of a jejunal Dieulafoy's lesion mimicking a submucosal tumor. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 37:438–42.
7. Kim JH, Lee YS. Medicine and the law. 2nd ed.Seoul: Epublic;2008. p. 148–55.
Go to : 




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download