Abstract
Purpose
Materials and Methods
Results
REFERENCES
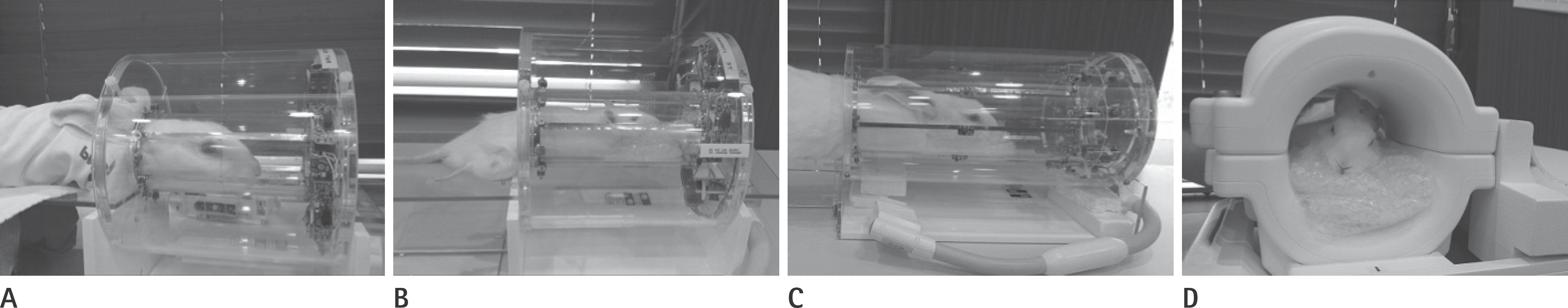 | Fig. 1.Surface coils used in the present study. Rat coil (5 cm in diameter) with a rabbit (A) and a rat (B) within the coil. Cat coil (C, 12 cm in di-ameter) and knee coil (D, 15.4 cm in diameter) with a rabbit within the coils. |
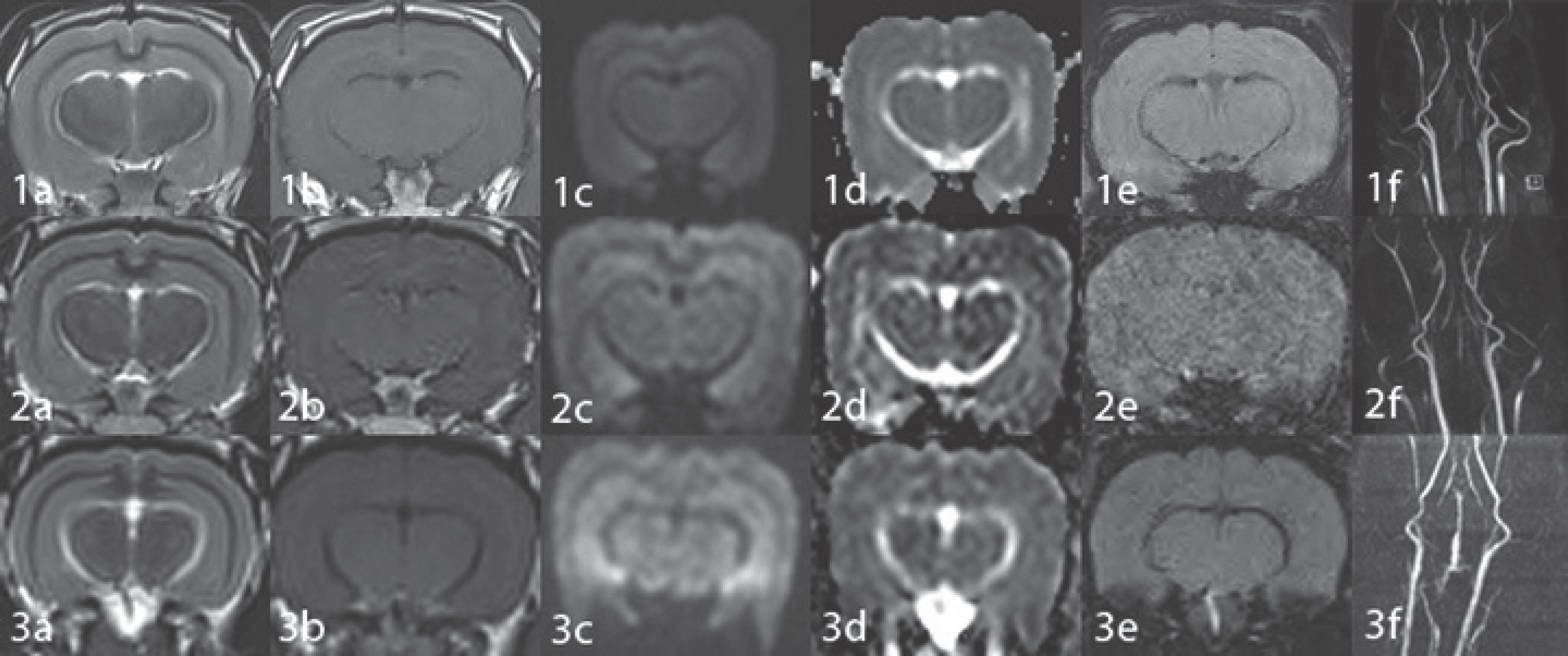 | Fig. 2.Brain MR images of a normal rabbit obtained with a rat coil (1), a cat coil (2) and a knee coil (3). T2WI (a), T1WI (b), DWI (c), ADC map image (d), SWI (e) and MRA (f). All MR images obtained with the rat coil reveal good differentiation of the gray/white matter and smoothness of the parenchyma. However, images obtained with the rat coil (1) show better quality compared to those obtained with the cat (2) or knee coil (3). The sharpness of MRA is best on the image obtained with the rat coil (1f) compared to the image obtained with the cat (2f) or knee coil (3f). ADC = apparent diffusion coefficient, DWI = diffusion-weighted image, MRA = MR angiography image, SWI = susceptibility-weighted image, T1WI = T1-weighted image, T2WI = T2-weighted image |
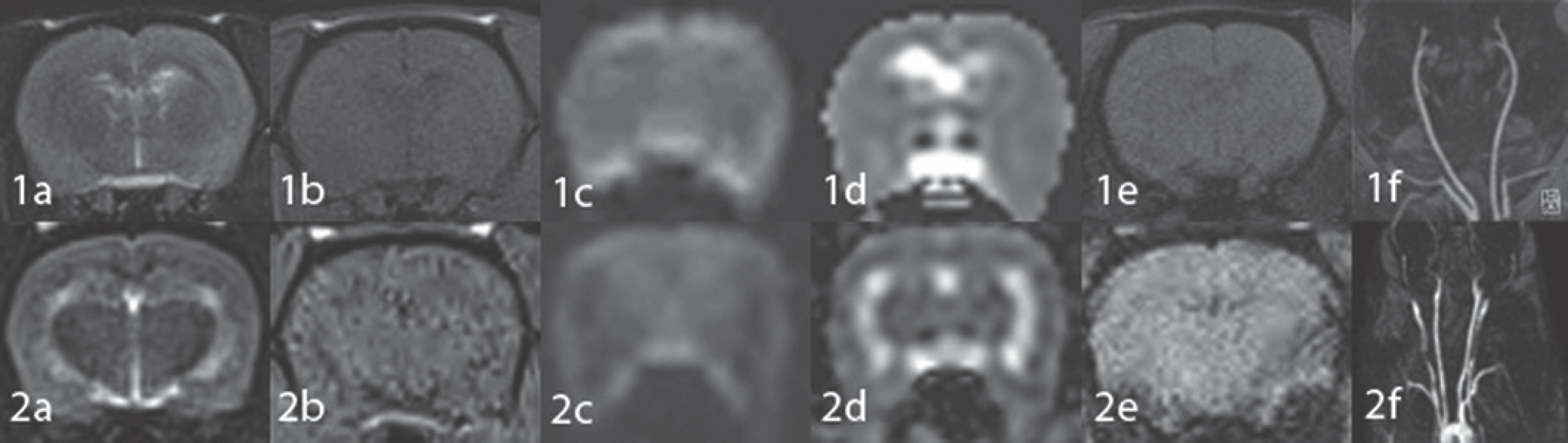 | Fig. 3.Brain MR images of a normal rat obtained with the rat coil (1) and with the cat coil (2). T2WI (a), T1WI (b), DWI (c), ADC map image (d), SWI (e) and MRA (f). MR images obtained with the rat coil (1) reveal better quality in terms of gray/white matter differentiation and smooth-ness compared to those obtained with the cat coil (2). MRA image obtained with the rat coil (1f) shows better sharpness compared to that ob-tained with the cat coil (2f). ADC = apparent diffusion coefficient, DWI = diffusion-weighted image, MRA = MR angiography image, SWI = susceptibility-weighted image, T1WI = T1-weighted image, T2WI = T2-weighted image |
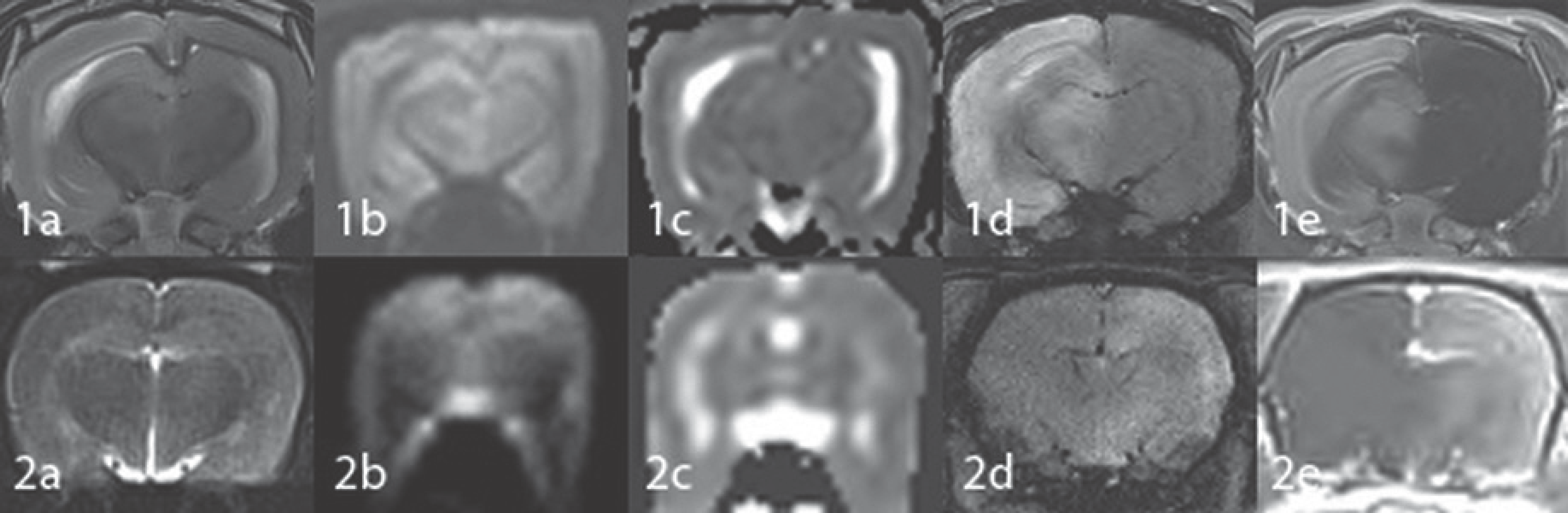 | Fig. 4.MR images of a rabbit (1) and a rat (2) obtained with the rat coil 2 hours after embolization of triolein emulsion into the carotid artery. Embolized hemispheres show mild hyperintensity on T2WI (a), no evidence of diffusion restriction (b, c), no hemorrhage on SWI (d) and diffuse contrast enhancement on Gd-T1WI (e). Lesion conspicuity is better on images obtained from the rabbit (1) compared with those obtained from the rat (2). SWI = susceptibility-weighted image, T1WI = T1-weighted image, T2WI = T2-weighted image |
Table 1.
bV = b value, DWI = diffusion-weighted image, ET = echo train length, FA = flip angle, FOV = field of view, Mat = matrix number, NEX = number of excitation, ST = slice thickness, SWI = susceptibility-weighted image, TE = echo time, TR = repetition time, T1WI = T1-weighted image, T2WI = T2-weighted image
Table 2.
bV = b value, DWI = diffusion-weighted image, ET = echo train length, FA = flip angle, FOV = field of view, Mat = matrix number, NEX = number of excitation, ST = slice thickness, SWI = susceptibility-weighted image, TE = echo time, TR = repetition time, T1WI = T1-weighted image, T2WI = T2-weighted image




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download