Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the results of two-injection ethanol sclerotherapy in simple renal cysts performed with 5-minute ethanol exposure time.
Materials and Methods
We retrospectively reviewed 30 renal cysts in 30 patients treated by ethanol sclerotherapy between November 2002 and October 2015. Under ultrasound guidance, the renal cyst was punctured and a 7 Fr pigtail catheter was in-serted, and then complete aspiration of the cystic fluid was performed. Then, 99.9% ethanol in a quantity amounting to 1/3–1/2 of the aspirated volume was infused into the cyst and it was immediately removed. The same amount of ethanol was re-infused and removed after 5 minutes. Follow-up examination was performed using ultra-sound or CT images at least 3 months after the procedure and pre- and post-treat-ment cyst volumes were estimated. The therapeutic response was classified as either complete success (volume reduction, ≥ 95%), partial success (volume reduction, 50–95%), or failure (volume reduction, < 50%) based on the volume reduction rate.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
3.Gasparini D., Sponza M., Valotto C., Marzio A., Luciani LG., Zatto-ni F. Renal cysts: can percutaneous ethanol injections be con-sidered an alternative to surgery? Urol Int. 2003. 71:197–200.

4.Cheng D., Amin P., Ha TV. Percutaneous sclerotherapy of cys-tic lesions. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2012. 29:295–300.

5.Skolarikos A., Laguna MP., de la Rosette JJ. Conservative and radiological management of simple renal cysts: a compre-hensive review. BJU Int. 2012. 110:170–178.

6.Efesoy O., Tek M., Bozlu M., Doruk HE. Comparison of single-session aspiration and ethanol sclerotherapy with laparo-scopic de-roofing in the management of symptomatic sim-ple renal cysts. Turk J Urol. 2015. 41:14–19.

7.Bean WJ. Renal cysts: treatment with alcohol. Radiology. 1981. 138:329–331.
8.Lucey BC., Kuligowska E. Radiologic management of cysts in the abdomen and pelvis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006. 186:562–573.

9.Paananen I., Hellström P., Leinonen S., Merikanto J., Perälä J., Päivänsalo M, et al. Treatment of renal cysts with single-session percutaneous drainage and ethanol sclerotherapy: long-term outcome. Urology. 2001. 57:30–33.

10.Mohsen T., Gomha MA. Treatment of symptomatic simple renal cysts by percutaneous aspiration and ethanol sclero-therapy. BJU Int. 2005. 96:1369–1372.

11.Hanna RM., Dahniya MH. Aspiration and sclerotherapy of symptomatic simple renal cysts: value of two injections of a sclerosing agent. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996. 167:781–783.

12.Akinci D., Akhan O., Ozmen M., Gumus B., Ozkan O., Kar-caaltincaba M, et al. Long-term results of single-session percutaneous drainage and ethanol sclerotherapy in simple renal cysts. Eur J Radiol. 2005. 54:298–302.

13.Park SH., Yang HC., Shin SK., Kim DJ., Park SM. Comparison of alcohol-retention sclerotherapy for simple cysts: single-session prolonged and multi-session techniques. J Korean Soc Radiol. 2009. 61:215–220.

14.Touloupidis S., Fatles G., Rombis V., Papathanasiou A., Balaxis E. Percutaneous drainage of simple cysts of the kidney: a new method. Urol Int. 2004. 73:169–172.

15.D'Ippolito G., Torres LR., Ribeiro ACR., Roque ADJ., Ortiz V., Ajzen S. Percutaneous ethanol sclerotherapy of renal cysts: treatment outcomes and literature review. Radiol Bras. 2009. 42:225–230.
16.Larssen TB., Rosendahl K., Horn A., Jensen DK., Rørvik J. Sin-gle-session alcohol sclerotherapy in symptomatic benign hepatic cysts performed with a time of exposure to alcohol of 10 min: initial results. Eur Radiol. 2003. 13:2627–2632.
17.S¸ims¸ek M., Kulog˘lu T., Pala S¸., Boztosun A., Can B., Atilgan R. The effect of ethanol sclerotherapy of 5 minutes duration on cyst diameter and rat ovarian tissue in simple ovarian cysts. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. 9:1341–1347.
18.Sample WF., Lippe BM., Gyepes MT. Gray-scale ultrasonogra-phy of the normal female pelvis. Radiology. 1977. 125:477–483.

19.Raskin MM., Poole DO., Roen SA., Viamonte M Jr. Percutane-ous management of renal cysts: results of a four-year study. Radiology. 1975. 115:551–553.

20.Holmberg G., Hietala SO. Treatment of simple renal cysts by percutaneous puncture and instillation of bismuth-phos-phate. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 1989. 23:207–212.

21.Ohkawa M., Tokunaga S., Orito M., Shimamura M., Hirano S., Okasho A, et al. Percutaneous injection sclerotherapy with minocycline hydrochloride for simple renal cysts. Int Urol Nephrol. 1993. 25:37–43.

22.Phelan M., Zajko A., Hrebinko RL. Preliminary results of per-cutaneous treatment of renal cysts with povidone-iodine sclerosis. Urology. 1999. 53:816–817.

23.Li L., Chen CC., Zeng XQ. One-year results of single-session sclerotherapy with bleomycin in simple renal cysts. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2012. 23:1651–1656.

24.Baysal T., Soylu A. Percutaneous treatment of simple renal cysts with n-butyl cyanoacrylate and iodized oil. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2009. 15:148–152.
25.Cho YJ., Shin JH. Comparison of acetic acid and ethanol sclerotherapy for simple renal cysts: clinical experience with 86 patients. Springerplus. 2016. 5:299.

26.Choi YD., Cho SY., Cho KS., Lee DH., Lee SH. Percutaneous treatment of renal cysts with OK-432 sclerosis. Yonsei Med J. 2007. 48:270–273.

27.Chung BH., Kim JH., Hong CH., Yang SC., Lee MS. Comparison of single and multiple sessions of percutaneous sclerothera-py for simple renal cyst. BJU Int. 2000. 85:626–627.

28.Lee CB., Lee JH., Jang H., Lee KB., Ha U., Cho DH. The efficacy of repeated sclerotherapy after percutaneous aspiration of the simple renal cyst. Korean J Urol. 2006. 47:252–256.

29.Cho DS., Ahn HS., Kim SI., Kim YS., Kim SJ., Jeon GS, et al. Sclerotherapy of renal cysts using acetic acid: a comparison with ethanol sclerotherapy. Br J Radiol. 2008. 81:946–949.

30.Lin YH., Pan HB., Liang HL., Chung HM., Chen CY., Huang JS, et al. Single-session alcohol-retention sclerotherapy for simple renal cysts: comparison of 2- and 4-hr retention techniques. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005. 185:860–866.

31.Omerovic´ S., Zerem E. Alcohol sclerotherapy in the treat-ment of symptomatic simple renal cysts. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2008. 8:337–340.
32.Kairaluoma MI., Leinonen A., Ståhlberg M., Päivänsalo M., Ki-viniemi H., Siniluoto T. Percutaneous aspiration and alcohol sclerotherapy for symptomatic hepatic cysts. An alternative to surgical intervention. Ann Surg. 1989. 210:208–215.
Go to : 
 | Fig. 1.A representative case of complete success in a 58-year-old woman. A. Pre-procedural contrast enhanced axial CT image shows a simple renal cyst with a volume of 449.78 mL (10 × 8.6 × 10 cm) in the right kidney. B, C. The renal cyst is punctured under ultrasound guidance (B) and a cystogram (C) shows neither extravasation of the contrast material nor a connection with the collecting system. D. At the 6-month follow-up, contrast enhanced axial CT image shows the remaining cyst with a volume of 3.14 mL (2.2 × 1.3 × 2.1 cm). Volume reduction rate is 99.3%. |
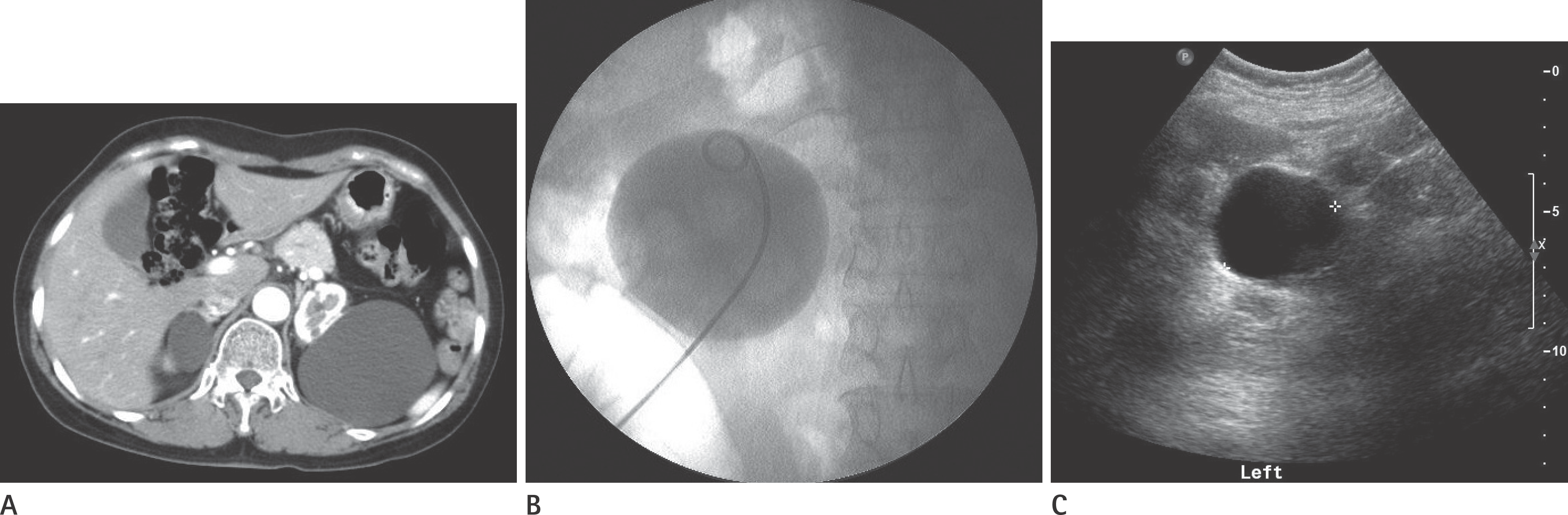 | Fig. 2.A representative case of partial success in a 56-year-old man. A. Pre-procedural contrast enhanced axial CT image shows a simple renal cyst with a volume of 234.3 mL (8 × 7 × 8 cm) in the left kidney. B. A 7Fr pigtail catheter is inserted into the renal cyst and a cystogram is obtained. C. At the 6-month follow-up, US image shows the remaining cyst with a volume of 41.49 mL (4.5 × 4.1 × 4.3 cm). Volume reduction rate is 82.3%. |
Table 1.
Variable Techiques of Ethanol Sclerotherapy on Simple Renal Cysts as Reported by Different Authors
Table 2.
Characteristics of Patients and Renal Cysts




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download