Abstract
Purpose
To present the typical and atypical magnetic resonance image (MRI) findings of intramedullary spinal ependymomas, and compare these findings with path-ological subtypes.
Materials and Methods
Between January 2003 to November 2014, 47 patients who had spinal ependymoma with pathologic confirmation, were retrospectively reviewed with all electronic medical records and MR images. MR imaging was done in all cases, and the images of spinal ependymomas and associated enhancement patterns were correlated with pathologic findings.
Results
The enhancement patterns were categorized into four categories: homogeneous, heterogeneous, rim-enhancement, and non-enhancement. Heterogeneous enhancement was observed in 50% of the cases. Among the 47 cases, 35 cases were well-marginated, with 21 being cervically located. All lesions were centrally located in the axial axis. Most of the cases showed T1-iso signal intensity (81%) and T2-high sig-nal intensity (72%). The hemosiderin cap sign, syringomyelia, tumoral and non-tu-moral cysts were well demonstrated. The most common pathologic type was cellular ependymoma. However, due to the small sample size, we believe it inappropriate to statistically discuss the MRI findings according to the pathologic subtype.
Go to : 
Index terms
Ependymoma, Spinal Cord Neoplasms, Magnetic Resonance ImagingREFERENCES
1. Abul-Kasim K, Thurnher MM, McKeever P, Sundgren PC. In-tradural spinal tumors: current classification and MRI features. Neuroradiology. 2008; 50:301–314.

2. Koeller KK, Rosenblum RS, Morrison AL. Neoplasms of the spinal cord and filum terminale: radiologic-pathologic cor-relation. Radiographics. 2000; 20:1721–1749.

3. Fine MJ, Kricheff II, Freed D, Epstein FJ. Spinal cord ependymomas: MR imaging features. Radiology. 1995; 197:655–658.

4. Kim DH, Kim JH, Choi SH, Sohn CH, Yun TJ, Kim CH, et al. Differentiation between intramedullary spinal ependymoma and astrocytoma: comparative MRI analysis. Clin Radiol. 2014; 69:29–35.

5. Lowe GM. Magnetic resonance imaging of intramedullary spinal cord tumors. J Neurooncol. 2000; 47:195–210.
6. McCormick PC, Torres R, Post KD, Stein BM. Intramedullary ependymoma of the spinal cord. J Neurosurg. 1990; 72:523–532.

7. Waldron JN, Laperriere NJ, Jaakkimainen L, Simpson WJ, Payne D, Milosevic M, et al. Spinal cord ependymomas: a retrospective analysis of 59 cases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1993; 27:223–229.

8. Kahan H, Sklar EM, Post MJ, Bruce JH. MR characteristics of histopathologic subtypes of spinal ependymoma. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1996; 17:143–150.
9. Miyazawa N, Hida K, Iwasaki Y, Koyanagi I, Abe H. MRI at 1.5 T of intramedullary ependymoma and classification of pattern of contrast enhancement. Neuroradiology. 2000. 42:828–832.
Go to : 
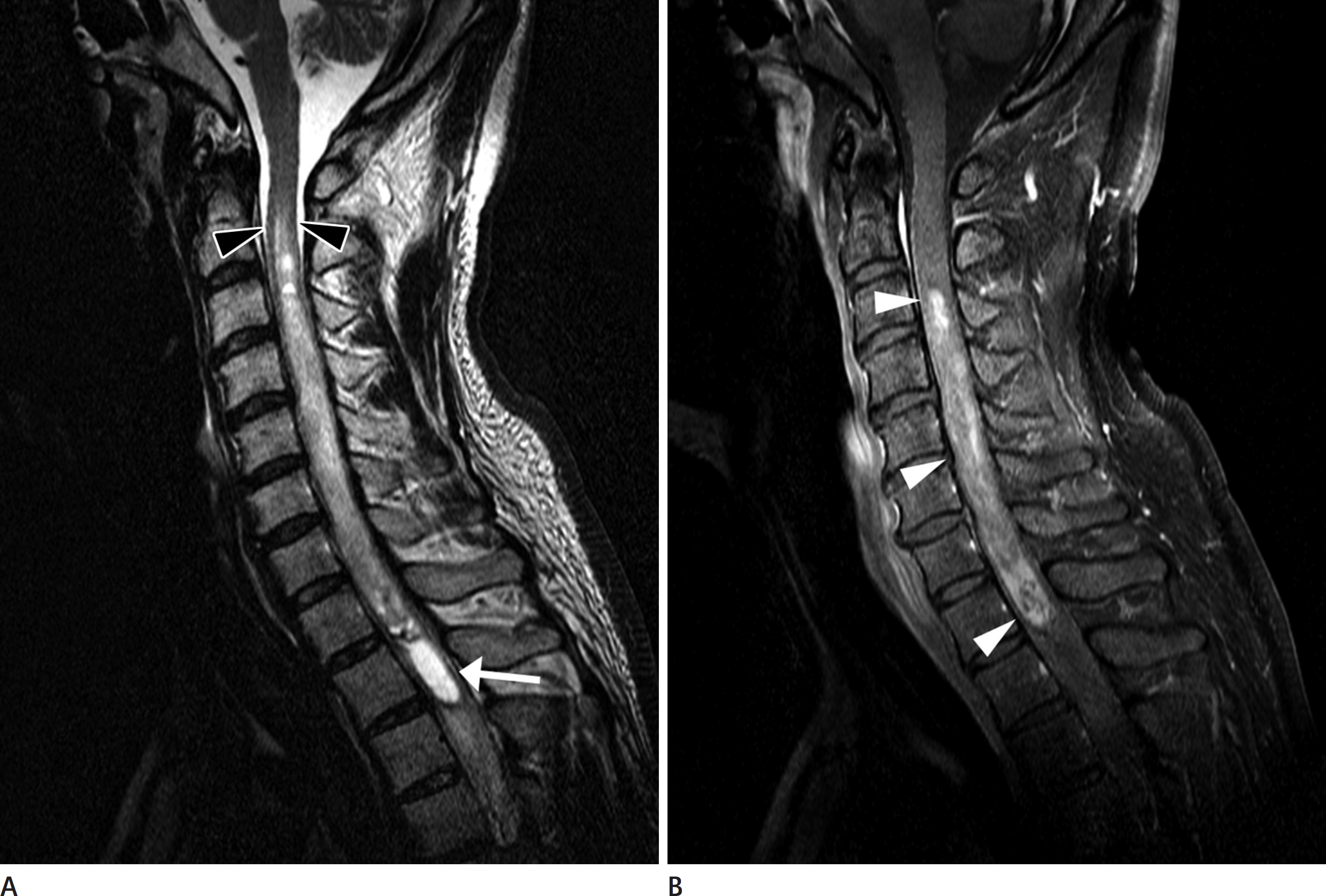 | Fig. 1.A 43-year-old male patient diagnosed as cellular ependymoma. A. Sagittal T2-weighted image shows heterogeneous hyperintense lesion throughout the cervical cord, with rostral non-tumoral cyst (white arrow) and spinal cord edema caudally (black arrowheads). B. Sagittal T1-weighted contrast enhancement image shows the heterogeneous enhancement of the tumor (white arrowheads). |
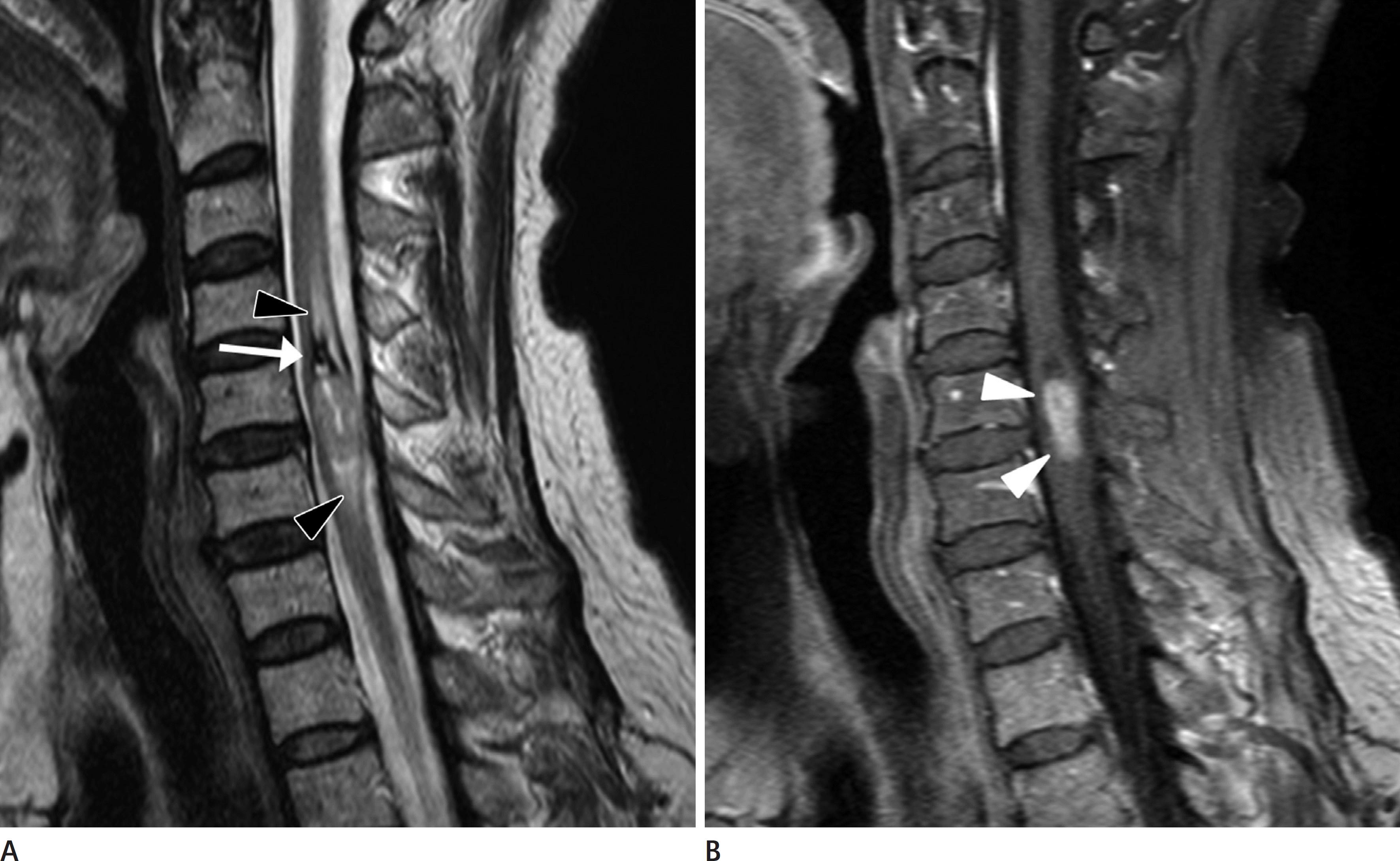 | Fig. 2.A 65-year-old female patient diagnosed as cellular ependymoma. A. Sagittal T2-weighted image demonstrates well-defined lesion with hemosiderin cap sign (white arrow) and cord edema (black arrowheads). B. Homogeneous enhancement (white arrowheads) of the solid lesion of the tumor is noted on sagittal T1-weighted contrast enhancement image. |
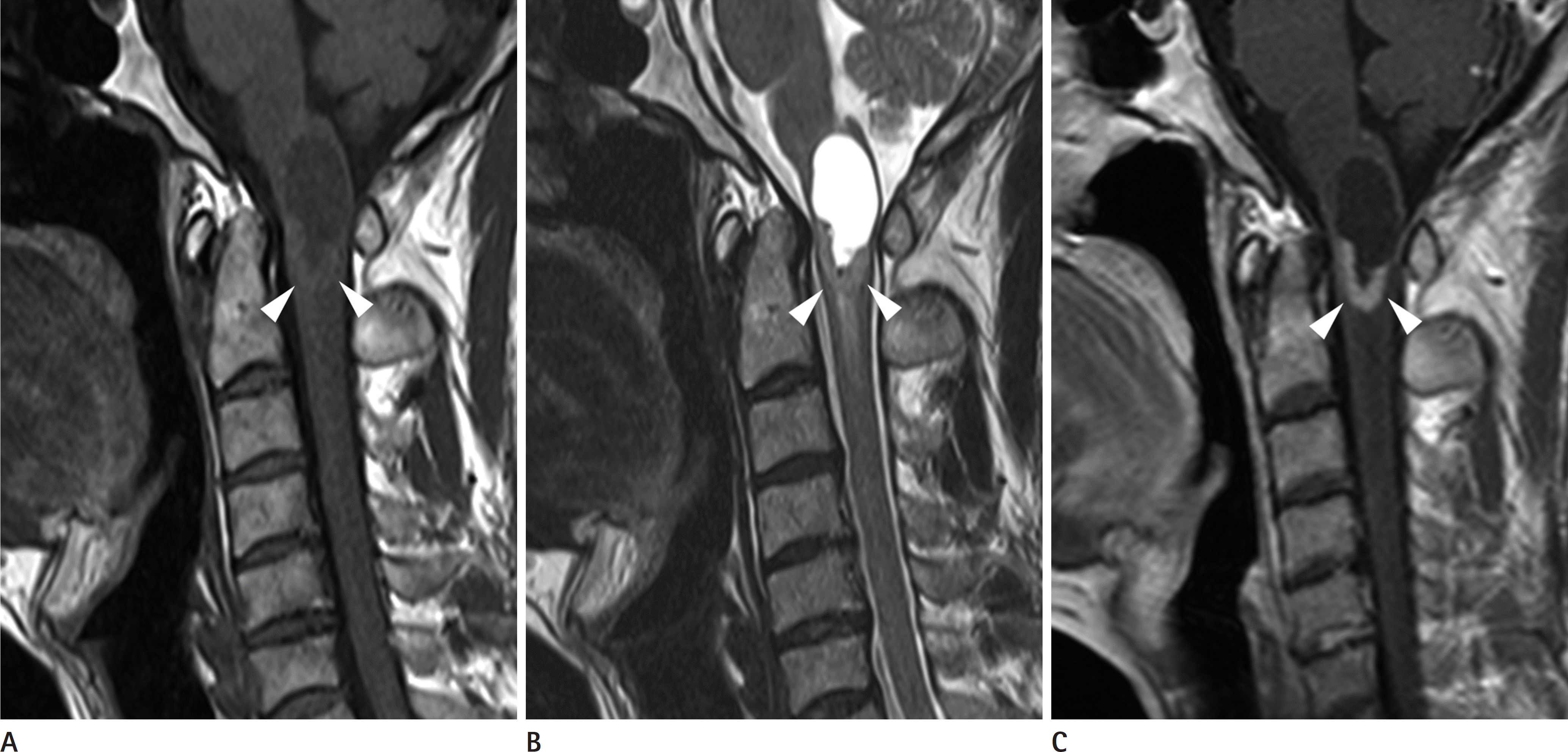 | Fig. 3.A 41-year-old male patient with cellular ependymoma. A. On the sagittal T1-weighted image, an approximately 3.5cm sized well-defined intramedullary mass in the cranio-cervical junction (white arrowheads). B. On the sagittal T2-weighted image, mass contained mainly cystic component with peripheral solid portion (white arrowheads) and rostral cord edema. C. On the sagittal contrast enhanced T1-weghted image, mass showed peripheral rim-enhancement (white arrowheads). |
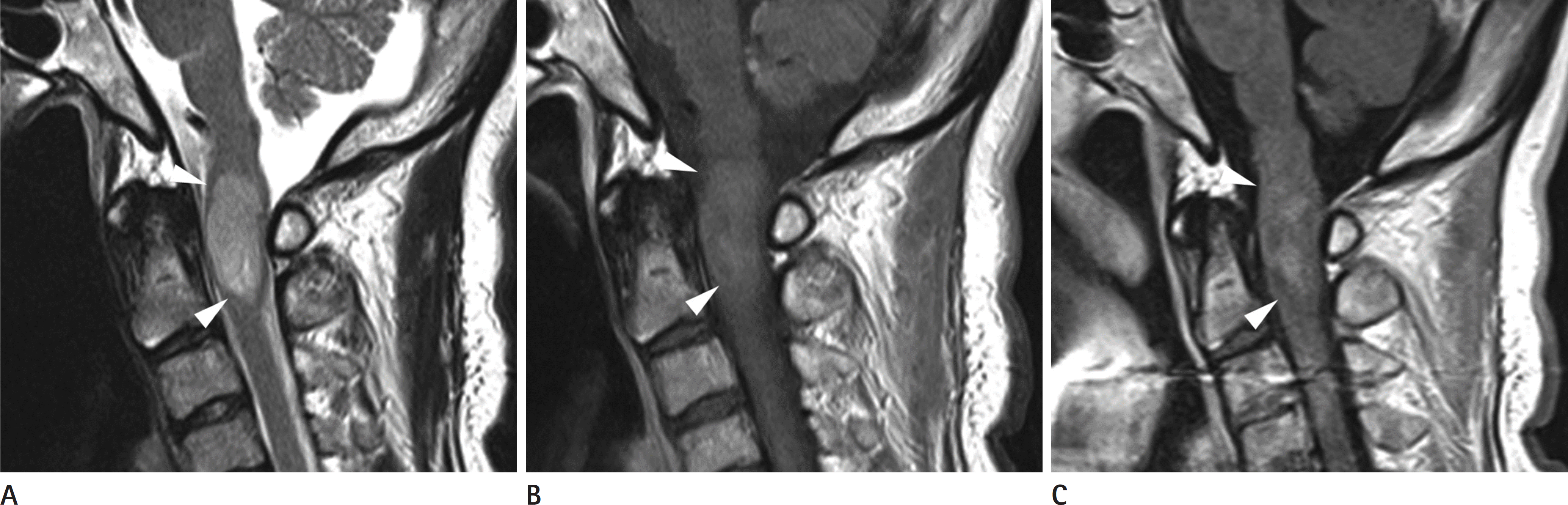 | Fig. 4.A 45-year-old female patient with cellular ependymoma. A-C. Sagittal T2, T1, and T1 contrast enhancement image shows heterogeneous T2 hyperintense, T1 isointense lesion with no enhancement (white arrowheads). |
 | Fig. 5.A 20-year-old female patient, who was finally diagnosed as anaplastic ependymoma. A. Initial sagittal T2-weighted and T1-weighted contrast enhancement image demonstrates heterogeneous enhancing lesion (white arrowheads) at thoracolumar spine, with caudal syrngomyelia (white arrows) and rostral tumoral cyst (black arrows). Initial diagnosis for the patient was cellular ependymoma. B. After tumor recurrence and reoperation, the patient was finally diagnosed as anaplastic ependymoma. The last MRI shows an extensive, heterogeneous enhancing lesion throughout the spine. |
Table 1.
MRI Appearance of Total 47 Ependymomas
| Image Findings | Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| Margin | |
| Well-defined | 35 (74) |
| Ill-defined | 12 (26) |
| T1 signal intensity | |
| Low signal intensity | 6 (13) |
| Iso signal intensity | 38 (81) |
| High signal intensity | 3 (6) |
| T2 signal intensity | |
| Low signal intensity | 0 (0) |
| Iso signal intensity | 13 (28) |
| High signal intensity | 34 (72) |
| Contrast-enhancement∗ | |
| Homogeneous | 17 (37) |
| Heterogeneous | 23 (50) |
| Rim | 5 (11) |
| None | 1 (2) |
| Hemosiderin cap | |
| Positive | 20 (43) |
| Negative | 27 (57) |
| Syringomyelia | |
| Positive | 31 (66) |
| Negative | 16 (34) |
| Tumoral cyst | |
| Positive | 22 (47) |
| Negative | 25 (53) |
| Nonetumoral cyst | |
| Positive | 10 (21) |
| Negative | 37 (79) |
Table 2.
Image Findings According to the Pathologic Type
| Conventional (39, 83%) | Anaplastic (1, 2%) | Myxopapillary (7, 15%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cellular (36, 77%) | Papillary (1, 2%) | Tanycytic (2, 4%) | |||
| Longitudinal location† | |||||
| Cervical | 19 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Thoracic | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Lumbo-sacral | 5 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 6 |
| Axial location | All central location | ||||
| Margin | |||||
| Well-defined | 25 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Ill-defined | 11 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| T1 | |||||
| Low signal intensity | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Iso signal intensity | 27 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 7 |
| High signal intensity | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| T2 | |||||
| Low signal intensity | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Iso signal intensity | 12 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| High signal intensity | 24 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 7 |
| Contrast-enhancement∗ | |||||
| Homogeneous | 12 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| Heterogeneous | 18 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| Rim | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| None | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download