Abstract
Purpose
Materials and Methods
Results
Conclusion
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Schematic illustration of application of the simplified ACR appropriateness criteria. All the ACR appropriateness criteria related to performing chest CT were selected and summarized into 37 topics. Based on the 1–9 rating scale of the ACR appropriateness criteria, all 37 topics were classified into 4 groups. If the topic had a 7–9 rating scale for chest CT with contrast, or chest CT without and with contrast, or CTA or CT venography chest with contrast, it fell into Group A. Group B had topics with a maximal 7–9 rating scale for chest CT without contrast and it was strongly recommended to perform chest CT without contrast. Among the remaining topics, if a topic had a 1–3 rating scale for all three; chest CT without contrast, chest CT with contrast, and chest CT without/with contrast, it was classified into Group D. The remaining topics, uncertainity of contrast usage for performing chest CT, belonged to Group C.
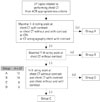
Fig. 2
A representative case of group B (strongly recommended to perform chest CT without contrast) with pulmonary thromboembolism.
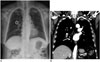
Table 1
The Simplified ACR Appropriateness Criteria Regarding Performing Chest CT

All the topics related to performing chest CT for carefully reviewed, and summarized into 37 topics. All the topics were then classified into 4 groups. There are 12 topics in Group A, 14 topics in Group B, 6 topics in Group C, and 5 topics in Group D.
ACR = American College of Radiology, CAD = coronary artery disease, CHF = congestive heart failure, COPD = chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, CPR = cardiopulmonary resuscitation, DVT = deep vein thrombosis, PEx = physical exam, SARS = severe acute respiratory syndrome, Sx = symptom
Table 2
Topics in the Group A–D

There are 12 topics of simplified ACR appropriateness criteria in the Group A with 491 patients. Among the topics, 69.6% of patients performed for suspected PE, and 14% were for the evaluation of suspected lower extremity DVT. 10.5% of patients in Group A had lung carcinoma, and performed chest CT for the evaluation of lung cancer. Group B contained 14 topics with 104 patients, that strongly recommend to perform chest CT without contrast. 72.1% of patients in Group B had extrathoracic malignancies and performed chest CT for the screening of pulmonary metastasis. About 14% of Group B patients were immunocompromised patients with acute respiratory illness, and presented positive findings on plain chest radiograph. There were 6 topics and 101 patients in Group C. 90 patients (86.5%) of Group C were immunocompetent and older than 40, and performed chest CT for acute respiratory illness. 5 topics in Group D were respiratory illness not necessary to perform chest CT. There wasn't any patient our study group who performed chest CT for these topics.
ACR = American College of Radiology, CAD = coronary artery disease, CHF = congestive heart failure, COPD = chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, CPR = cardiopulmonary resuscitation, DVT = deep vein thrombosis, PE = pulmonary embolism, PEx = physical exam, SARS = severe acute respiratory syndrome, Sx = symptom
Table 3
Clinical Features of Group A-C

The age, D-dimer, Hb, Hct, percentage of ICU admission, physical and consciousness status were significantly different among groups. All of the groups presented D-dimer levels above the normal range. Hb and Hct revealed significantly lower values in the Group B and C, possibly due to chronic illness such as malignancy of patients in the other groups.
Hb = hemoglobin, Hct = hematocrit, ICU = intensive care unit




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download