Abstract
Purpose
CT perfusion (CTP) is an important modality in the diagnosis of acute stroke, and the range of its use is gradually expanding from supratentorial to whole brain stroke. We assessed the diagnostic value of multichannel CTP in comparison with conventional CT (CT) in acute pontine infarct.
Materials and Methods
CTP and follow-up diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging were performed in 74 patients diagnosed with acute pontine infarct among 178 suspicious ones. Diagnostic accuracy of CTP and CT was evaluated and quantitative analysis was performed to define the factors that may influence the detection rate.
Results
In the diagnosis of acute pontine infarct, the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of CTP was 56.8%, 91.4%, and 77.0% and of conventional CT scan was 47.3%, 93.3%, and 74.2%, respectively. There was no statistically significant difference. Receiver operation characteristic curve revealed both types of imaging to have diagnostic usefulness (p < 0.01) in acute pontine infarct. Among the factors that may affect the detection rate, infarct volume was found to be statistically significant (CTP: p < 0.01, CT: p = 0.01).
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Toggling table technique.
A. The scanner obtains images during a single rotation at location upper half location of the object.
B. Table moves upward to locate the lower half of the object under the X-ray tube.
C. Scanner obtains images during a single rotation at location.
D. Table moves 4 cm in the opposite direction to the original position.
E. Second cycle of scanning is repeated.

Fig. 2
A case of abnormal finding on conventional CT, but not identified by CTP in right pontine infarction. Three days before examination, this 66-year-old man experienced dysarthria and left side weakness.
A, B. Early conventional CT scans show abnormal hypodensity (arrow) in the right pons (A: precontrast CT scan, B: enhanced CT scan).
C. All CTP maps confirm the absence of perfusion abnormality in the right pons.
D. Follow-up DWI of MRI, obtained 1 day after stroke, shows infarction (arrow) in the former ischemic portion of the right anteromedial pons. infarct volume: 0.501 mL, diffusion restriction value: 1893.3 (mean).
Note.-CBF = cerebral bloodflow, CBV = cerebral blood volume, CTP = CT perfusion, DWI = diffusion weighted imaging, MTT = mean transit time
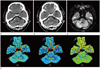
Fig. 3
A case of positive abnormal finding on CTP and but not identified by conventional CT in right pontine infarction. One day before examination, this 51-year-old man experienced dysarthria and left side weakness.
A, B. Early conventional CT scans appear normal in the right pons (A: precontrast CT scan, B: enhanced CT scan).
C. All CTP maps show perfusion abnormality (arrow) in the right pons.
D. Follow-up DWI of MRI, obtained 1 day after stroke, shows infarction (arrow) in the former ischemic portion of the right anteromedial pons. infarct volume: 0.976 mL, diffusion restriction value: 669.5 (mean).
Note.-CBF = cerebral blood flow, CBV = cerebral blood volume, CTP = CT perfusion, DWI = diffusion weighted imaging, MTT = mean transit time
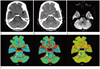
Fig. 4
Volumetric measurement of the infarct lesion. Boundary of the lesion was drawn and then the volume of the area was automatically calculated.

References
1. Ledezma CJ, Wintermark M. Multimodal CT in stroke imaging: new concepts. Radiol Clin North Am. 2009. 47:109–116.
2. Lee IH, You JH, Lee JY, Whang K, Kim MS, Kim YJ, et al. Accuracy of the detection of infratentorial stroke lesions using perfusion CT: an experimenter-blinded study. Neuroradiology. 2010. 52:1095–1100.
3. Roberts HC, Roberts TP, Smith WS, Lee TJ, Fischbein NJ, Dillon WP. Multisection dynamic CT perfusion for acute cerebral ischemia: the "toggling-table" technique. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001. 22:1077–1080.
4. Koenig M, Klotz E, Luka B, Venderink DJ, Spittler JF, Heuser L. Perfusion CT of the brain: diagnostic approach for early detection of ischemic stroke. Radiology. 1998. 209:85–93.
5. Axel L. Tissue mean transit time from dynamic computed tomography by a simple deconvolution technique. Invest Radiol. 1983. 18:94–99.
6. Wintermark M, Fischbein NJ, Smith WS, Ko NU, Quist M, Dillon WP. Accuracy of dynamic perfusion CT with deconvolution in detecting acute hemispheric stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005. 26:104–112.
7. Youn SW, Kim JH, Weon YC, Kim SH, Han MK, Bae HJ. Perfusion CT of the brain using 40-mm-wide detector and toggling table technique for initial imaging of acute stroke. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008. 191:W120–W126.
8. Röther J, Jonetz-Mentzel L, Fiala A, Reichenbach JR, Herzau M, Kaiser WA, et al. Hemodynamic assessment of acute stroke using dynamic single-slice computed tomographic perfusion imaging. Arch Neurol. 2000. 57:1161–1166.
9. Nabavi DG, Cenic A, Craen RA, Gelb AW, Bennett JD, Kozak R, et al. CT assessment of cerebral perfusion: experimental validation and initial clinical experience. Radiology. 1999. 213:141–149.
10. Choi JH, Seo JJ, Kim JK, Chung TW, Jeong YY, Park JG, et al. The usefulness of perfusion CT in acute cerebral ischemic infarction. J Korean Radiol Soc. 2003. 49:7–14.
11. Mayer TE, Hamann GF, Baranczyk J, Rosengarten B, Klotz E, Wiesmann M, et al. Dynamic CT perfusion imaging of acute stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000. 21:1441–1449.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download