Abstract
Purpose
To assess the effectiveness of pain control using ultrasound-guided steroid injection by the extra-articular and intra-articular approaches to femoroacetabular impingement patients.
Materials and Methods
From September through December 2010, 18 patients with clinical suspicion of femoroacetabular impingement syndrome underwent ultrasound-guided steroid and local anesthetics injection: a total of 20 cases, including 16 cases of ipsilateral and 2 cases of bilateral injection. Extra-articular or intra-articular approach was selected for each patient, randomly and alternately. Nine cases were performed by extra-articular approach and 11 cases were performed by intra-articular approach. Every patient was observed in the outpatient clinic and visual analogue scale (VAS) was taken and compared before and after the procedure in all patients.
Results
Pre-injection average VAS value of extra-articular approached cases was 5.22 ± 1.99 and post-injection average VAS value was 4.11 ± 1.96, which is statistically insignificant (p < 0.156). The average VAS value of intra-articular approached cases was decreased from 5.72 ± 2.15 to 2.91 ± 2.30 after injection, which is statistically significant (p < 0.006).
Figures and Tables
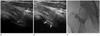 | Fig. 1Example of ultrasound-guided intra-articular steroid injection in a 40-year-old male patient.
A. On ultrasound image before contrast injection, tip of 22-gauge 3.5-inch spinal needle is placed in the hip joint cavity (arrowhead).
B. Intra-articular injection is performed. A hyperechoic line shows injectates (arrows).
C. A fluoroscopic image is checked and this image shows intra-articular contrast filling of the hip joint.
|
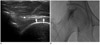 | Fig. 2Example of ultrasound-guided extra-articular steroid injection in a 51-year-old female patient.
A. On ultrasound image of extra-articular injection, tip of 22-gauge 3.5-inch spinal needle is placed at the undersurface of proximal rectus femoris muscle (arrowhead). A hyperechoic line shows injectates (arrows).
B. A fluoroscopic image is checked and this image shows extra-articular contrast filling of the hip joint.
|
References
1. Tannast M, Siebenrock KA, Anderson SE. Femoroacetabular impingement: radiographic diagnosis--what the radiologist should know. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007. 188:1540–1552.
2. Beall DP, Sweet CF, Martin HD, Lastine CL, Grayson DE, Ly JQ, et al. Imaging findings of femoroacetabular impingement syndrome. Skeletal Radiol. 2005. 34:691–701.
3. Hwang DS, Nam DC, Yang JH, Kang TH. Usefulness of hip joint AP plain X-ray radiographs in femoroacetabular impingement. J Korean Hip Soc. 2007. 19:105–111.
4. Şahin N, Atici T, Öztürk A, Özkaya G, Özkan Y, Avcu B. Prevalence of femoroacetabular impingement in asymptomatic contralateral hips in patients with unilateral idiopathic osteoarthritis. J Int Med Res. 2011. 39:790–797.
5. Palmer WE. Femoroacetabular impingement: caution is warranted in making imaging-based assumptions and diagnoses. Radiology. 2010. 257:4–7.
6. Clohisy JC, McClure JT. Treatment of anterior femoroacetabular impingement with combined hip arthroscopy and limited anterior decompression. Iowa Orthop J. 2005. 25:164–171.
7. Lavigne M, Parvizi J, Beck M, Siebenrock KA, Ganz R, Leunig M. Anterior femoroacetabular impingement: part I. Techniques of joint preserving surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004. 61–66.
8. Crawford JR, Villar RN. Current concepts in the management of femoroacetabular impingement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005. 87:1459–1462.
9. Wisniewski SJ, Grogg B. Femoroacetabular impingement: an overlooked cause of hip pain. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2006. 85:546–549.
10. Hart ES, Metkar US, Rebello GN, Grottkau BE. Femoroacetabular impingement in adolescents and young adults. Orthop Nurs. 2009. 28:117–124. quiz 125-126.
11. Emara K, Samir W, Motasem el H, Ghafar KA. Conservative treatment for mild femoroacetabular impingement. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2011. 19:41–45.
12. Ravaud P, Moulinier L, Giraudeau B, Ayral X, Guerin C, Noel E, et al. Effects of joint lavage and steroid injection in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee: results of a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 1999. 42:475–482.
13. Favejee MM, Huisstede BM, Koes BW. Frozen shoulder: the effectiveness of conservative and surgical interventions--systematic review. Br J Sports Med. 2011. 45:49–56.
14. Kivlan BR, Martin RL, Sekiya JK. Response to diagnostic injection in patients with femoroacetabular impingement, labral tears, chondral lesions, and extra-articular pathology. Arthroscopy. 2011. 27:619–627.
15. Panzer S, Augat P, Esch U. CT assessment of herniation pits: prevalence, characteristics, and potential association with morphological predictors of femoroacetabular impingement. Eur Radiol. 2008. 18:1869–1875.
16. Beck M, Kalhor M, Leunig M, Ganz R. Hip morphology influences the pattern of damage to the acetabular cartilage: femoroacetabular impingement as a cause of early osteoarthritis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005. 87:1012–1018.
17. Pfirrmann CW, Mengiardi B, Dora C, Kalberer F, Zanetti M, Hodler J. Cam and pincer femoroacetabular impingement: characteristic MR arthrographic findings in 50 patients. Radiology. 2006. 240:778–785.
18. Kassarjian A, Yoon LS, Belzile E, Connolly SA, Millis MB, Palmer WE. Triad of MR arthrographic findings in patients with cam-type femoroacetabular impingement. Radiology. 2005. 236:588–592.
19. Anderson SE, Siebenrock KA, Tannast M. Femoroacetabular impingement: evidence of an established hip abnormality. Radiology. 2010. 257:8–13.
20. Murphy S, Tannast M, Kim YJ, Buly R, Millis MB. Debride ment of the adult hip for femoroacetabular impingement: indications and preliminary clinical results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004. 178–181.
21. Chang JS, Son HC, Park JH, Kim KH. Periacetabular osteotomy for acetabular retroversion: a case report. J Korean Hip Soc. 2003. 15:158–161.
22. Hwang DS, Lee CH, Lee CH. Arthroscopic treatment of osseous abnormalities as a cause of femoroacetabular impingement: preliminary clinical results. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2006. 41:778–784.
23. Sung YB. Osteotomy around the hip: overview. J Korean Hip Soc. 2007. 19:236–239.
24. Hwang DS, Nam DC, Yang JH. Arthroscopic treatment of osseous abnormalities as a cause of femoroacetabular impingement: preliminary clinical results. J Korean Hip Soc. 2007. 19:112–120.
25. Byrd JW, Jones KS. Arthroscopic femoroplasty in the management of cam-type femoroacetabular impingement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009. 467:739–746.
26. Philippon MJ, Stubbs AJ, Schenker ML, Maxwell RB, Ganz R, Leunig M. Arthroscopic management of femoroacetabular impingement: osteoplasty technique and literature review. Am J Sports Med. 2007. 35:1571–1580.
27. Ayeni OR, Wong I, Chien T, Musahl V, Kelly BT, Bhandari M. Surgical indications for arthroscopic management of femoroacetabular impingement. Arthroscopy. 2012. 28:1170–1179.
28. Rebello G, Spencer S, Millis MB, Kim YJ. Surgical dislocation in the management of pediatric and adolescent hip deformity. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009. 467:724–731.
29. Bardakos NV, Villar RN. Predictors of progression of osteoarthritis in femoroacetabular impingement: a radiological study with a minimum of ten years follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009. 91:162–169.
30. Hartofilakidis G, Bardakos NV, Babis GC, Georgiades G. An examination of the association between different morphotypes of femoroacetabular impingement in asymptomatic subjects and the development of osteoarthritis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011. 93:580–586.
31. Espinosa N, Rothenfluh DA, Beck M, Ganz R, Leunig M. Treatment of femoro-acetabular impingement: preliminary results of labral refixation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006. 88:925–935.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download