Abstract
Purpose
Materials and Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
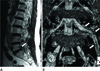 | Fig. 1Sixty-five-year-old female with left leg pain.
A. Sagittal T2-weighted image shows a stenotic foramen (arrow) at L5-S1.
B. On 3D MR lumbosacral radiculography by Proset imaging, the swelling of the nerve root and dorsal root ganglion is demonstrated (arrows).
Note.-MR = magnetic resonance, Proset = principles of the selective excitation technique, 3D = three-dimension
|
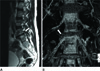 | Fig. 2Thirty-two-year-old female with right leg pain.
A. Sagittal T2-weighted image shows a stenotic foramen (arrow) at L5-S1.
B. On 3D MR lumbosacral radiculography by Proset imaging, the indentation of the nerve root is demonstrated (arrow).
Note.-MR = magnetic resonance, Proset = principles of the selective excitation technique, 3D = three-dimension
|
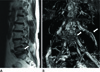 | Fig. 3Seventy-nine-year-old female with left leg pain.
A. Sagittal T2-weighted image shows a stenotic foramen (arrow) at L5-S1.
B. On a 3D MR lumbosacral radiculography by Proset imaging, the swelling and tilting angle abnormality of the nerve root are demonstrated (arrows).
Note.-MR = magnetic resonance, Proset = principles of the selective excitation technique, 3D = three-dimension
|
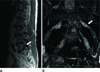 | Fig. 4Seventy-three-year-old female with back pain without radiculopathy.
A. Sagittal T2-weighted image shows a stenotic foramen (arrow) at L5-S1.
B. On 3D MR lumbosacral radiculography by Proset imaging, the morphologic change of the nerve root is not demonstrated (arrow).
Note.-MR = magnetic resonance, Proset = principles of the selective excitation technique, 3D = three-dimension
|
Table 2
Incidence of Nerve Root Swelling in Lumbar Foraminal Stenosis on 3D Lumbosacral Radiculography

Number of nerve roots with swelling/total number of nerve roots.
There was statistically significant difference in swelling of the nerve root among asymptomatic and symptomatic foraminal stenosis (χ2 test, p < 0.001).
Note.-FN = false negative, FP = false positive, NA = not assessed, TN = true negative, TP = true positive, 3D = three-dimension
Table 3
Incidence of Indentation of Nerve Root in Lumbar Foraminal Stenosis on 3D Lumbosacral Radiculography

Number of the nerve root with indentation/total number of nerve root.
There was statistically significant difference in indentation of the nerve root among asymptomatic and symptomatic foraminal stenosis (χ2 test, p = 0.047).
Note.-FN = false negative, FP = false positive, NA = not assessed, TN = true negative, TP = true positive, 3D = three-dimension
Table 4
Incidence of the Tilting Angle Abnormality of Nerve Root in Lumbar Foraminal Stenosis on 3D Lumbosacral Radiculography

Number of nerve roots with tilting angle abnormality/total number of nerve roots.
There was no statistically significant difference in the tilting angle abnormality of the nerve root among asymptomatic and symptomatic foraminal stenosis (χ2 test, p = 0.100).
Note.-FN = false negative, FP = false positive, NA = not assessed, TN = true negative, TP = true positive, 3D = three-dimension
Table 5
Incidence of Three Morphologic Changes of Nerve Root in Lumbar Foraminal Stenosis on 3D Lumbosacral Radiculography

Number of nerve roots with one or more of the three morphologic changes/total number of nerve roots.
There was statistically significant difference in three morphologic findings of the nerve root among asymptomatic and symptomatic foraminal stenosis (χ2 test, p < 0.001).
Note.-FN = false negative, FP = false positive, NA = not assessed, TN = true negative, TP = true positive, 3D = three-dimension




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download