Abstract
Intramural esophageal dissection (IED) is an uncommon disorder characterized by a seperation between the esophageal mucosa and submucosa with or without perforation. IED is usually related with an abrupt increase in intraesophageal pressure, history of recent instrumentation, and a coagulation disorder. We report a case of IED showing extensive dissection into the wall of the stomach, which successfully subsided by conservative treatment.
Figures and Tables
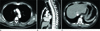
Fig. 1
A initial findings of 45-year-old man with abrupt onset sore throat during gastroendoscopy.
A. A transaxial CT image shows the esophageal double lumen (arrow) in sub-aortic arch level.
B. A sagittal lung window setting CT image shows a long longitudinal canal (arrows) consist of true and false lumen in the thoracic esophagus.
C. A transaxial CT image shows continuous through to the lesser curvature of stomach of submucosal dissection (white arrow) and small amount perigastric pneumoperitoneum (black arrow).
D. Gastrograffin esophagography image shows the typical double-barreled appearance of esophagus.

References
1. Young CA, Menias CO, Bhalla S, Prasad SR. CT features of esophageal emergencies. Radiographics. 2008; 28:1541–1553.
2. Marks IN, Keet AD. Intramural rupture of the oesophagus. Br Med J. 1968; 3:536–537.
3. Soulellis CA, Hilzenrat N, Levental M. Intramucosal esophageal dissection leading to esophageal perforation: case report and review of the literature. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2008; 4:362–365.
4. Kim KH, Kuh JH, Lee JM. Intramural dissection and mucosal laceration of the esophagus in a patient who was on antiplatelets medication: a case report. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2009; 42:657–661.
5. Byun JH, Cho SR, Cho SH. Spontaneous intramural esophageal dissection occurred in middle aged woman: one case experience. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2006; 39:569–571.
6. Steadman C, Kerlin P, Crimmins F, Bell J, Robinson D, Dorrington L, et al. Spontaneous intramural rupture of the oesophagus. Gut. 1990; 31:845–849.
7. Phan GQ, Heitmiller RF. Intramural esophageal dissection. Ann Thorac Surg. 1997; 63:1785–1786.
8. Hutchinson R, Ahmed AR, Menzies D. A case of intramural oesophageal dissection secondary to nasogastric tube insertion. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2008; 90:W4–W7.
9. Kerr WF. Spontaneous intramural rupture and intramural haematoma of the oesophagus. Thorax. 1980; 35:890–897.
10. Wang S, Ruan Z, Liu F, Huang H, Zheng J, Song K. A rare case of circumferential intramural dissection of the thoracic esophagus. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010; 58:494–495.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download