Abstract
A breast ultrasonography is the most frequently performed radiologic study along with the mammography. As in the mammography, breast ultrasonography renders the final evaluation by examining the shape, orientation, margin, border, echogenicity, patterns of the posterior shadowing, and changes of surrounding tissue of the breast mass according to BI-RADS (Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System). Apocrine proliferation of the breast is a common aging phenomenon, but the radiologic features are rarely reported. We described the radiologic features of breast apocrine lesions.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Apocrine metaplasia in 48-year-old woman with incidentally detected breast mass.
US shows a 1.97 cm sized, well circumscribed, ovoid, anechoic cyst at subareola, associated with posterior enhancement.
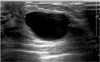
Fig. 2
Apocrine metaplasia in 45-year-old woman with incidentally detected breast mass.
US shows a 2 cm sized, clustered microcysts with thin internal septations at 12H direction, 1.8 cm far from the nipple.
Fig. 3
Apocrine adenosis in 66-year-old woman.
US shows a 0.9 cm, intracystic solid mass that represented as complex cyst. It looks like intraductal papilloma.
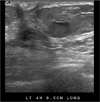
Fig. 4
Apocrine adenosis in 20-year-old woman with palpable breast mass.
US shows a 1.35 cm, ill defined, ovoid mixed echoic mass at 10 H direction, 5 cm fat from the right nipple (arrow).
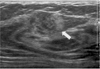
Fig. 5
Intraductal papilloma with apocrine metaplasia in 38-year-old woman with palpable breast mass.
US shows a 1.5 cm sized, complex cyst, having thin septation and peripherally attached solid portion (arrow).
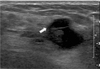
Fig. 6
Fibroadenoma with apocrine metaplasia in 22-year-old woman with palpable breast mass and pain.
US shows a 2.0 cm sized, well circumscribed, ovoid isoechoic mass with small cystic changes (arrow).
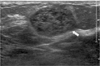
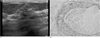
Fig. 7
Apocrine intraductal carcinoma in 61-year-old woman with incidentally detected breast mass.
A. US shows a 1.7 cm sized, irregular inhomogeneously hypoechoic mass with ill-defined margin at the 9H direction, 7 cm far from the nipple.
B. Pathology demonstrates cystically dilated ducts lined by apocrine cells showing eosinophillic cytoplasm on H & E stain (×400)
References
1. Trenkic S, Katic V, Pashalina M, Zivkovic V, Milentijevic M, Kostov M. The histologic spectrum of apocrine lesions of the breast. Arch Oncol. 2004; 12:61–65.
2. Wells CA, El-Ayat GA. Non-operative breast pathology: apocrine lesions. J Clin Pathol. 2007; 60:1313–1320.
3. Warner JK, Kumar D, Berg WA. Apocrine metaplasia: mammographic and sonographic appearances. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998; 170:1375–1379.
4. Berg WA. Sonographically depicted breast clustered microcysts: is follow-up appropriate? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005; 185:952–959.
5. O'Malley FP, Bane AL. The spectrum of apocrine lesions of the breast. Adv Anat Pathol. 2004; 11:1–9.
6. Gill HK, Ioffe OB, Berg WA. When is a diagnosis of sclerosing adenosis acceptable at core biopsy? Radiology. 2003; 228:50–57.
7. Zagorianakou P, Zagorianakou N, Stefanou D, Makrydimas G, Agnantis NJ. The enigmatic nature of apocrine breast lesions. Virchows Arch. 2006; 448:525–531.
8. Leal C, Henrique R, Monteiro P, Lopes C, Bento MJ, De Sousa CP, et al. Apocrine ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast: histologic classification and expression of biologic markers. Hum Pathol. 2001; 32:487–493.
9. Haagensen CD. Diseases of the breast. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders;1986. p. .
10. Kopans DB, Nguyen PL, Koerner FC, White G, McCarthy KA, Hall DA, et al. Mixed form, diffusely scattered calcifications in breast cancer with apocrine features. Radiology. 1990; 177:807–811.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download