Abstract
Background
Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
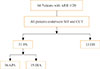 | Fig. 1The flow diagram of the study subjects. All patients underwent both saline infusion test (SIT) and captopril challenge test (CCT). If positive result of SIT and CCT, adrenal venous sampling was conducted for distinguishing aldosterone producing adenoma (APA) and idiopathic hyperaldosteronism (IHA). ARR, aldosterone-to-renin ratio; PA, primary aldosteronism; EH, essential hypertension. |
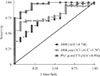 | Fig. 2Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis for aldosterone-to-renin ratio (ARR), ARR post-captopril challenge test (CCT), and plasma aldosterone concentration (PAC) post-CCT for the diagnosis of primary aldosteronism. PAC post-CCT showed very accruable with large area under the curve (AUC). The black line represents the results equivalent to chance. |
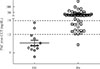 | Fig. 3Plasma aldosterone concentration (PAC) post-captopril challenge test (CCT) at 90 minutes in patients with essential hypertension (EH) and primary aldosteronism (PA). |
Table 1
Clinical and Biochemical Characteristics of Study Subjects with Essential Hypertension or Primary Aldosteronism

Values are expressed as mean±SD or number (%).
EH, essential hypertension; APA, aldosterone producing adenoma; IHA, idiopathic hyperaldosteronism; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; PRA, plasma rennin activity; PAC, plasma aldosterone concentration; ARR, aldosterone-renin ratio; GFR, glomerular filtration rate; SIT, saline infusion test; CCT, captopril challenge test.
aThe lowest values at 60 or 90 minutes are shown.
Table 2
Comparison of Diagnostic Performance among Different Cut-off Values of PAC Post-Captopril Challenge Test




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download