Abstract
We report here on a case of genetically confirmed type Ia glycogen storage disease (GSD) that was diagnosed in the military hospital. A twenty-year old soldier was admitted to the hospital with abdominal fullness. He had a past medical history of hepatomegaly that was firstly recognized at six months after birth, and he had been followed-up at an outpatient clinic with the presumptive diagnosis of type III GSD. He also had a history of growth hormone therapy because of growth retardation. However, he arbitrarily refused medical observation from 14 years of age. On the physical examination, the height of the patient was 163.1 cm and significant hepatomegaly was observed. Significantly abnormal liver-associated paramters were observed on the laboratory findings and multiple hepatic adenomas were observed on the CT exam and MRI scan. To determine the proper treatment, we tried to confirm the exact type of GSD in the patient. By mutational analysis, we found the c.648G>T homozygote splicing mutation in the G6PC gene and the patient was confirmed as having the type Ia GSD.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Physical examination findings of the patient. A. Relatively short stature (163.1 cm); B, C. Significant abdominal distension with hepatomegaly was observed.
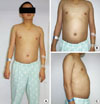
Fig. 2
Radiologic findings of the patient. In abdominal CT (A-C) and hepatic MRI (D-F) scans, significant hepatomegaly without splenomegaly was identified and multiple various sized mass lesions at both lobes of liver with arterial enhancing and delayed isodensity were observed.

Table 1
Primers used for PCR amplification of exons in the G6PC gene
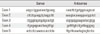
Primers were designed with primer 3 cgi v.2.0 served from Whitehead Institute (http://frodo.wi.mit.deu/cgi-bin/primer3www.cgi) using sequences from GenBank accession number of NT_010755.15.
References
1. Rake JP, Visser G, Labrune P, Leonard JV, Ullrich K, Smit GP. Glycogen storage disease type I: diagnosis, management, clinical course and outcome. Results of the European Study on Glycogen Storage Disease Type I (ESGSD I). Eur J Pediatr. 2002. 161:Suppl 1. S20–S34.
2. Lei KJ, Shelly LL, Pan CJ, Sidbury JB, Chou JY. Mutations in the glucose-6-phosphatase gene that cause glycogen storage disease type 1a. Science. 1993. 262:580–583.
3. Matern D, Seydewitz HH, Bali D, Lang C, Chen YT. Glycogen storage disease type I: diagnosis and phenotype/genotype correlation. Eur J Pediatr. 2002. 161:Suppl 1. S10–S19.
4. Chou JY, Matern D, Mansfield BC, Chen YT. Type I glycogen storage diseases: disorders of the glucose-6-phosphatase complex. Curr Mol Med. 2002. 2:121–143.
5. Moses SW. Historical highlights and unsolved problems in glycogen storage disease type 1. Eur J Pediatr. 2002. 161:Suppl 1. S2–S9.
6. Rake JP, ten Berge AM, Visser G, Verlind E, Niezen-Koning KE, Buys CH, Smit GP, Scheffer H. Glycogen storage disease type Ia: recent experience with mutation analysis, a summary of mutations reported in the literature and a newly developed diagnostic flow chart. Eur J Pediatr. 2000. 159:322–330.
7. Trioche P, Francoual J, Chalas J, Capel L, Lindenbaum A, Odievre M, Labrune P. Genetic heterogeneity of glycogen storage disease type Ia in France: a study of 48 patients. Hum Mutat. 2000. 16:444.
8. Akanuma J, Nishigaki T, Fujii K, Matsubara Y, Inui K, Takahashi K, Kure S, Suzuki Y, Ohura T, Miyabayashi S, Ogawa E, Iinuma K, Okada S, Narisawa K. Glycogen storage disease type Ia: molecular diagnosis of 51 Japanese patients and characterization of splicing mutations by analysis of ectopically transcribed mRNA from lymphoblastoid cells. Am J Med Genet. 2000. 91:107–112.
9. Chiang SC, Lee YM, Chang MH, Wang TR, Ko TM, Hwu WL. Glucose-6-phosphatase gene mutations in Taiwan Chinese patients with glycogen storage disease type Ia. J Hum Genet. 2000. 45:197–199.
10. Goto M, Taki T, Sugie H, Miki Y, Kato H, Hayashi Y. A novel mutation in the glucose-6-phosphatase gene in Korean twins with glycogen storage disease type Ia. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2000. 23:851–852.
11. Kajihara S, Matsuhashi S, Yamamoto K, Kido K, Tsuji K, Tanae A, Fujiyama S, Itoh T, Tanigawa K, Uchida M, Setoguchi Y, Motomura M, Mizuta T, Sakai T. Exon redefinition by a point mutation within exon 5 of the glucose-6-phosphatase gene is the major cause of glycogen storage disease type 1a in Japan. Am J Hum Genet. 1995. 57:549–555.
12. Ki CS, Han SH, Kim HJ, Lee SG, Kim EJ, Kim JW, Choe YH, Seo JK, Chang YJ, Park JY. Mutation spectrum of the glucose-6-phosphatase gene and its implication in molecular diagnosis of Korean patients with glycogen storage disease type Ia. Clin Genet. 2004. 65:487–489.
13. Lee HJ, Eun JR, Jang BI, Lee JH, Lee HW, Choi JH, Ki CS. A case of glycogen storage disease type Ia performed molecular genetic analysis. Korean J Med. 2006. 71:91–96.
14. Choi J, Ko JM, Kim GH, Yoo HW. Clinical manifestation and effect of corn starch on height growth in Korean patients with glycogen storage disease type Ia. J Korean Soc Pediatr Endocrinol. 2007. 12:35–40.
15. Applegarth DA, Toone JR, Lowry RB. Incidence of inborn errors of metabolism in British Columbia, 1969-1996. Pediatrics. 2000. 105:e10.
16. Talente GM, Coleman RA, Alter C, Baker L, Brown BI, Cannon RA, Chen YT, Crigler JF Jr, Ferreira P, Haworth JC, Herman GE, Issenman RM, Keating JP, Linde R, Roe TF, Senior B, Wolfsdorf JI. Glycogen storage disease in adults. Ann Intern Med. 1994. 120:218–226.
17. Choi YI, Choi YI, Park JW, Chung YS, Kim HJ. A case of type ia glycogen storage disease. J Korean Soc Endocrinol. 1999. 14:786–792.
18. Ko JS, Yang HR, Kim JW, Seo JK. Clinical findings of genotypes in Korean patients with glycogen storage disease type Ia. Korean J Pediatr. 2005. 48:877–880.
19. Chen YT, Cornblath M, Sidbury JB. Cornstarch therapy in type I glycogen-storage disease. N Engl J Med. 1984. 310:171–175.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download