Abstract
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious and demanding medical emergency for the field of endocrinology, and the identification and correction of the precipitating factors is equally important. Many patients of diabetic ketoacidosis show gastrointestinal symptoms as an initial presentation, and coincidental gastrointestinal diseases can be neglected or misdiagnosed. Emphysematous gastritis is a rare and lethal disease in which gas bubbles form in the stomach wall. The predisposing factors include ingestion of corrosive substances, alcohol abuse, diabetes, and immunosuppressive therapy. Thus, it may be difficult to detect emphysematous gastritis early, especially when it is developed in conjunction with diabetic ketoacidosis. We report a case of diabetic ketoacidosis associated with emphysematous gastritis in a young male without medical history.
Figures and Tables
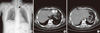
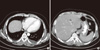
Fig. 1
Simple chest X-ray, computed tomography (CT). A. Chest radiography showed pneumomediastinum (arrow). B. Thorax CT showed pneumomediastinum (arrow). C. Abdomen CT showed mottled air bubbles in the stomach wall (arrow) and portal venous system (arrow).
References
1. Allan K, Barriga J, Afshani M, Davila R, Tombazzi C. Emphysematous gastritis. Am J Med Sci. 2005. 329:205–207.
2. Fraenkel E. A case of emphysematous gastritis probably of mucormycotic origin. Virchows Arch A. 1889. 118:526–535.
3. Yoh KG, Lee DK, Baek SG, Lee SW, Bae SW, Kwon SO. A case of emphysematous gastritis caused by acetic acid. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1993. 25:1322–1325.
4. Cheong JY, Lee DH, Park WI, Park JH, Kim HW, Heo J, Kim GH, Kang DH, Song GA, Cho M, Yang US. Emphysematous gastritis developed in a patient with Klatskin's tumor. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2004. 28:34–38.
5. Jung JH, Choi HJ, Yoo J, Kang SJ, Lee KY. Emphysematous gastritis associated with invasive gastric mucormycosis: a case report. J Korean Med Sci. 2007. 22:923–927.
6. Gweon TG, Shin AY, Bae SH, Lee JM, Lee SN, Jung MH, Ju YB, Kim TH, Park IJ, Yoo JH. A case of necrotizing fasciitis and severe sepsis complicated by emphysematous gastritis. Infect Chemother. 2010. 42:303–306.
7. Kitabchi AE, Umpierrez GE, Miles JM, Fisher JN. Hyperglycemic crises in adult patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009. 32:1335–1343.
8. Bashour CA, Popovich MJ, Irefin SA, Esfandiari S, Ratliff NB, Hoffman WD, Averbook AW. Emphysematous gastritis. Surgery. 1998. 123:716–718.
9. Gutierrez O, Cantalapiedra A, Tabuyo MI, Del Villar R, Peñarrubia MJ, Sales R, García-Frade LJ. Emphysematous gastritis and severe aplastic anemia. Hematol J. 2003. 4:82–84.
10. Shipman PJ, Drury P. Emphysematous gastritis: case report and literature review. Australas Radiol. 2001. 45:64–66.
11. Ocepek A, Skok P, Virag M, Kamenik B, Horvat M. Emphysematous gastritis-case report and review of the literature. Z Gastroenterol. 2004. 42:735–738.
12. van Mook WN, van der Geest S, Goessens ML, Schoon EJ, Ramsay G. Gas within the wall of the stomach due to emphysematous gastritis: case report and review. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002. 14:1155–1160.
13. See C, Elliott D. Images in clinical medicine. Pneumatosis intestinalis and portal venous gas. N Engl J Med. 2004. 350:e3.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download