INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Search strategy
Selection criteria
Excluded studies
Data extraction and management
Table 1
Characteristics of the included studies
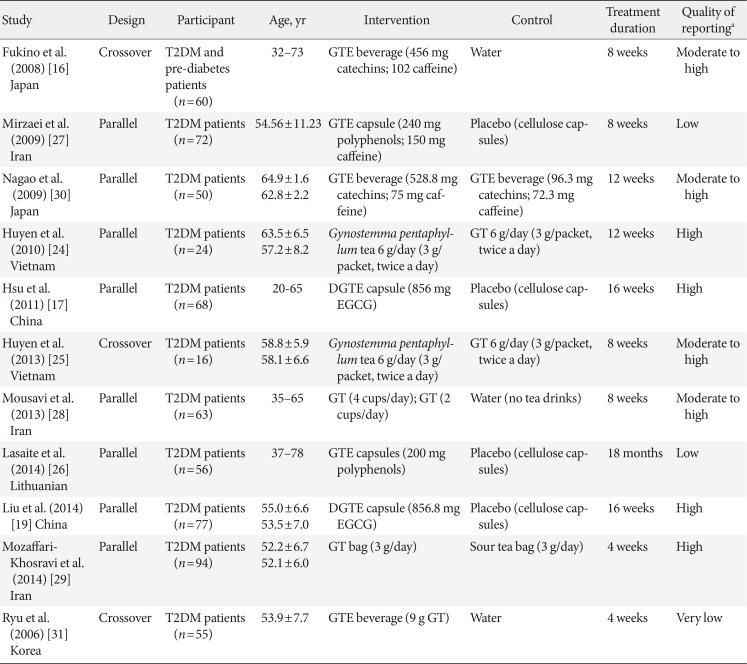
| Study | Design | Participant | Age, yr | Intervention | Control | Treatment duration | Quality of reportinga |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Fukino et al. (2008) [16] Japan |
Crossover |
T2DM and pre-diabetes patients (n=60) |
32–73 | GTE beverage (456 mg catechins; 102 caffeine) | Water | 8 weeks | Moderate to high |
|
Mirzaei et al. (2009) [27] Iran |
Parallel | T2DM patients (n=72) | 54.56±11.23 | GTE capsule (240 mg polyphenols; 150 mg caffeine) | Placebo (cellulose capsules) | 8 weeks | Low |
|
Nagao et al. (2009) [30] Japan |
Parallel | T2DM patients (n=50) |
64.9±1.6 62.8±2.2 |
GTE beverage (528.8 mg catechins; 75 mg caffeine) | GTE beverage (96.3 mg catechins; 72.3 mg caffeine) | 12 weeks | Moderate to high |
|
Huyen et al. (2010) [24] Vietnam |
Parallel | T2DM patients (n=24) |
63.5±6.5 57.2±8.2 |
Gynostemma pentaphyllum tea 6 g/day (3 g/packet, twice a day) | GT 6 g/day (3 g/packet, twice a day) | 12 weeks | High |
|
Hsu et al. (2011) [17] China |
Parallel | T2DM patients (n=68) | 20-65 | DGTE capsule (856 mg EGCG) | Placebo (cellulose capsules) | 16 weeks | High |
|
Huyen et al. (2013) [25] Vietnam |
Crossover | T2DM patients (n=16) |
58.8±5.9 58.1±6.6 |
Gynostemma pentaphyllum tea 6 g/day (3 g/packet, twice a day) | GT 6 g/day (3 g/packet, twice a day) | 8 weeks | Moderate to high |
|
Mousavi et al. (2013) [28] Iran |
Parallel | T2DM patients (n=63) | 35–65 | GT (4 cups/day); GT (2 cups/day) | Water (no tea drinks) | 8 weeks | Moderate to high |
|
Lasaite et al. (2014) [26] Lithuanian |
Parallel | T2DM patients (n=56) | 37–78 | GTE capsules (200 mg polyphenols) | Placebo (cellulose capsules) | 18 months | Low |
| Liu et al. (2014) [19] China | Parallel | T2DM patients (n=77) |
55.0±6.6 53.5±7.0 |
DGTE capsule (856.8 mg EGCG) | Placebo (cellulose capsules) | 16 weeks | High |
|
Mozaffari-Khosravi et al. (2014) [29] Iran |
Parallel | T2DM patients (n=94) |
52.2±6.7 52.1±6.0 |
GT bag (3 g/day) | Sour tea bag (3 g/day) | 4 weeks | High |
|
Ryu et al. (2006) [31] Korea |
Crossover | T2DM patients (n=55) | 53.9±7.7 | GTE beverage (9 g GT) | Water | 4 weeks | Very low |
Values are presented as range or mean±standard deviation.
T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; GTE, green tea extract; GT, green tea; DGTE, decaffeinated green tea extract; EGCG, epigallocatechin gallate.
aAssessed by the CONSORT (CONsolidated Standards of Reporting Trials) checklist for randomized controlled trials.
Methodological quality and risk of bias assessment
Data analysis
Ethical approval
RESULTS
Results of the search
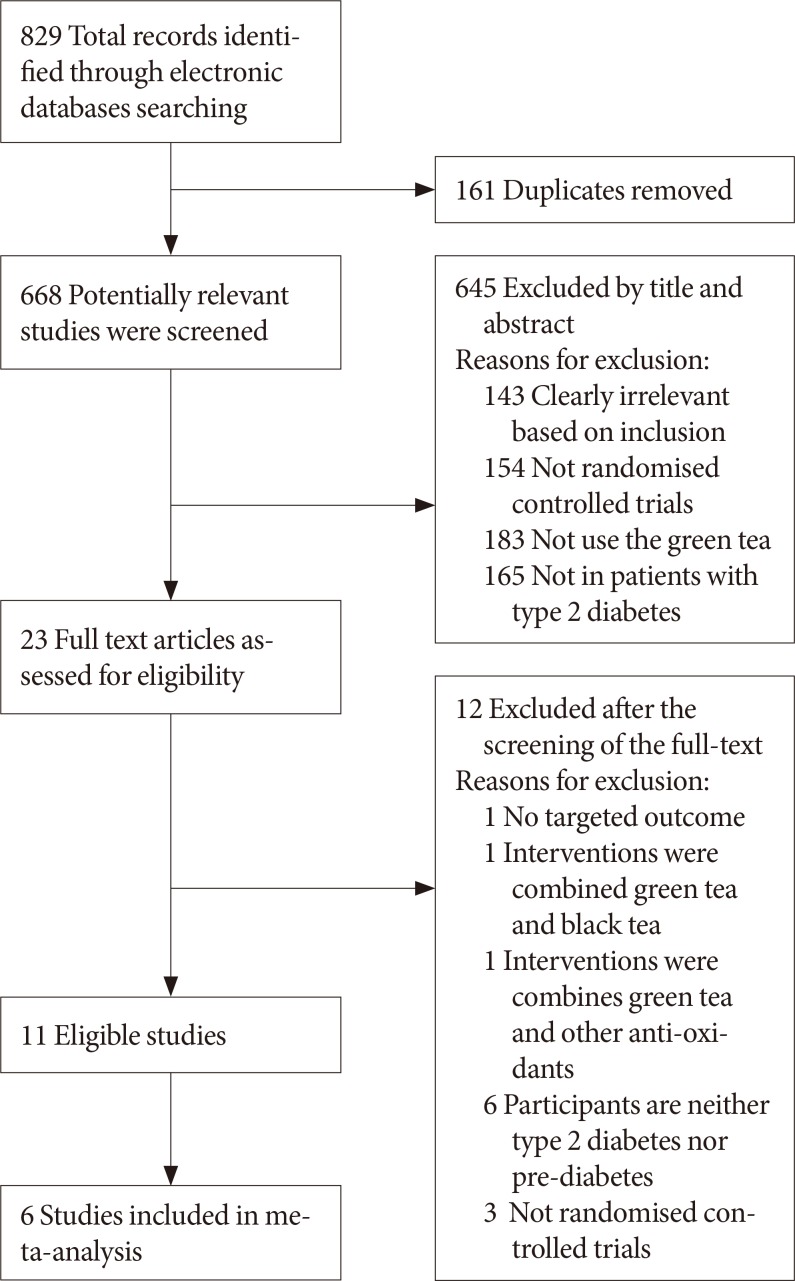 | Fig. 1Flow-chart of study selection and exclusion in details.Adapted from www.mdpi.com/link.
|
Table 2
Outcomes and results of the included studies
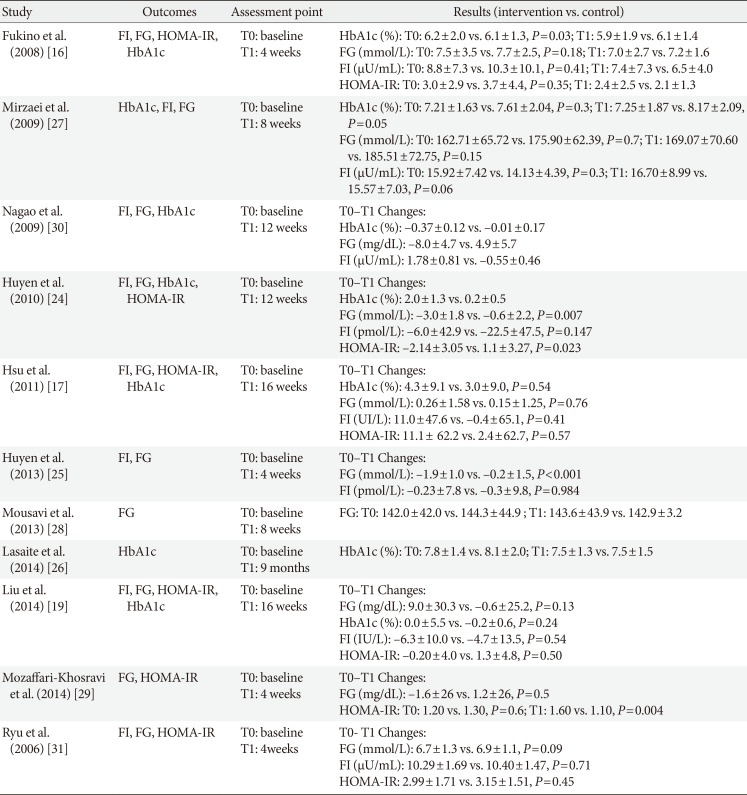
| Study | Outcomes | Assessment point | Results (intervention vs. control) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fukino et al. (2008) [16] | FI, FG, HOMA-IR, HbA1c |
T0: baseline T1: 4 weeks |
HbA1c (%): T0: 6.2±2.0 vs. 6.1±1.3, P=0.03; T1: 5.9±1.9 vs. 6.1±1.4 FG (mmol/L): T0: 7.5±3.5 vs. 7.7±2.5, P=0.18; T1: 7.0±2.7 vs. 7.2±1.6 FI (µU/mL): T0: 8.8±7.3 vs. 10.3±10.1, P=0.41; T1: 7.4±7.3 vs. 6.5±4.0 HOMA-IR: T0: 3.0±2.9 vs. 3.7±4.4, P=0.35; T1: 2.4±2.5 vs. 2.1±1.3 |
| Mirzaei et al. (2009) [27] | HbA1c, FI, FG |
T0: baseline T1: 8 weeks |
HbA1c (%): T0: 7.21±1.63 vs. 7.61±2.04, P=0.3; T1: 7.25±1.87 vs. 8.17±2.09, P=0.05 FG (mmol/L): T0: 162.71±65.72 vs. 175.90±62.39, P=0.7; T1: 169.07±70.60 vs. 185.51±72.75, P=0.15 FI (µU/mL): T0: 15.92±7.42 vs. 14.13±4.39, P=0.3; T1: 16.70±8.99 vs. 15.57±7.03, P=0.06 |
| Nagao et al. (2009) [30] | FI, FG, HbA1c |
T0: baseline T1: 12 weeks |
T0–T1 Changes: HbA1c (%): –0.37±0.12 vs. –0.01±0.17 FG (mg/dL): –8.0±4.7 vs. 4.9±5.7 FI (µU/mL): 1.78±0.81 vs. –0.55±0.46 |
| Huyen et al. (2010) [24] | FI, FG, HbA1c, HOMA-IR |
T0: baseline T1: 12 weeks |
T0–T1 Changes: HbA1c (%): 2.0±1.3 vs. 0.2±0.5 FG (mmol/L): –3.0±1.8 vs. –0.6±2.2, P=0.007 FI (pmol/L): –6.0±42.9 vs. –22.5±47.5, P=0.147 HOMA-IR: –2.14±3.05 vs. 1.1±3.27, P=0.023 |
| Hsu et al. (2011) [17] | FI, FG, HOMA-IR, HbA1c |
T0: baseline T1: 16 weeks |
T0–T1 Changes: HbA1c (%): 4.3±9.1 vs. 3.0±9.0, P=0.54 FG (mmol/L): 0.26±1.58 vs. 0.15±1.25, P=0.76 FI (UI/L): 11.0±47.6 vs. –0.4±65.1, P=0.41 HOMA-IR: 11.1± 62.2 vs. 2.4±62.7, P=0.57 |
| Huyen et al. (2013) [25] | FI, FG |
T0: baseline T1: 4 weeks |
T0–T1 Changes: FG (mmol/L): –1.9±1.0 vs. –0.2±1.5, P<0.001 FI (pmol/L): –0.23±7.8 vs. –0.3±9.8, P=0.984 |
| Mousavi et al. (2013) [28] | FG |
T0: baseline T1: 8 weeks |
FG: T0: 142.0±42.0 vs. 144.3±44.9 ; T1: 143.6±43.9 vs. 142.9±3.2 |
| Lasaite et al. (2014) [26] | HbA1c |
T0: baseline T1: 9 months |
HbA1c (%): T0: 7.8±1.4 vs. 8.1±2.0; T1: 7.5±1.3 vs. 7.5±1.5 |
| Liu et al. (2014) [19] | FI, FG, HOMA-IR, HbA1c |
T0: baseline T1: 16 weeks |
T0–T1 Changes: FG (mg/dL): 9.0±30.3 vs. –0.6±25.2, P=0.13 HbA1c (%): 0.0±5.5 vs. –0.2±0.6, P=0.24 FI (IU/L): –6.3±10.0 vs. –4.7±13.5, P=0.54 HOMA-IR: –0.20±4.0 vs. 1.3±4.8, P=0.50 |
| Mozaffari-Khosravi et al. (2014) [29] | FG, HOMA-IR |
T0: baseline T1: 4 weeks |
T0–T1 Changes: FG (mg/dL): –1.6±26 vs. 1.2±26, P=0.5 HOMA-IR: T0: 1.20 vs. 1.30, P=0.6; T1: 1.60 vs. 1.10, P=0.004 |
| Ryu et al. (2006) [31] | FI, FG, HOMA-IR |
T0: baseline T1: 4weeks |
T0- T1 Changes: FG (mmol/L): 6.7±1.3 vs. 6.9±1.1, P=0.09 FI (µU/mL): 10.29±1.69 vs. 10.40±1.47, P=0.71 HOMA-IR: 2.99±1.71 vs. 3.15±1.51, P=0.45 |
Table 3
Excluded studies after screening of the full text

| Excluded study | Reasons for exclusion |
|---|---|
| MacKenzie et al. (2007) [32] | Intervention are combined green tea and black tea |
| Fenercioglu et al. (2010) [33] | Intervention are combined green tea and pomegranate extract |
| Stote et al. (2012) [34] | Participants are neither T2DM or pre-diabetes patients |
| Vieira Senger et al. (2012) [35] | Participants are neither T2DM or pre-diabetes patients |
| Huang et al. (2013) [36] | Not RCT |
| Pham et al. (2014) [37] | Participants are neither T2DM or pre-diabetes patients |
| Takahash et al. (2014) [38] | No targeted outcomes reported |
| Keske et al. (2015) [39] | Not RCT |
| Dower et al. (2015) [40] | Participants are neither T2DM or pre-diabetes patients |
| Peristiowati et al. (2015) [41] | Not RCT |
| Dostal et al. (2016) [42] | Participants are neither T2DM or pre-diabetes patients |
| Lu et al. (2016) [43] | Participants are neither T2DM or pre-diabetes patients |
Trial characteristics
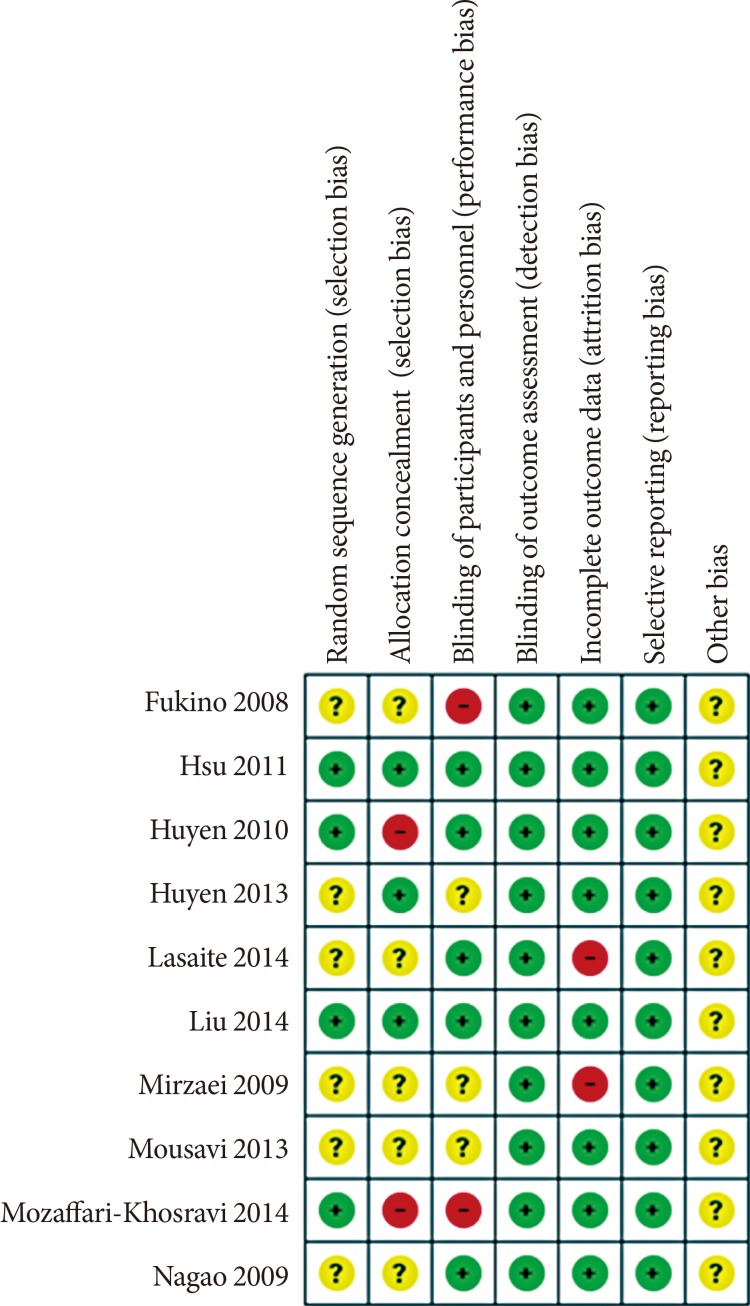
Quality of reporting
Meta-analysis
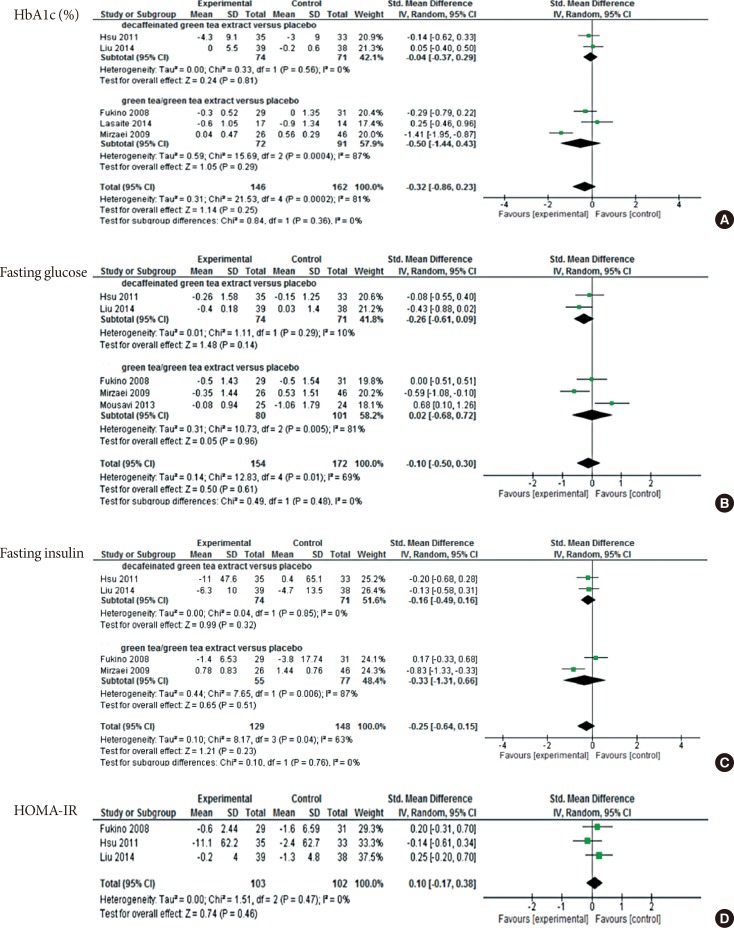 | Fig. 3Meta-analysis results for each assessed outcome. (A) Comparison between decaffeinated green tea extract and placebo, outcome: glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c, %). (B) Comparison between decaffeinated green tea extract and green tea extract, outcome: fasting glucose. (C) Comparison between decaffeinated green tea extract and green tea extract, outcome: fasting insulin. (D) Comparison between decaffeinated green tea extract and green tea extract versus placebo, outcome: homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR). SD, standard deviation; IV, independent variable; CI, confidence interval. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download