Abstract
Background
Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Kaplan-Meier curves for progression of diabetic nephropathy according to serum ceruloplasmin tertile categories.
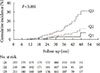
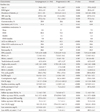
Table 1
Clinical and biochemical characteristics of the study subjects according to serum ceruloplasmin tertile categories at baseline

Values are presented as mean±standard deviation, median (range) unless otherwise indicated.
BMI, body mass index; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; CVD, cardiovascular disease; OHA, oral hypoglycemic agent; ACEi, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin II receptor blocker; HTN, hypertension; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; hsCRP, high sensitivity C-reactive protein; UACR, urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate.
aLast UACR represent UACR in spot urine sample at last follow-up or at the time of event occurrence.
Table 2
Baseline and follow-up clinical and biochemical characteristics of progressors and nonprogressors of diabetic nephropathy
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation, median (range) unless otherwise indicated.
BMI, body mass index; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; CVD, cardiovascular disease; OHA, oral hypoglycemic agent; ACEi, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin II receptor blocker; HTN, hypertension; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; hsCRP, high sensitivity C-reactive protein; UACR, urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate.
aLast UACR represent UACR in spot urine sample at last follow-up or at the time of event occurrence.
Table 3
HRs and 95% CI for progression of diabetic nephropathy based on serum ceruloplasmin tertile categories

Model 1: adjusted for conventional diabetic nephropathy risk factors (age, body mass index, duration of diabetes, current smoker, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACEi) or angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) use, other hypertension medication, high sensitivity C-reactive protein, baseline urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR), baseline creatinine, follow-up mean glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), follow-up mean systolic blood pressure (SBP), follow-up mean diastolic blood pressure). Model 2: adjusted for factors that showed a statistically significant (P<0.05, i.e., antidiabetic medication, ACEi or ARB use, fasting plasma glucose, total cholesterol, uric acid, baseline UACR, baseline creatinine, follow-up mean HbA1c) or borderline significant (P<0.10, i.e., duration of diabetes, baseline SBP, past history of cardiovascular disease, retinopathy) association in the univariate analysis. Model 3: adjusted for all the variables in models 1 and 2.
HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval.
Table 4
Other risk factors for progression of diabetic nephropathy demonstrated by multivariate Cox regression analysis

HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; UACR, urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; ACEi, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin II receptor blocker; HTN, hypertension; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; hsCRP, high sensitivity C-reactive protein.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download