Abstract
Background
We developed for the first time a smartphone application designed for diabetes self-management in Korea and registered a patent for the relevant algorithm. We also investigated the user satisfaction with the application and the change in diabetes related self-care activities after using the application.
Methods
We conducted a questionnaire survey on volunteers with diabetes who were using the application. Ninety subjects responded to the questionnaire between June 2012 and March 2013. A modified version of the Summary of Diabetes Self-Care Activities (SDSCA) was used in this study.
Results
The survey results exhibited a mean subject age of 44.0 years old, and males accounted for 78.9% of the subjects. Fifty percent of the subjects had diabetes for less than 3 years. The majority of respondents experienced positive changes in their clinical course after using the application (83.1%) and were satisfied with the structure and completeness of the application (86.7%). Additionally, the respondents' answers indicated that the application was easy to use (96.7%) and recommendable to others (97.7%) and that they would continue using the application to manage their diabetes (96.7%). After using the Diabetes Notepad application, diabetes related self-care activities assessed by SDSCA displayed statistically significant improvements (P<0.05), except for the number of days of drinking.
Diabetes is a chronic, progressive disease that is difficult to cure completely and requires the management of blood glucose and comorbidities over one's lifetime. The self-measurement of blood glucose, diabetes journaling, exercise, maintaining the diet for diabetes, and regular medication are generally recommended for the self-management of diabetes [123]. However, due to cumbersomeness, these self-management techniques are not practiced by many patients, and some patients even experienced exhaustion of diabetes management [45].
Recently, attempts to develop new management models using information technology (IT) for chronic diseases including diabetes occurred [6]. In particular, mobile health intervention for the management of chronic diseases has positive effects [789]. Among the latest IT technologies for such mobile health interventions, a smartphone is one of the most promising tools with a wide user base and easy utility [10].
Korea has a smartphone use rate as high as 85% [11] and a high preference for mobile application use [12]. Therefore, inconveniences related to diabetes self-management such as blood glucose measurement and diabetes journaling can be effectively improved by utilizing smartphone applications [13].
However, few studies exist on the effect of a smartphone-based diabetes self-management system in Korea, and thus, more evidence is needed. In previous studies on the efficacy of smartphone-based applications for controlling blood glucose levels, glycosylated hemoglobin levels decreased more in subjects who displayed higher satisfaction with the use of the smartphone applications than in subjects with lower satisfaction. Therefore, satisfaction with the application was an important factor for controlling blood glucose [14]. In the current study, the investigators developed the 'Diabetes Notepad' application designed to enable self-management of diabetes using a smartphone. This study was conducted to obtain basic data pertaining to the usefulness of the application, including whether diabetes self-management activities improved and to what extent the diabetes self-management activities improved according to the satisfaction with the smartphone application.
The 'Diabetes Notepad' application used in the present study is a diabetes self-management system that records personal information, blood glucose levels and test records for comorbidities. The application also includes additional features such as diabetes education material and a cardiovascular risk calculator (Fig. 1A). Additionally, the application allows easy access to the saved blood glucose history through the blood glucose record sheet and a graph (Fig. 1B). The algorithm of the 'Diabetes Notepad' application has been patented in recognition of its originality (10-1075596). The application is free of charge, available for anyone with a smartphone and is renowned as the most widely distributed diabetes self-management application in Korea with approximately 50,000 downloads (as of March 30, 2013).
Subjects included those who were using the 'Diabetes Notepad' application and willing to give consent to participate in the research study. A final analysis was performed on data from 90 patients who completed the questionnaire.
A questionnaire on the satisfaction with the Korea National Diabetes Program Diabetes Notepad application used in this study consisted of personal information of the subjects and the diabetes management status before and after application use. The study was designed to identify user satisfaction and changes in the Summary of Diabetes Self-Care Activities (SDSCA) after the use of the application. For the management status of diabetes, the questionnaire asked subjects to state the number of days (out of a week) that the patient measured blood glucose levels, had regular meals, drank alcohol, smoked, exercised, took regular medication, weighed themselves, and kept regular hours. These correspond to items that SDSCA measures. SDSCA is the most widely used tool to measure the degree of diabetes self-management, and its usefulness has been verified through various studies involving Korean subjects [1516].
Subjects who agreed to participate in the survey sent their agreement via email to the investigators. Next, the investigators emailed the subject the SDSCA questionnaire and received the survey results from the subjects via email. In addition, patients wanting an additional consultation were asked to email the clinical information recorded in the application to the investigators.
This study was carried out with subjects who agreed to participate in the research among those using the Diabetes Notepad application. The study subjects were recruited using the notice board window on the smartphone without direct interviews, and email was used as the primary communication method to send the questionnaire and receive its answers. Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Kyung Hee University Hospital approval for the exemption of a written agreement of study subjects and investigators was obtained before starting the study (KMC IRB 1217-01). The study design was registered in the national clinical trial registry (CRIS, No. KCT0000714).
The SPSS version 18.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used for the statistical analysis of the survey results. Subjects' characteristics and survey results were represented through descriptive statistics, and outcomes are shown as the mean±standard deviation. In addition, the internal consistency of questions of the questionnaire or the reliability was represented as a Cronbach's α value.
The Wilcoxon signed rank test was used for the comparison of SDSCA items before and after the use of the diabetes application, and a Mann-Whitney U test was performed for the comparison of changes in SDSCA between the group with high satisfaction and the group with low satisfaction with using the application. Additionally, the Mann-Whitney U test and Kruskal-Wallis test were conducted to identify the difference in the satisfaction with the application and the changes in SDSCA according to the demographic characteristics of the subjects. The significance of all statistical analyses was verified at P<0.05.
The survey results showed that 90 patients, corresponding to 30.8% of those who had originally agreed to participate in the survey, completed the final questionnaire as of March 30, 2013. The clinical characteristics of the subjects who completed the survey are shown in Table 1. The mean age of the subjects was 44.0 years old, and 71 subjects were male, which accounted for 78.9% of the total subjects. At least 50% of the subjects had diabetes for less than 3 years. Eighty-two percent of the subjects had used the Diabetes Notepad application for less than 6 months, 14.6% for 6 months to 1 year, and only 3.4% for more than 1 year. Eighty percent of the subjects graduated from a university or had a higher degree, and 51.7% were high-income earners with a monthly income of 3 million won or more. Subjects without other comorbidities besides diabetes accounted for 56.7% of the respondents. Because each subject used the Diabetes Notepad application through his/her own will, data from the questionnaire were obtained from subjects living all over the country, which was a clear advantage. The nationwide distribution of users of this application is shown in Fig. 2.
As shown in Table 2, survey results of the user satisfaction with the application showed that 83.1% of subjects indicated positive changes in the clinical course of diabetes after using the application, and 86.7% were satisfied with the structure and completeness of the application. Furthermore, 96.7% of respondents stated that the application was easy to use. Almost all (97.7%) of the subjects were willing to actively recommend the application to other people, and 96.7% would continue to manage their diabetes by using the application. The internal consistency of the survey questions about satisfaction before and after the use of the application was 0.791 as estimated with Cronbach's α.
Subjects responding to questions pertaining to satisfaction selected their response from a 4-point scale including (1) strongly agree, (2) agree, (3) disagree, and (4) strongly disagree. Then, in the statistical analysis, scores were given to each response as follows: (1) 4 points to strongly agree, (2) 3 points to agree, (3) 2 points to disagree, and (4) 1 point to strongly disagree. Subsequently, the scores for all the questions were added up, and the high rank and low rank groups were classified relative to the 50% point of the maximum total score of all the questions pertaining to satisfaction. This resulted in 53 subjects in the high satisfaction group and 37 in the low satisfaction group. In the next paragraph, the difference in the changes in SDSCA items between these two groups will be discussed.
Table 3 shows the difference in satisfaction with the application according to the demographic characteristics, and the male patients (3.54±0.50) found it easier to use the application than the female patients (3.16±0.69), which was statistically significant (P=0.026). In other questions pertaining to satisfaction, gender, age, the duration of diabetes, the duration of using the application, the smartphone model, education level, and the presence of a comorbidity did not impact the satisfaction with the application.
Table 4 shows the difference in the management status of diabetes before and after the use of the Diabetes Notepad application. The mean number of days the subject measured their blood glucose, had regular meals, drank alcohol, smoked, exercised, took their regular medication, weighed themselves and kept regular hours during a week before and after the use of the application were compared using the Wilcoxon signed rank test for 90 patients who completed the questionnaire.
All items displayed statistically significant differences with a P=0.000 except for the number of drinking days. Additionally, the frequencies of measuring blood glucose levels, having regular meals, exercising, taking regular medication, weighing oneself, and keeping regular hours increased, while of the frequency of smoking decreased after the use of the application.
Tables 5 and 6 show the differences in the changes in SDSCA items according to the demographic characteristics and the level of satisfaction, respectively, after defining the difference between the numbers of SDSCA items before and after the use of the application as the changes in SDSCA items.
Tables 5 shows the changes in SDSCA items according to gender, age, the duration of diabetes, the duration of using the application, education level, income, and comorbidities. The changes were analyzed, and the significance of the analysis was verified at P<0.05 using the Mann-Whitney U test and Kruskal-Wallis test. The changes in the number of days the subject measured their blood glucose and kept regular hours were significantly different between males and females (P=0.020). The changes in SDSCA items other than those above were not affected by gender, age, the duration of diabetes, the duration of using the application, education level, and the presence of comorbidities.
Table 6 shows the difference in the change in SDSCA items according to the groups with high or low satisfaction with the application. The changes in the number of days the patient measured their blood glucose (P=0.020), exercised (P=0.000), weighed themselves (P=0.003), and kept regular hours (P= 0.000) displayed statistically significant difference between the high satisfaction and low satisfaction groups.
Several recent studies show the positive effects of mobile health intervention on the management of chronic diseases [789]. Other studies report that data input through a personal digital assistant (PDA) and handheld computer was more effective than hand written diabetes journaling [1718]. A smartphone is a device that can be used for internet access, data storage, setting an alarm, email, and running many applications [19], and a smartphone is much more powerful than an existing mobile phone or PDA for applying mobile technology to clinical practice. Applications run on smartphones helped patients monitor meals and medication for the management of chronic diseases including diabetes and also improved communication with medical staff as well as the patient's compliance [20].
This study demonstrates positive changes in the clinical course of diabetes when using a smartphone application as investigated by a user satisfaction survey and changes in the SDSCA. The survey was conducted with subjects who use the Diabetes Notepad application, which is the most widely available diabetes smartphone application in Korea. In particular, this study showed significant changes in the SDSCA, which is the most frequently used tool for the evaluation of diabetes self-management in Koreans [1516].
Previous studies on diabetes self-management using a smartphone showed that a specific application tailored to the respective study design was often used within a limited region and for limited patients. Additionally, only one study has investigated the actual environment for an application that was more common and widespread than 'Diabetes Notepad' [10]. In the current study, 90 users of 'Diabetes Notepad,' the most widely available application in Korea, responded to the survey, and significant changes in diabetes self-management occurred before and after using the application.
However, like other studies [910], this study only confirmed positive changes with the short term use of the application because 82% of the subjects had only used the application for less than 6 months. So speculating the persistence and compliance of diabetes self-management with the use of a smartphone application as well as the future role of the application in the entire healthcare system is difficult. The self-care and monitoring of diabetes is considered necessary for life, as opposed to patients fully recovering from diabetes [2]. Additionally, longterm studies on the effects of a smartphone-based self-management system are needed.
Therefore, the investigators of this study are planning to conduct a follow-up study for patients who have been using the Diabetes Notepad application for more than 1 year. The investigators recently released a new version of the application that allows synchronizing measurements obtained from a blood glucose tester with the Diabetes Notepad application. This synchronization would enable patients who are not familiar with smartphones to store their blood glucose information in the application by connecting their smartphone to the blood glucose tester rather than typing their own blood glucose levels into the smartphone application. One study suggests improved blood glucose control and a decreased hospital admission rate when patients and medical staff share and manage blood glucose information effectively [21]. Subsequently, the use of smartphone applications that can synchronize with a blood glucose tester will open a new horizon for future diabetes management. In particular, coupling a blood glucose tester with the Diabetes Notepad application is more likely to be advantageous to the elderly who usually find it difficult to use smartphone applications [13]. Therefore, we expect that patients older than 44.0 years old, which was the average age in this study, and those with difficulties using smartphones could more easily use this application.
As mentioned in the results, the majority of subjects in this study were males in their 40s without specific comorbidities who were highly educated and earn a high-income. Moreover, the subjects voluntarily participated in the study after reading the application notice. Subsequently, these subjects likely have high accessibility to smartphones and do not have difficulties in using them due to their economic means and high level of education. In addition, as these subjects were more active in managing their disease as voluntary participants and thus are less likely to represent the entire population of diabetes patients, selection bias should be considered.
Therefore, limitations of this study include not analyzing the long-term effects of the use of the application and the selection bias. However, this study still has great significance in that the statistically significant positive changes in the clinical course of diabetes were displayed among users of the widely available application.
Emerging evidence suggests that smartphones induce positive changes on the management of chronic diseases including diabetes. This study shows that the 'Diabetes Notepad' application developed by the investigators also showed a high level of user satisfaction and had a positive effect on diabetes self-management. In addition, this study demonstrated that improvement in diabetes self-management activities is greater when user satisfaction is high. After confirming the long-term effects of the use of smartphone applications, one may hypothesize that smartphone applications could play a pivotal role in the management of diabetes if the application can easily be used by more people and at lower prices.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Smart phone application outline. (A) The "Diabetes Notepad" application records personal information, blood glucose levels and test records for comorbidities and includes additional features such as diabetes education materials and a cardiovascular risk calculator. (B) The application allows easy access to the saved blood glucose history through the blood glucose record sheet and a graph.

Fig. 2
Users of the application were widely distributed across the nation. Users were from Seoul (28.9%), Gyeonggi (24.4%), Incheon (5.6%), Gangwon (0.0%), Chungcheong (5.6%), Jeolla (5.6%), Daejeon (3.3%), Daegu (8.9%), Gwangju (2.2%), Gyeongsang (7.8%), Ulsan (2.2%), Busan (5.6%), and Jeju (0.0%).
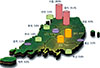
Table 1
Demographic characteristics of the study subjects
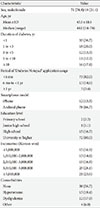
Table 2
Results for user satisfaction

Table 3
User satisfaction with the application according to demographic characteristics
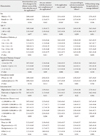
Table 4
Changes in diabetes related self-care activities as assessed by the Summary of Diabetes Self-Care Activities

Table 5
Changes in the Summary of Diabetes Self-Care Activities items according to demographic characteristics
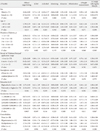
Table 6
Changes in the Summary of Diabetes Self-Care Activities items according to the satisfaction with the application

Values are presented as mean±standard deviation. Statistics were analyzed by the Mann-Whitney U test. ΔMeans the difference between the numbers of SDSCA items before and after the use of the application. ΔVariables (day/wk)=after use of application (day/wk)-before use of application (day/wk).
aStatistically significant differences (P<0.05).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was supported by a grant from the Korea Healthcare Technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (HI10C2020) and a grant (SYR, 2009, 2010) from the Korean Diabetes Association.
References
1. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993; 329:977–986.
2. Hill-Briggs F. Problem solving in diabetes self-management: a model of chronic illness self-management behavior. Ann Behav Med. 2003; 25:182–193.
3. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes: 2012. Diabetes Care. 2012; 35:Suppl 1. S11–S63.
4. Zgibor JC, Simmons D. Barriers to blood glucose monitoring in a multiethnic community. Diabetes Care. 2002; 25:1772–1777.
5. Ahola AJ, Groop PH. Barriers to self-management of diabetes. Diabet Med. 2013; 30:413–420.
6. Siriwardena LS, Wickramasinghe WA, Perera KL, Marasinghe RB, Katulanda P, Hewapathirana R. A review of telemedicine interventions in diabetes care. J Telemed Telecare. 2012; 18:164–168.
7. Beratarrechea A, Lee AG, Willner JM, Jahangir E, Ciapponi A, Rubinstein A. The impact of mobile health interventions on chronic disease outcomes in developing countries: a systematic review. Telemed J E Health. 2014; 20:75–82.
8. de Jongh T, Gurol-Urganci I, Vodopivec-Jamsek V, Car J, Atun R. Mobile phone messaging for facilitating self-management of long-term illnesses. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012; 12:CD007459.
9. Liang X, Wang Q, Yang X, Cao J, Chen J, Mo X, Huang J, Wang L, Gu D. Effect of mobile phone intervention for diabetes on glycaemic control: a meta-analysis. Diabet Med. 2011; 28:455–463.
10. Holtz B, Lauckner C. Diabetes management via mobile phones: a systematic review. Telemed J E Health. 2012; 18:175–184.
11. 2013 Internet Trends. Kleiner Perkins Caufield & Byers (KPCB);updated 2013 May 29. Available from: http://www.kpcb.com/blog/2013-internet-trends.
12. 2012 The second half of survey result on the use of smartphones. Korea Internet & Security Agency;updated 2013 Jan 29. Available from: http://isis.kisa.or.kr/board/index.jsp?pageId=060200&bbsId=3&itemId=799&pageIndex=1.
13. Rao A, Hou P, Golnik T, Flaherty J, Vu S. Evolution of data management tools for managing self-monitoring of blood glucose results: a survey of iPhone applications. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2010; 4:949–957.
14. Kim HS, Choi W, Baek EK, Kim YA, Yang SJ, Choi IY, Yoon KH, Cho JH. Efficacy of the smartphone-based glucose management application stratified by user satisfaction. Diabetes Metab J. 2014; 38:204–210.
15. Toobert DJ, Hampson SE, Glasgow RE. The summary of diabetes self-care activities measure: results from 7 studies and a revised scale. Diabetes Care. 2000; 23:943–950.
16. Choi EJ, Nam M, Kim SH, Park CG, Toobert DJ, Yoo JS, Chu SH. Psychometric properties of a Korean version of the summary of diabetes self-care activities measure. Int J Nurs Stud. 2011; 48:333–337.
17. Dale O, Hagen KB. Despite technical problems personal digital assistants outperform pen and paper when collecting patient diary data. J Clin Epidemiol. 2007; 60:8–17.
18. Lane SJ, Heddle NM, Arnold E, Walker I. A review of randomized controlled trials comparing the effectiveness of hand held computers with paper methods for data collection. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2006; 6:23.
19. Demidowich AP, Lu K, Tamler R, Bloomgarden Z. An evaluation of diabetes self-management applications for Android smartphones. J Telemed Telecare. 2012; 18:235–238.
20. Bloomgarden Z, Dagogo-Jack S. Five Ms of adherence. J Diabetes. 2011; 3:169–171.
21. Polisena J, Tran K, Cimon K, Hutton B, McGill S, Palmer K. Home telehealth for diabetes management: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2009; 11:913–930.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download