Abstract
Recurrent infection after an acute urinary tract infection (UTI) episode is common in adult women. It is onerous to both the patient and the physician to treat frequent recurrent UTI. Every time when UTI recurs, patients experience lower urinary tract symptoms, fatigue, and limitation in everyday life, while the physician has difficulty in counseling patients with a disease entity whose pathophysiology is less known. Currently, prophylactic treatment for recurrent UTI is limited, is ineffective in most cases, and sometimes accompanies unexpected side effects. In this guideline, we aimed to establish feasible and effective recommendations for the treatment of recurrent UTI in healthy adult women.
Urinary tract infection (UTI) often recurs in healthy adult women [1]. In a study in which healthy female college students were followed up for 6 months after UTI, symptomatic UTI recurred at least once in 20.9% [2]. In another study which followed up 179 Finnish women for 1 year after UTI caused by Escherichia coli, recurrence occurred at least once in 44% and 3 times or more in 5% [3]. According to natural history studies of the disease, UTI recurrence is concentrated in 3-4 months after the first occurrence. The likelihood of recurrence is the highest between 30 and 60 days after the first occurrence, after which the frequency of recurrent UTI decreases [45].
In most cases, recurrent UTI has been thought to be caused by reinfection due to factors external to the urinary tract such as the genitalia and the anorectal area. But recently it has been shown that uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC) invades the urinary tract epithelium to potentially establish quiescent intracellular bacterial reservoirs (QIRS) in the cells. Thus, QIRS is suspected to provide the environment for persistent survival of bacteria and elements to cause recurrent UTI [678].
The first step to treat recurrent UTI is a detailed review of patient history and comprehensive physical examination. Through detailed inquiry of patient history, the number and frequency of UTI in the past can be learned, as well as menopausal status, recent experience of taking antibiotics, and coital history (the number of sexual partners, presence of a new sexual partner, whether a spermicide or a barrier contraceptive is used, etc.). In a physical examination, vaginal condition and the presence of pelvic organ prolapse should be examined, in addition to the presence of urethral diverticulum, Skene's gland cyst, or infection. Generally, urine culture test is recommend, but additional imaging test is unnecessary in most cases of uncomplicated lower UTI [1]. A study with 100 healthy women has reported that abdominal plain X-ray, bladder endoscopy, intravenous pyelography, and abdominal sonography showed normal findings in most cases [9]. If disease history review or physical examination shows a finding suggesting complicated UTI, it is advisable to consider additional testing such as post-void residual urine test, urinary tract sonography, and cystoscopy (Table 1).
According to a study, women with recurrent UTI are sexually active. Active sexual activity, sexually more active within the last 12 months, and more frequent in coitus in the last 1 month are reported to have an independent association with increased risk of recurrent UTI [510]. In addition, the use of a spermicide or a barrier contraceptive, a new sexual partner, multiple sexual partners, and a history of sexually transmitted disease have also been reported as independent risk factors to increase the frequency of recurrent UTI [10]. If the patient is sexually active and uses a barrier contraceptive or a spermicide, it is recommended to stop using it. Some studies have reported that generally known risk factors such as postcoital urination, urination frequency, fluid intake, personal hygiene (the direction of wiping the buttocks), soaking in warm water, vaginal wash, and tampon use did not show a clear association with recurrent UTI [1011]. There is not enough evidence that increased water intake, changes in personal hygiene, and urination before and after sexual intercourse are necessary for the prevention of recurrent UTIs.
A study on the relationship between obesity and UTI reported that the likelihood to be diagnosed with UTI was higher in obese women than in normal-weight women. But statistical significance was found only in body mass index of 30 to 34.9 (odds ratio, 1.22; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.15-1.28) kg/m2 [12]. Therefore, further research is needed to confirm whether obesity can be considered as a risk factor for UTI.
Numerous studies have been conducted to investigate whether estrogen supplementation can reduce the occurrence of recurrent UTI in women with postmenopausal vaginal atrophy [13]. Nine randomized controlled trial (RCT) studies with a total of 3,345 postmenopausal women reported that oral estrogen did not prevent the occurrence of recurrent UTI and caused adverse effects like vaginal bleeding and mastodynia [13]. Two other RCT studies reported a decrease in the frequency of recurrent UTI when estrogen was locally administered into the vagina [14]. Raz and Stamm [15] reported in a study conducted over 8 months that intravaginal estrogen therapy significantly decreased the occurrence of recurrent UTI (0.5 vs. 5.9 time/person per year, p<0.001) [15]. It has also been reported that the risk ratio for UTI decreased to 0.64 (95% CI, 0.47-0.86) in postmenopausal women 36 weeks after using an estrogen vaginal ring [16]. Intravaginal estrogen treatment of postmenopausal women with vaginal atrophy is considered as safe and efficacious in the prevention of recurrent UTI.
Prior to antibiotic prophylaxis, previous UTIs should be confirmed to be completely terminated by follow-up culture at 1 to 2 weeks after treatment. Antibiotic prophylaxis for UTI should be used only after adequate counseling and behavioral modification therapy have been carried out but failed [17]. Clinically significant residual urine should first be treated. Hormone supplement therapy should also be considered for postmenopausal women. In cases recurrent uncomplicated UTI, self-start antibiotic therapy can be an option to consider [18].
In self-start antibiotic therapy, patients are provided with guidelines and medications that can be used to diagnose and treat symptoms when they occur. Among patients with recurrent UTI, those who are strongly motivated and know how to self-diagnose and how to treat not only have high accuracy of self-diagnosis (88-92%) but also can effectively treat themselves [181920]. This treatment approach results in a higher reinfection rate compared to continuous antibiotic prophylaxis (2.2 vs. 0.2 times per year) [20], but satisfaction is higher and treatment is faster clinically and microbiologically with lower side effects [181920]. Recurrent UTI like acute uncomplicated cystitis can be effectively treated with the approach. Individual patients' allergies and resistance to specific antibiotics should be thoroughly examined. Infectious Diseases of Society of America and the European Society for Microbiology and Infectious Diseases recommend a 5 day course of nitrofuratoin macrocrystals 100 mg bid (twice a day), a 3 day course of trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole 160/800 mg bid, a 1 day course of fosfomycin trometamol 3 g qd (once a day), and a 5 day course of pivmecillinam 400 mg bid. If any of these antibiotics cannot be used, a fluoroquinolone or β-lactam can be administered [21].
One-time administration of an antibiotic after coitus can be effective in the prevention of recurrent UTI in sexually active women. An RCT compared one-time postcoital use of an antibiotic (trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, TMP-SMX) with placebo in healthy premenopausal women with a history of recurrent UTI and found that UTI occurred in 9 out of 11 women administered with placebo (3.6 UTI/patient-year) and 2 out of 16 women administered with the antibiotic (0.3 UTI/patient-year). TMP-SMX is reported to be effective regardless of coital frequency [22]. Postcoital antibiotic prophylaxis is considered to have an effect similar to continuous prophylactic drug administration. In a study in which 152 women with a history of recurrent UTI were randomly assigned to 2 groups and administered ciprofloxacin 125 mg daily or postcoitally, the occurrence rate decreased in both groups (3.66 to 0.031 episodes per year vs. 3.62 to 0.043 episodes per year), but the differences were not statistically significant (p=0.7) [23]. Drugs that can be used for postcoital antibiotic prophylaxis are presented Table 2.
A Cochrane review of 19 RCT studies with a total of 1,120 healthy women reported that continuous antibiotic prophylaxis decreased the recurrence of UTI during the treatment period when compared with placebo. Particularly, the frequency of recurrent UTI was not different between groups even after antibiotic prophylaxis was discontinued (relative risk [RR], 0.82; 95% CI, 0.44-1.53). Side effect occurred more frequently in the group that received antibiotic prophylaxis (RR, 1.58; 95% CI, 0.47-5.28) with an adverse effect occurring every 13.5 doses. Because design and research process were different among different studies, efficacy and safety of individual antibiotics could not be compared [17]. The ideal dosage or schedule of continuous antibiotic prophylaxis is still unclear. Weekly antibiotic administration is reported to be more effective than monthly administration, although daily vs. every-other-day administration has not been compared. Guibert et al. [24] conducted a study in which women with recurrent UTI were treated with pefloxacin 400 mg weekly or monthly and followed up for 4 years, and found that 17 out of 185 (9.2%) women treated weekly experienced recurrence at least once during the follow-up, whereas 52 out of 176 (29.5%) women treated monthly experienced recurrence (p<0.0001).
Cranberry contains a high level of proanthocyanidins. Several experimental studies reported the dose-dependent effect of proanthocyanidins on the adsorption and desorption of E. coli in uroepithelial cells [262728]. A few clinical studies have shown that Vaccinium macrocarpon is effective in decreasing the occurrence of lower UTI in women [2930]. Stothers [30] randomly assigned 150 healthy women (21 to 72 years) with a recurrent UTI to placebo, placebo juice, cranberry juice or cranberry juice and placebo, and found that the proportion of patients experiencing recurrent symptomatic UTI at least once during a 12-month follow-up was significantly lower in the groups treated with cranberry tablets and juice compared to the placebo group (20%; cranberry juice, 18%; cranberry extracts vs. 32%; placebo; p<0.05).
However, discrepant findings have been reported in large-scale clinical trials. Recently, a double-blind RCT reported that cranberry juice did not prevent recurrent UTI from occurring; in the study, 319 female college students consumed 8 oz. of 27% low-fat cranberry juice or placebo juice twice a day, and followed up for 6 months or until the occurrence of recurrent UTI. The recurrence rate was similar in two groups (19.3% vs. 14.6%, p=0.21) [31]. Cranberry may be useful in the prevention of recurrent UTI, but research for standardization should be preceded.
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) is recommended for the prevention of recurrent UTI through acidification of the urine. However, evidence supportive of the phenomenon in healthy adult women is insufficient. Foxman and Chi [11] have reported that in young women, vitamin C intake through food was hardly associated with UTI risk reduction. In a study with 110 pregnant women, a group taking ferrous sulfate 200 mg/day, folic acid 5 mg/day and ascorbic acid 100mg/day was compared with a group taking only ferrous sulfate and folic acid, and the finding showed that the frequency of UTI was lower in the group taking ascorbic acid for 3 months [32]. Currently, it is found in vitro experiments that vitamin C has bacteriostatic effect in urine, and the effect is thought to arise by vitamin C restoring urinary nitrites to active nitrogen oxides rather than by decreasing urinary pH [3334].
Methenamine salts are hydrolyzed in urine to form ammonia and formaldehyde. Formaldehyde has a wide bacteriostatic effect and low bacterial resistance. Based on such effects, an attempt is currently being made to develop methenamine salts into an effective preventive therapy for recurrent UTI, although information on side effect is insufficient. However, there is a lack of evidence to apply these doses to clinical practice. Several small-scale studies are presently underway, which have shown that methenamine salts were more effective than placebo in the prevention of recurrent UTI [3536373839]. According to a Cochrane review, methenamine hippurate may be safe and efficacious in short-term prevention of recurrent UTI in patients without a neurogenic bladder or urogenital tract malformation [40].
Studies using rodent and human uroepithelial cells confirmed that a FimH (microbiological binder) inhibitor based on D-Mannose prevents UPEC from grafting onto and invading the uroepithelium [4142]. Based on this basic scientific data, D-mannose was used to prevent recurrent UTI in humans, but there is no clinical evidence yet. Although there is experimental evidence that theoretically, it may be effective in recurrent UTIs because it can inhibit the activity of macrophages that delay bacterial clearance in the urinary tract [43], it is ineffective if strains do not specifically express type I pili and FimH [44].
It is worth considering once or twice weekly vaginal administration of probiotics such as Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1 and L. reuteri RC-14 to prevent recurrent UTI [45]. Taking daily oral product containing GR-1 and RC-14 can also be a prophylactic option [46]. Another option that can be used in premenopausal women for the prevention of recurrent UTI is vaginal administration of L. crispatus [47]. In a study with 100 premenopausal women of age between 18 and 40 years with a history of UTI at least once within the last 12 months, vaginal administrations of 108 CFU/ml of L. crispatus CTV-05 and placebo were compared. The dosing schedule of vaginal administration was once daily for 5 days and then once weekly for 10 weeks. After the completion of 10-week long administration, the frequency of recurrent UTI was lower in the group who received L. cirspatus CTV-05 compared to the placebo group (RR, 0.5; 95% CI, 0.2-1.2). Adverse effects such as vaginal discharge, vaginal pruritus and abdominal discomfort were similar in two groups (56% for L. crispatus CTV-05 and 50% for placebo).
Damiano et al. [48] investigated safety and efficacy of bladder administration of hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate (iAluRil®; IBSA Farmaceutici, Lodi, Italy) with an aim to maintain the glycosaminoglycan layer of the bladder; 57 women frequently showing recurrent UTI were assigned either to a group administered with 1.6% hyaluronic acid and 2.0% chondroitin sulfate 50 ml or to a placebo group. The results showed that the frequency of UTI significantly decreased in the group in which iAluRil® (sodium pentosane sulfate) was administered to the bladder for 12 months (-86.6%±47.6% vs. -9.6%±24.6%) [48]. The study may highlight the use of hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate in the prevention of UTI, but long-term results are needed and additional research should be conducted on versatility, cost effectiveness, etc.
Many studies were conducted to introduce immunostimulants in the prevention of recurrent UTI. Naber et al. [49] systemically examined the usage of lysate created with dead UTI-causing bacteria was used in immunostimulating prophylaxis. Currently, two products, Uro-Vaxom® (OM Pharma, Meyrin, Switzerland) and SolcoUrovac® (Solco Basel, Basel, Switzerland), have been investigated. Uro-Vaxom® is an oral capsule containing 18 types of E. coli strains, taken once daily, and can be recommended for immunoprophylaxis of recurrent UTI [4950]. A meta-analysis on 5 double-blind placebo-controlled trials showed that UTI occurrence rate was 0.15-0.82 per year among participants taking oral Uro-Vaxom®, indicating that it was more effective than placebo [5051]. In a large-scale controlled study conducted subsequently in which 453 women took oral Uro-Vaxom® for a year, the occurrence of UTI was reduced by 34% [51]. In the trial, participants took Uro-Vaxom® once daily for 3 months, discontinued for 3 months, took it again but only for the first 10 days of a month once daily for 3 months, and then discontinued for the next 3 months. According to a study conducted in Korea in which 42 perimenopausal women with recurrent UTI were followed up for 6 months after 3 months of taking Uro-Vaxom®, the occurrence of UTI during the 6-month follow-up was 0.35 per patient, which was significantly decreased from 4.26 for 6 months prior to treatment (p<0.001) [52]. In many clinical trials on Uro-Vaxom®, fatal or critical adverse effects were not reported and only mild adverse effects such as headache and digestive problem were observed [53]. Since 2011 the European Association of Urology has recommended Uro-Vaxom® as a prophylaxis of recurrent UTI. SolcoUrovac® is a vaginal tablet containing 10 types of urologic microbiological strains. It is reported to have a prophylactic effect against moderate UTI but the effect is limited to the period during which the drug is taken [4954]. Recent advances in technology have led to greater understanding of the effects of E. coli on UTI, and it is anticipated that a longer-lasting and more specific recurrent UTI-enhancing agent or vaccine could be developed.
In all patients with recurrent UTI, a detailed review of patient history and a thorough physical examination are necessary, based on which any accompanied malformations and correctible risk factors should first be confirmed. Antibiotics are the most effective prophylaxis, but not without side effects. The type, formulation, and dosing schedule of an antibiotic should be determined according to individual patients' characteristics. Aside from antibiotic prophylaxis, cranberry, vitamin C, methenamine salts, etc. are actively investigated but the evidence is still lacking. Thus, immunostimulators like Uro-Vaxom® may be a realistic alternative. Fig. 1 shows recommendations from a treatment algorithm for recurrent UTI. A variety of new approaches to prevention of recurrent UTIs are underway, requiring additional basic scientific research and a large RCT.
Figures and Tables
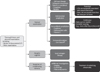 | Fig. 1Algorithm for the treatment of recurrent UTI (adapted from Asian Association of UTI & STI). UTI: urinary tract infection. |
Table 1
Cases in which additional testing is needed in recurrent UTI

Table 2
Postcoital antibiotic prophylaxis to prevent recurrent UTI
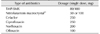
| Type of antibiotics | Dosage (single dose, mg) |
|---|---|
| TMP-SMX | 80/400 |
| Nitrofurantoin macrocrystala) | 50 or 100 |
| Cefaclor | 250 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 250 |
| Norfloxacin | 200 |
| Ofloxacin | 100 |
References
1. Fowler JE Jr, Pulaski ET. Excretory urography, cystography, and cystoscopy in the evaluation of women with urinary-tract infection: a prospective study. N Engl J Med. 1981; 304:462–465.

2. Foxman B, Gillespie B, Koopman J, Zhang L, Palin K, Tallman P, et al. Risk factors for second urinary tract infection among college women. Am J Epidemiol. 2000; 151:1194–1205.

3. Ikaheimo R, Siitonen A, Heiskanen T, Karkkainen U, Kuosmanen P, Lipponen P, et al. Recurrence of urinary tract infection in a primary care setting: analysis of a 1-year follow-up of 179 women. Clin Infect Dis. 1996; 22:91–99.
4. Kraft JK, Stamey TA. The natural history of symptomatic recurrent bacteriuria in women. Medicine (Baltimore). 1977; 56:55–60.

5. Stamm WE, McKevitt M, Roberts PL, White NJ. Natural history of recurrent urinary tract infections in women. Rev Infect Dis. 1991; 13:77–84.
6. Berry RE, Klumpp DJ, Schaeffer AJ. Urothelial cultures support intracellular bacterial community formation by uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 2009; 77:2762–2772.

7. Mulvey MA, Schilling JD, Hultgren SJ. Establishment of a persistent Escherichia coli reservoir during the acute phase of a bladder infection. Infect Immun. 2001; 69:4572–4579.

8. Rosen DA, Hooton TM, Stamm WE, Humphrey PA, Hultgren SJ. Detection of intracellular bacterial communities in human urinary tract infection. PLoS Med. 2007; 4:e329.

9. van Haarst EP, van Andel G, Heldeweg EA, Schlatmann TJ, van der Horst HJ. Evaluation of the diagnostic workup in young women referred for recurrent lower urinary tract infections. Urology. 2001; 57:1068–1072.

10. Scholes D, Hooton TM, Roberts PL, Stapleton AE, Gupta K, Stamm WE. Risk factors for recurrent urinary tract infection in young women. J Infect Dis. 2000; 182:1177–1182.

11. Foxman B, Chi JW. Health behavior and urinary tract infection in college-aged women. J Clin Epidemiol. 1990; 43:329–337.

12. Semins MJ, Shore AD, Makary MA, Weiner J, Matlaga BR. The impact of obesity on urinary tract infection risk. Urology. 2012; 79:266–269.

13. Perrotta C, Aznar M, Mejia R, Albert X, Ng CW. Oestrogens for preventing recurrent urinary tract infection in postmenopausal women. Obstet Gynecol. 2008; 112:689–690.

14. Brostrøm S, Lose G. [Oestrogen for prevention of recurrent urinary tract infections in postmenopausal women--a survey of a Cochrane review]. Ugeskr Laeger. 2009; 171:2568–2571. Danish.
15. Raz R, Stamm WE. A controlled trial of intravaginal estriol in postmenopausal women with recurrent urinary tract infections. N Engl J Med. 1993; 329:753–756.

16. Eriksen B. A randomized, open, parallel-group study on the preventive effect of an estradiol-releasing vaginal ring (Estring) on recurrent urinary tract infections in postmenopausal women. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999; 180:1072–1079.

17. Albert X, Huertas I, Pereiro II, Sanfelix J, Gosalbes V, Perrota C. Antibiotics for preventing recurrent urinary tract infection in non-pregnant women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004; (3):CD001209.

18. Schaeffer AJ, Stuppy BA. Efficacy and safety of self-start therapy in women with recurrent urinary tract infections. J Urol. 1999; 161:207–211.

19. Gupta K, Hooton TM, Roberts PL, Stamm WE. Patient-initiated treatment of uncomplicated recurrent urinary tract infections in young women. Ann Intern Med. 2001; 135:9–16.

20. Wong ES, McKevitt M, Running K, Counts GW, Turck M, Stamm WE. Management of recurrent urinary tract infections with patient-administered single-dose therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1985; 102:302–307.

21. Gupta K, Hooton TM, Naber KG, Wullt B, Colgan R, Miller LG, et al. International clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis in women: A 2010 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Clin Infect Dis. 2011; 52:e103–e120.

22. Stapleton A, Latham RH, Johnson C, Stamm WE. Postcoital antimicrobial prophylaxis for recurrent urinary tract infection. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. JAMA. 1990; 264:703–706.

23. Melekos MD, Asbach HW, Gerharz E, Zarakovitis IE, Weingaertner K, Naber KG. Post-intercourse versus daily ciprofloxacin prophylaxis for recurrent urinary tract infections in premenopausal women. J Urol. 1997; 157:935–939.

24. Guibert J, Humbert G, Meyrier A, Jardin A, Vallancien G, Piccoli S, et al. [Antibioprevention of recurrent cystitis. A randomized double-blind comparative trial of 2 dosages of pefloxacin]. Presse Med. 1995; 24:213–216. French.
25. Cetti RJ, Venn S, Woodhouse CR. The risks of long-term nitrofurantoin prophylaxis in patients with recurrent urinary tract infection: a recent medico-legal case. BJU Int. 2009; 103:567–569.

26. Howell AB, Botto H, Combescure C, Blanc-Potard AB, Gausa L, Matsumoto T, et al. Dosage effect on uropathogenic Escherichia coli anti-adhesion activity in urine following consumption of cranberry powder standardized for proanthocyanidin content: a multicentric randomized double blind study. BMC Infect Dis. 2010; 10:94.

27. Lavigne JP, Bourg G, Combescure C, Botto H, Sotto A. In-vitro and in-vivo evidence of dose-dependent decrease of uropathogenic Escherichia coli virulence after consumption of commercial Vaccinium macrocarpon (cranberry) capsules. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2008; 14:350–355.

28. Schmidt DR, Sobota AE. An examination of the anti-adherence activity of cranberry juice on urinary and nonurinary bacterial isolates. Microbios. 1988; 55:173–181.
29. Kontiokari T, Sundqvist K, Nuutinen M, Pokka T, Koskela M, Uhari M. Randomised trial of cranberry-lingonberry juice and Lactobacillus GG drink for the prevention of urinary tract infections in women. BMJ. 2001; 322:1571.

30. Stothers L. A randomized trial to evaluate effectiveness and cost effectiveness of naturopathic cranberry products as prophylaxis against urinary tract infection in women. Can J Urol. 2002; 9:1558–1562.
31. Barbosa-Cesnik C, Brown MB, Buxton M, Zhang L, DeBusscher J, Foxman B. Cranberry juice fails to prevent recurrent urinary tract infection: results from a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Clin Infect Dis. 2011; 52:23–30.

32. Ochoa-Brust GJ, Fernandez AR, Villanueva-Ruiz GJ, Velasco R, Trujillo-Hernandez B, Vasquez C. Daily intake of 100 mg ascorbic acid as urinary tract infection prophylactic agent during pregnancy. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2007; 86:783–787.

33. Carlsson S, Govoni M, Wiklund NP, Weitzberg E, Lundberg JO. In vitro evaluation of a new treatment for urinary tract infections caused by nitrate-reducing bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003; 47:3713–3718.

34. Carlsson S, Wiklund NP, Engstrand L, Weitzberg E, Lundberg JO. Effects of pH, nitrite, and ascorbic acid on nonenzymatic nitric oxide generation and bacterial growth in urine. Nitric Oxide. 2001; 5:580–586.

35. Brumfitt W, Cooper J, Hamilton-Miller JM. Prevention of recurrent urinary infections in women: a comparative trial between nitrofurantoin and methenamine hippurate. J Urol. 1981; 126:71–74.

36. Brumfitt W, Hamilton-Miller JM, Gargan RA, Cooper J, Smith GW. Long-term prophylaxis of urinary infections in women: comparative trial of trimethoprim, methenamine hippurate and topical povidone-iodine. J Urol. 1983; 130:1110–1114.

37. Cronberg S, Welin CO, Henriksson L, Hellsten S, Persson KM, Stenberg P. Prevention of recurrent acute cystitis by methenamine hippurate: double blind controlled crossover long term study. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1987; 294:1507–1508.

38. Gundersen R, Hoivik HO, Osmundsen K. [Frequent cystitis in elderly women. A double-blind comparison of Hiprex and placebo in general practice]. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 1986; 106:2048–2049. Norwegian.
39. Hoivik HO, Gundersen R, Osmundsen K, Halvorsen P, Hjortdahl P, Stokke JG. [Prevention of recurrent cystitis in fertile women. A double-blind comparison of Hiprex and placebo in general practice]. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 1984; 104:1150–1152. Norwegian.
40. Lee BS, Bhuta T, Simpson JM, Craig JC. Methenamine hippurate for preventing urinary tract infections. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012; 10:CD003265.

41. Michaels EK, Chmiel JS, Plotkin BJ, Schaeffer AJ. Effect of D-mannose and D-glucose on Escherichia coli bacteriuria in rats. Urol Res. 1983; 11:97–102.

42. Wellens A, Garofalo C, Nguyen H, Van Gerven N, Slattegard R, Hernalsteens JP, et al. Intervening with urinary tract infections using anti-adhesives based on the crystal structure of the FimH-oligomannose-3 complex. PLoS One. 2008; 3:e2040.

43. Felipe I, Bochio EE, Martins NB, Pacheco C. Inhibition of macrophage phagocytosis of Escherichia coli by mannose and mannan. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1991; 24:919–924.
44. van der Bosch JF, Verboom-Sohmer U, Postma P, de Graaff J, MacLaren DM. Mannose-sensitive and mannose-resistant adherence to human uroepithelial cells and urinary virulence of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1980; 29:226–233.

45. Anukam KC, Osazuwa E, Osemene GI, Ehigiagbe F, Bruce AW, Reid G. Clinical study comparing probiotic Lactobacillus GR-1 and RC-14 with metronidazole vaginal gel to treat symptomatic bacterial vaginosis. Microbes Infect. 2006; 8:2772–2776.

46. Wagenlehner FM, Vahlensieck W, Bauer HW, Weidner W, Piechota HJ, Naber KG. Prevention of recurrent urinary tract infections. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2013; 65:9–20.
47. Stapleton AE, Au-Yeung M, Hooton TM, Fredricks DN, Roberts PL, Czaja CA, et al. Randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial of a Lactobacillus crispatus probiotic given intravaginally for prevention of recurrent urinary tract infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2011; 52:1212–1217.

48. Damiano R, Quarto G, Bava I, Ucciero G, De Domenico R, Palumbo MI, et al. Prevention of recurrent urinary tract infections by intravesical administration of hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulphate: a placebo-controlled randomised trial. Eur Urol. 2011; 59:645–651.

49. Naber KG, Cho YH, Matsumoto T, Schaeffer AJ. Immunoactive prophylaxis of recurrent urinary tract infections: a meta-analysis. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2009; 33:111–119.

50. Bauer HW, Rahlfs VW, Lauener PA, Blessmann GS. Prevention of recurrent urinary tract infections with immuno-active E. coli fractions: a meta-analysis of five placebo-controlled double-blind studies. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2002; 19:451–456.

51. Bauer HW, Alloussi S, Egger G, Blumlein HM, Cozma G, Schulman CC. Multicenter UTI Study Group. A long-term, multicenter, double-blind study of an Escherichia coli extract (OM-89) in female patients with recurrent urinary tract infections. Eur Urol. 2005; 47:542–548. discussion 548

52. Kim KS, Kim JY, Jeong IG, Paick JS, Son H, Lim DJ, et al. A prospective multi-center trial of Escherichia coli extract for the prophylactic treatment of patients with chronically recurrent cystitis. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25:435–439.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download