Abstract
While endoscopic subureteral injection of bulking agents has become a first-line therapy for the treatment of vesicoureteral reflux (VUR), mainly due to its high success rates with minimal complications, polydimethylsiloxane (PDS) administration can be associated with bladder calcification in a minority of patients. A 10-year-old girl with prior history of subureteral administration of PDS as a treatment modality for bilateral VUR six years ago showed recurrent lower urinary tract symptoms, including dysuria, frequency, and urgency, for the past 6 months. She was admitted to our institution for right pyelonephritis with hydronephrosis. Radiologic examination had revealed two yellowish impacted stones attached to the previous site of PDS administration without recurrence of VUR. The stones were completely removed by cystolitholapaxy. This study suggests that such a late-complication should be considered in patients with recurrent urinary tract infection or lower urinary tract symptom despite complete disappearance of VUR by prior subureteral administration therapy.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.van Capelle JW., de Haan T., El Sayed W., Azmy A. The long-term outcome of the endoscopic subureteric implantation of polydimethylsiloxane for treating vesico-ureteric reflux in children: a retrospective analysis of the first 195 consecutive patients in two European centres. BJU Int. 2004. 94:1348–51.

2.Aboutaleb H., Bolduc S., Upadhyay J., Farhat W., Bagli DJ., Khoury AE. Subureteral polydimethylsiloxane injection versus extra-vesical reimplantation for primary low grade vesicoureteral reflux in children: a comparative study. J Urol. 2003. 169:313–6.

3.Elder JS., Diaz M., Caldamone AA., Cendron M., Greenfield S., Hurwitz R, et al. Endoscopic therapy for vesicoureteral reflux: a meta-analysis. I. Reflux resolution and urinary tract infection. J Urol. 2006. 175:716–22.

4.Bae YD., Park MG., Oh MM., Moon DG. Endoscopic subureteral injection for the treatment of vesicoureteral reflux in children: Polydimethylsiloxane (MacroplastiqueⓇ) versus Dextranomer/Hyaluronic Acid Copolymer (DefluxⓇ). Korean J Urol. 2010. 51:128–31.
5.Capozza N., Caione P. Dextranomer/hyaluronic acid copolymer implantation for vesico-ureteral reflux: a randomized comparison with antibiotic prophylaxis. J Pediatr. 2002. 140:230–4.

6.Solomon LZ., Birch BR., Cooper AJ., Davies CL., Holmes SA. Nonhomologous bioinjectable materials in urology: ‘size matters'? BJU Int. 2000. 85:641–5.

7.Lakgren G., Wahlin N., Skoldenberg E., Stenberg A. Long-term followup of children treated with dextranomer/hyaluronic acid copolymer for vesicoureteral reflux. J Urol. 2001. 166:1887–92.
8.Puri P., Chertin B., Velayudham M., Dass L., Colhoun E. Treatment of vesicoureteral reflux by endoscopic injection of dextranomer/hyaluronic acid copolymer: preliminary results. J Urol. 2003. 170:1541–4.

Go to : 
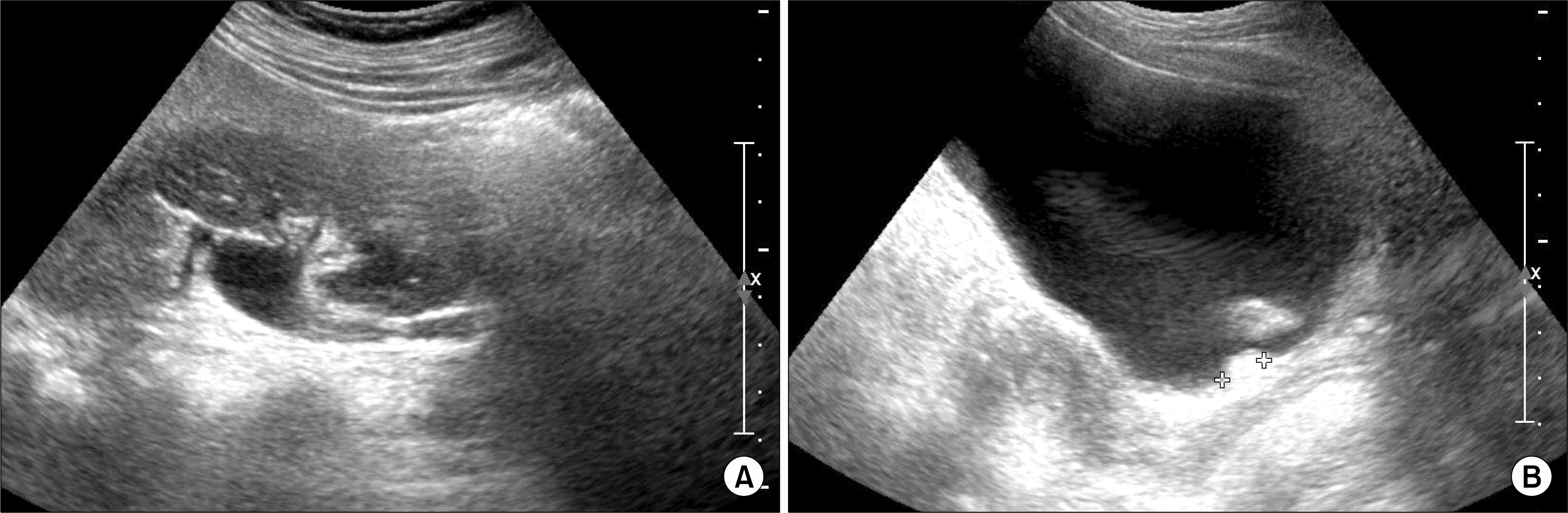 | Fig. 1.(A) Ultrasonography revealed a moderate degree hydronephrosis on right kidney. (B) On bladder imaging, 2.0 cm and 1.3 cm sized calcifications were identified around the trigonal area. |
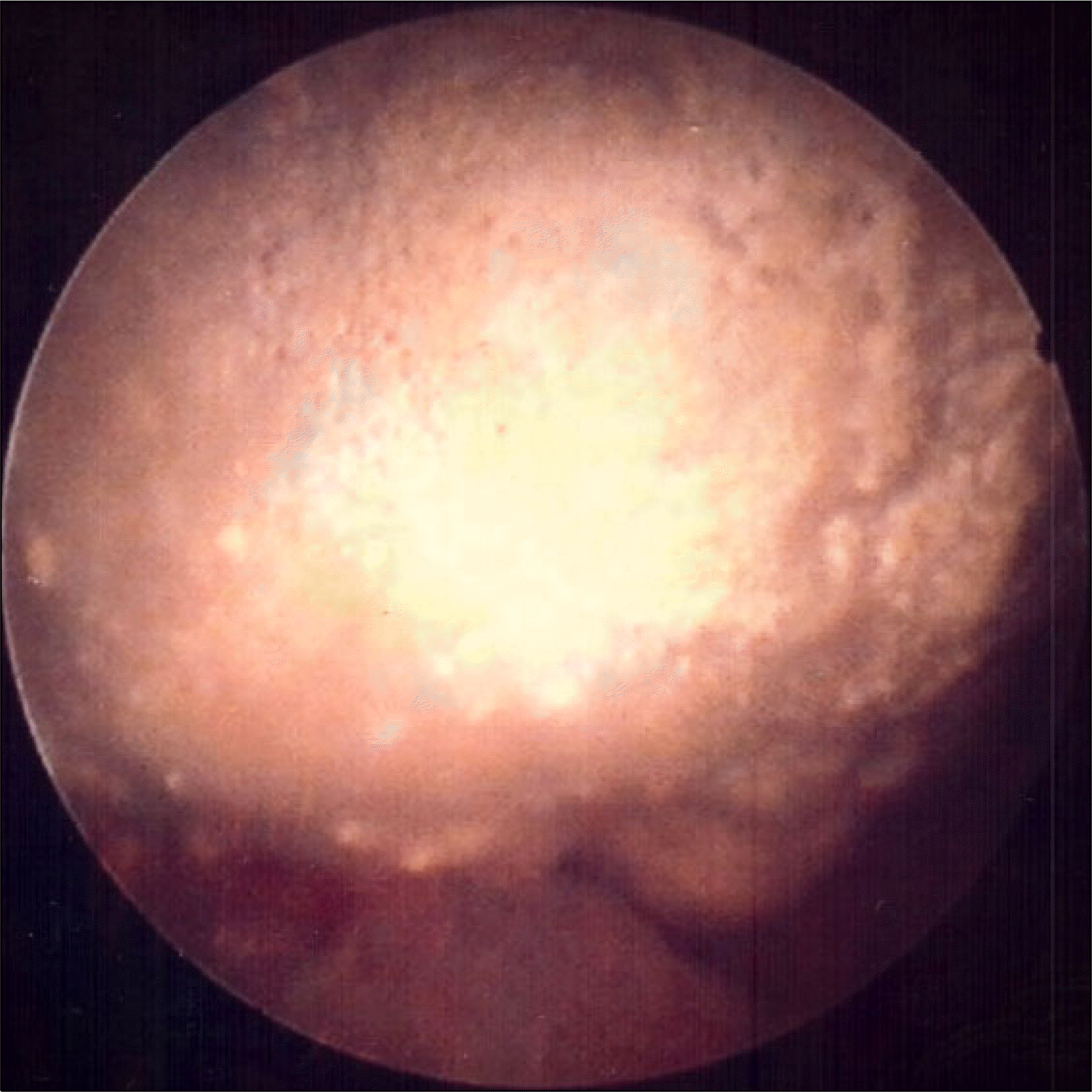 | Fig. 2.About 2 cm sized yellowish impacted stone was observed at the site of previous polydimethylsiloxane administration on cystoscopic findings. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download