Abstract
Primary aldosteronism is one of the most common cause of secondary hypertension and can be accompanied with hypokalemia. Rhabdomyolysis with hypokalemia in primary aldosteronism has been rarely reported. We describe a patient of primary aldosteronism who presented with limb-girdle type weakness. (Korean J Clin Neurophysiol 2016;18:21-24)
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Funder JW., Carey RM., Fardella C., Gomez-Sanchez CE., Mantero F., Stowasser M, et al. Case detection, diagnosis, and treatment of patients with primary aldosteronism: An endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008. 93:3266–3281.

2.Omura M., Sasano H., Saito J., Yamaguchi K., Kakuta Y., Nishikawa T. Clinical characteristics of aldosterone-producing microadenoma, macroadenoma, and idiopathic hyperaldosteronism in 93 patients with primary aldosteronism. Hypertens Res. 2006. 29:883–889.

3.Lee JH., Kim E., Chon S. Hypokalemia-induced rhabdomyolysis by primary aldosteronism coexistent with sporadic inclusion body myositis. Ann Rehabil Med. 2015. 39:826–832.

4.Park W., Kim DH., Han KC., Bae YH., Kim SH., Ju JH, et al. A case of primary aldosteronism with rhabdomyolysis. Korean J Nephrol. 2005. 24:845–850.
5.Kim B., No HJ., Lim YH., Kim HJ., Kim HY., Park BH, et al. A case of primary aldosteronism accompanied by rhabdomyolysis. Korean J Med. 2006. 70:261–266.
Go to : 
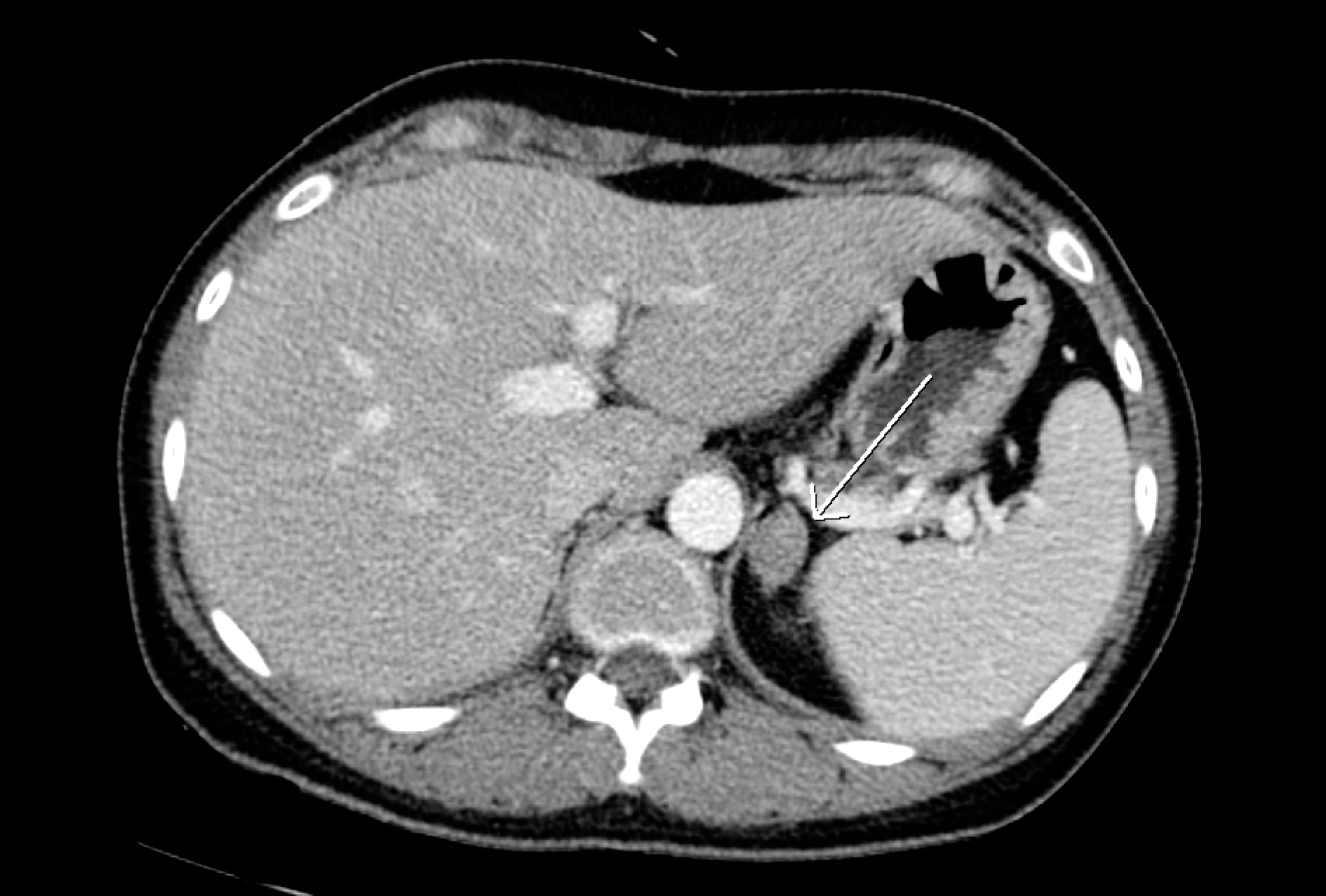 | Figure 1.Abdomen computer tomography. Computed tomography shows a 2.3 cm sized enhancing nodule in left adrenal gland (arrow). |
Table 1.
Summarization of previous Korean cases




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download