Abstract
Japanese-B viral encephalitis (JE) usually has a monophasic illness pattern. A 45-year-old woman in an altered mentality had improved over 1 month. About 1 week after the initial improvement, the patient became comatose with aggravated EEG and MRI findings. Assays of cerebrospinal fluid and serum were positive for the IgM antibody to Japanese-B virus. After intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) infusion, the patient recovered. We report a patient with JE who showed a biphasic illness pattern and recovered after IVIG therapy. (Korean J Clin Neurophysiol 2014;16:35-38)
REFERENCES
1.Misra UK., Kalita J. Prognosis of Japanese encephalitis patients with dystonia compared to those with parkinsonian features only. Postgrad Med J. 2002. 78:238–241.

2.Dickerson RB., Newton JR., Hansen JE. Diagnosis and immediate prognosis of Japanese B encephalitis; observations based on more than 200 patients with detailed analysis of 65 serologically confirmed cases. Am J Med. 1952. 12:277–288.
3.Pradhan S., Gupta RK., Singh MB., Mathur A. Biphasic illness pattern due to early relapse in Japanese-B virus encephalitis. J Neurol Sci. 2001. 183:13–18.

4.Zimmerman HM. The pathology of Japanese B encephalitis. Am J Pathol. 1946. 22:965–991.
5.Lai CC., Liu WL., Lin SC., Hsiao YC., Ding LW. Diagnostic MR images of Japanese encephalitis. J Emerg Med. 2008. 35:305–307.

6.Mathur A., Arora KL., Chaturvedi UC. Host defence mechanisms against Japanese encephalitis virus infection in mice. J Gen Virol. 1983. 64:805–811.

7.Sharma S., Mathur A., Prakash V., Kulshreshtha R., Kumar R., Chaturvedi UC. Japanese encephalitis virus latency in peripheral blood lymphocytes and recurrence of infection in children. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991. 85:85–89.

Figure 1.
Brain magnetic resonance images on hospital day 2. Fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) images show high signal intensities of bilateral hippocampus (arrow).
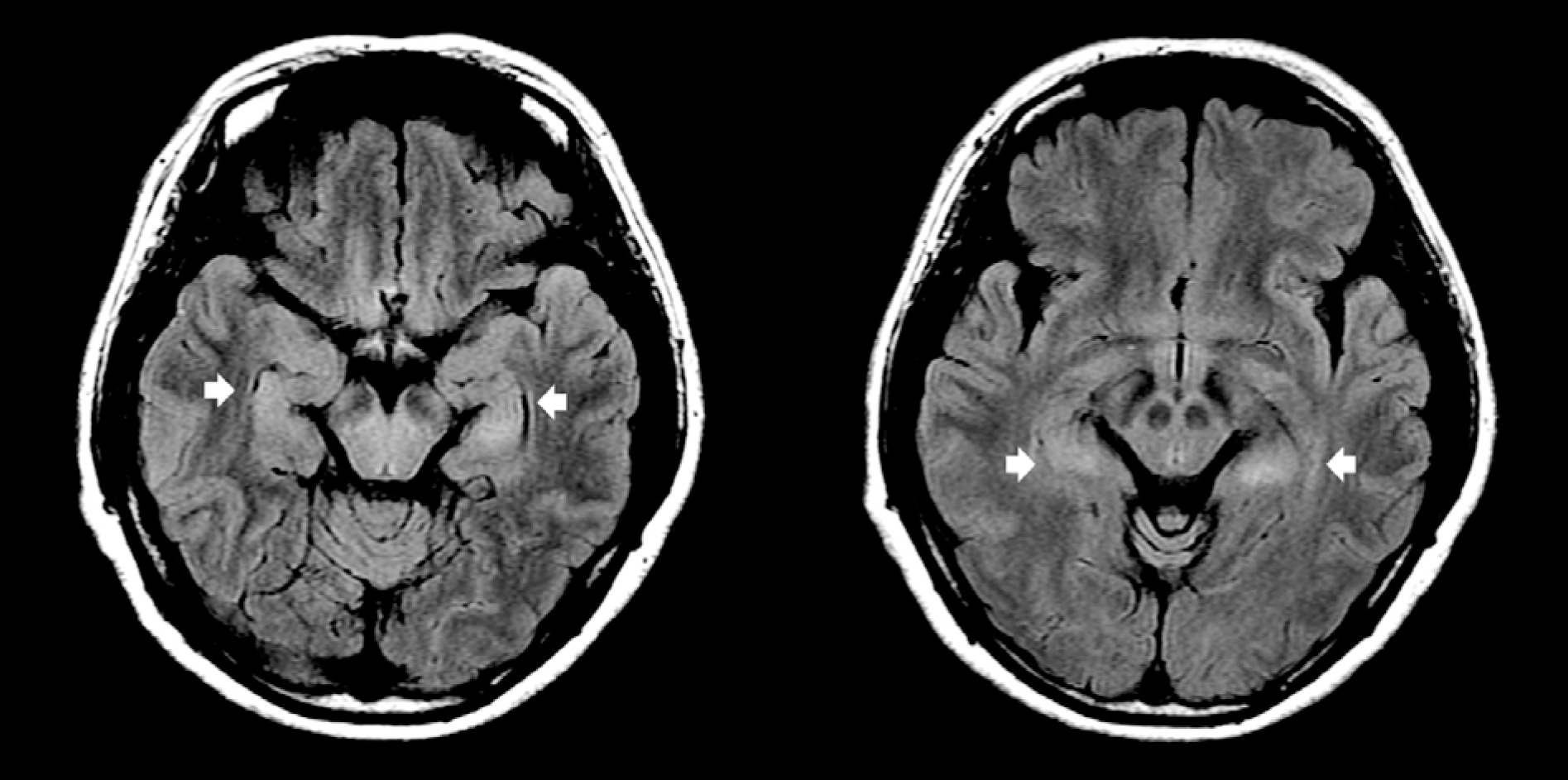
Figure 2.
Electroencephalographies on hospital days 7, 46, and 53. On hospital day 7 (A), EEG showed frontal intermittent rhythmic delta activity (FIRDA). On hospital day 46 (B), the patient was comatose, and EEG showed continuous generalized delta activity. After intravenous immune globulin (IVIG) therapy, on hospital day 53 (C), EEG was normalized.
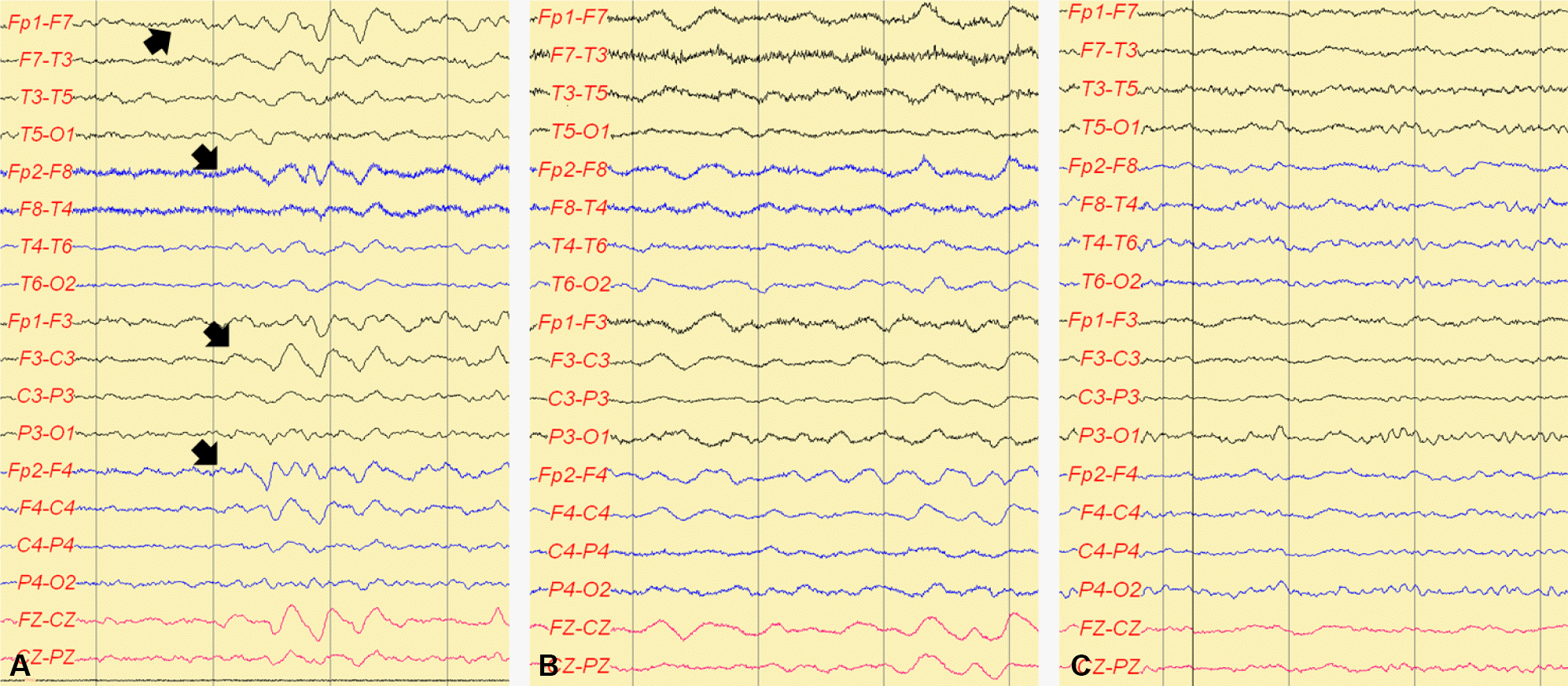
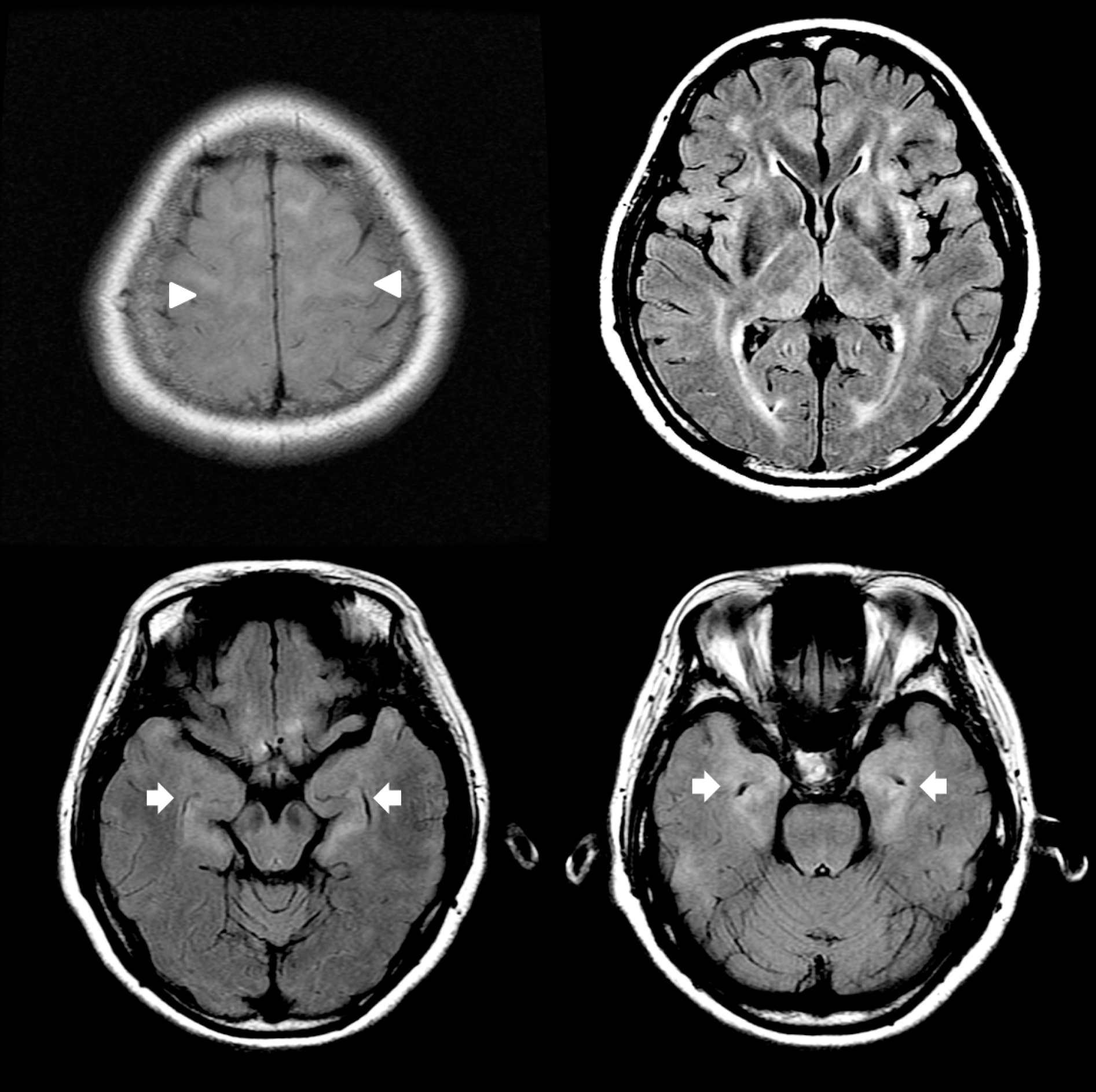
Figure 3.
Follow up brain magnetic resonance images on hospital day 39. Follow up fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) images showed increased high signal intensity lesions of bilateral hippocampus (arrow) and additional high signal intensity lesions of bilateral medial thalamus, basal ganglia, periventricular white matter, and juxtacortical white matter (arrow head).




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download