Abstract
Some patients with leprosy may present with atypical features, such as isolated peripheral neuropathy without skin lesions, or marked proprioceptive dysfunction. We report a 56-year-old female who presented with predominant proprioceptive loss without skin lesion, but was finally confirmed as leprous neuropathy by sural nerve biopsy. It is postulated that large myelinated fibers were affected by chronic immunological reactions triggered by inactive bacterial particles, producing a peripheral neuropathy presenting as predominant proprioceptive sensory loss without typical skin lesions.
REFERENCES
1.Ooi WW., Srinivasan J. Leprosy and the peripheral nervous system: basic and clinical aspects. Muscle Nerve. 2004. 30:393–409.

2.WHO. Global leprosy situation, 2010. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2010. 85:337.
3.Agrawal A., Pandit L., Dalal M., Shetty JP. Neurological manifestations of Hansen’s disease and their management. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2005. 107:445–454.

4.Skacel M., Antunes SL., Rodrigues MM., Nery JA., Valentim VD., Morais RP, et al. The diagnosis of leprosy among patients with symptoms of peripheral neuropathy without cutaneous lesions: a follow-up study. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2000. 58:800–807.

5.Pandya SS., Bhakti WS. Severe pan-sensory neuropathy in leprosy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1994. 62:24–31.
6.van Brakel WH., Nicholls PG., Das L., Barkataki P., Suneetha SK., Jadhav RS, et al. The INFIR Cohort Study: Investigating prediction, detection and pathogenesis of neuropathy and reactions in leprosy, Methods and baseline results of a cohort of multibacillary leprosy patients in north India. Lepr Rev. 2005. 76:14–34.

7.Khadilkar SV., Benny R., Kasegaonkar PS. Proprioceptive loss in leprous neuropathy: a study of 19 patients. Neurol India. 2008. 56:450–455.

8.Rosenberg NR., Faber WR., Vermeulen M. Unexplained delayed nerve impairment in leprosy after treatment. Lepr Rev. 2003. 74:357–365.

9.Ha YM. Relapse of Leprosy. Korean Lepr Bull. 1994. 27:27–29.
10.THELEP: Persisting Mycobacterium leprae among THELEP trial patients in Bamako and Chingleput. Subcommittee on Clinical Trials of the Chemotherapy of Leprosy (THELEP) Scientific Working Group of the UNDP/World Bank/WHO Special Programme for Research and Training in Tropical Diseases. Lepr Rev. 1987. 58:325–337.
Figure 1.
Sural nerve biopsy findings of the patient. (A) Almost complete loss of myelinated nerve fibers was observed with thickening and hypertrophy of epineurial sheath (H&E stain ×100). (B) On longitudinal sections, perivascular inflammatory infiltrates were prominent (Modified Gomori-trichrome stain ×100). (C) A non-caseating granuloma with giant cells are seen (H&E stain ×400). (D) On Fite stain, no acid-fast bacilli were observed (Fite stain, ×100). The black bars represent 100 μm.
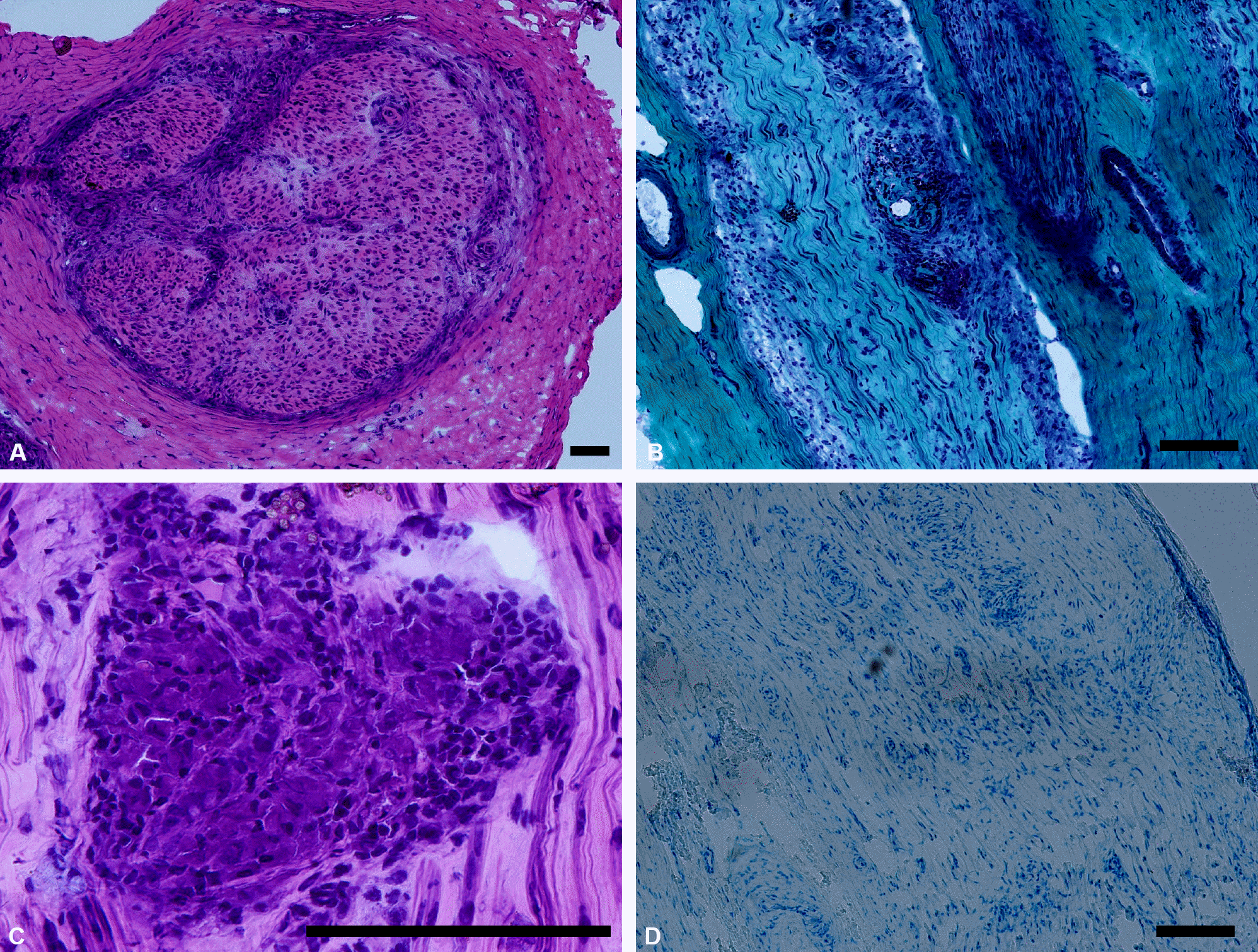
Table 1.
Results of motor nerve conduction studies
| Stimulation site | Latency (ms) | Amplitude (mV) | Velocity (m/s) | Stimulation site | Latency (ms) | Amplitude (mV) | Velocity (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right median nerve (recorded from abductor pollicis brevis muscle) | Left median nerve (recorded from abductor pollicis brevis muscle) | ||||||
| Wrist | 3.3 | 17.0 | - | Wrist | 3.3 | 13.9 | - |
| Elbow | 7.0 | 16.2 | 59.5 | Elbow | 7.1 | 13.5 | 57.9 |
| Axilla | 8.4 | 15.7 | 85.7 | Axilla | 9.0 | 13.5 | 63.2 |
| F-response | 25.0 | F-response | 25.5 | ||||
| Right ulnar nerve (recorded from abductor digiti minimi muscle) | Left ulnar nerve (recorded from abductor digiti minimi muscle) | ||||||
| Wrist | 2.4 | 12.2 | - | Wrist | 2.4 | 15.7 | - |
| Below elbow | 5.5 | 11.1 | 64.5 | Below elbow | 4.9 | 15.4 | 74.0 |
| Above elbow | 7.2 | 11.0 | 58.8 | Above elbow | 6.6 | 15.6 | 58.8 |
| Axilla | 8.9 | 9.8 | 64.7 | Axilla | 8.3 | 15.1 | 64.7 |
| F-response | 27.4 | F-response | 25.9 | ||||
| Right peroneal nerve (recorded from extensor digitorum brevis muscle) | Left peroneal nerve (recorded from extensor digitorum brevis muscle) | ||||||
| Ankle | 2.9 | 3.8 | - | Ankle | 3.1 | 10.0 | - |
| Fibular head | 10.1 | 3.3 | 41.7 | Fibular head | 9.3 | 8.8 | 45.2 |
| Poplitea fossa | 11.8 | 3.1 | 55.9 | Poplitea fossa | 10.8 | 8.6 | 63.3 |
| F-response | No response | F-response | 44.4 | ||||
| Right posterior tibial nerve (recorded from abductor hallucis muscle) | Left posterior tibial nerve (recorded from abductor hallucis muscle) | ||||||
| Ankle | 2.7 | 20.9 | - | Ankle | 3.7 | 18.2 | - |
| Poplitea fossa | 10.8 | 16.3 | 42.0 | Poplitea fossa | 11.5 | 14.0 | 43.6 |
| F-response | 48.2 | F-response | 49.1 | ||||
| H-reflex* | No response | H-reflex* | No response | ||||
Table 2.
Results of sensory and mixed nerve conduction studies




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download