Abstract
REFERENCES
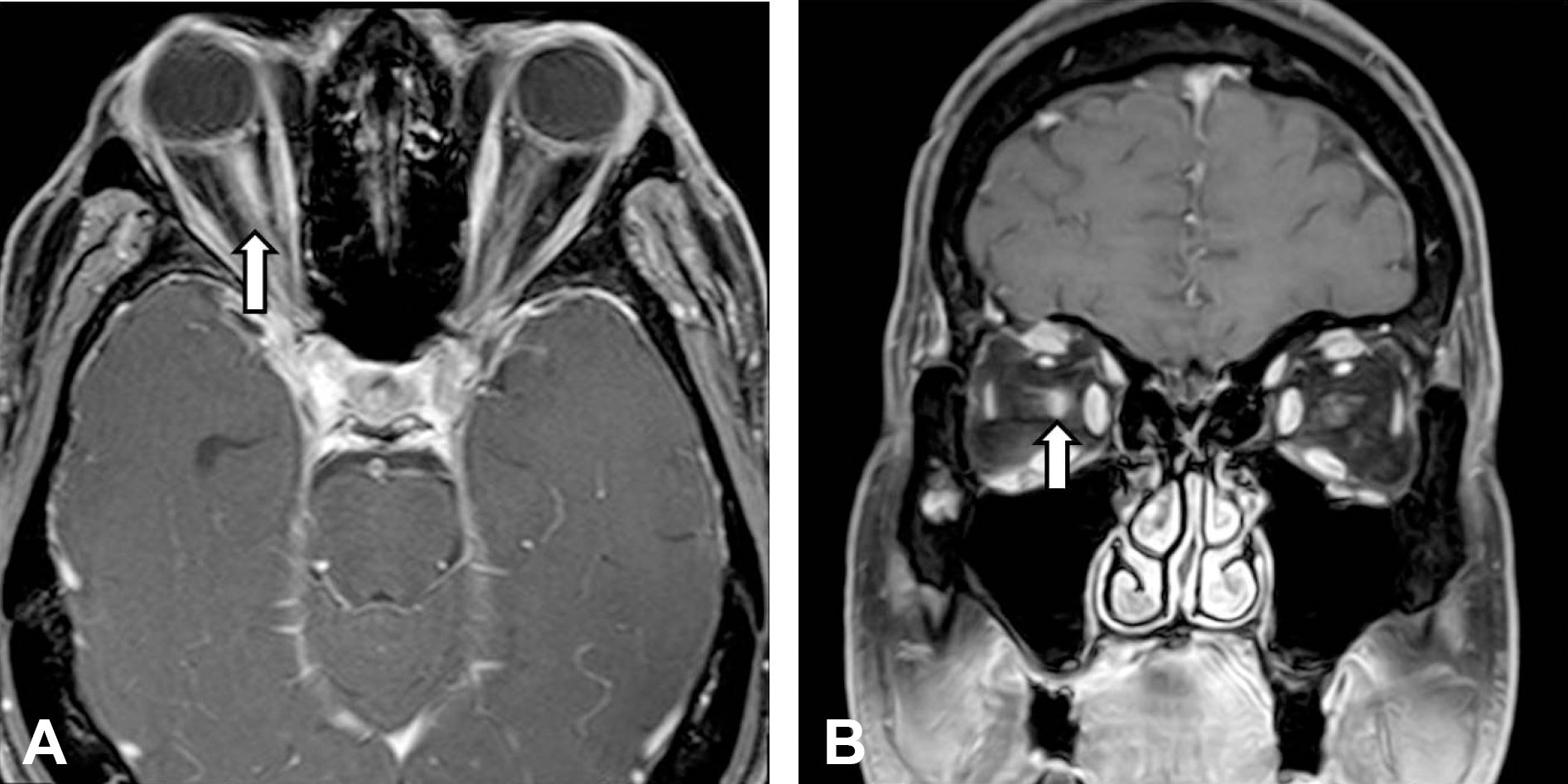 | Figure 1.Brain MRI of patient. Fat suppression T1 post-gadolinium scan showed the edema and enhancement of the right optic nerve (arrow) (A: axial, B: coronal). |
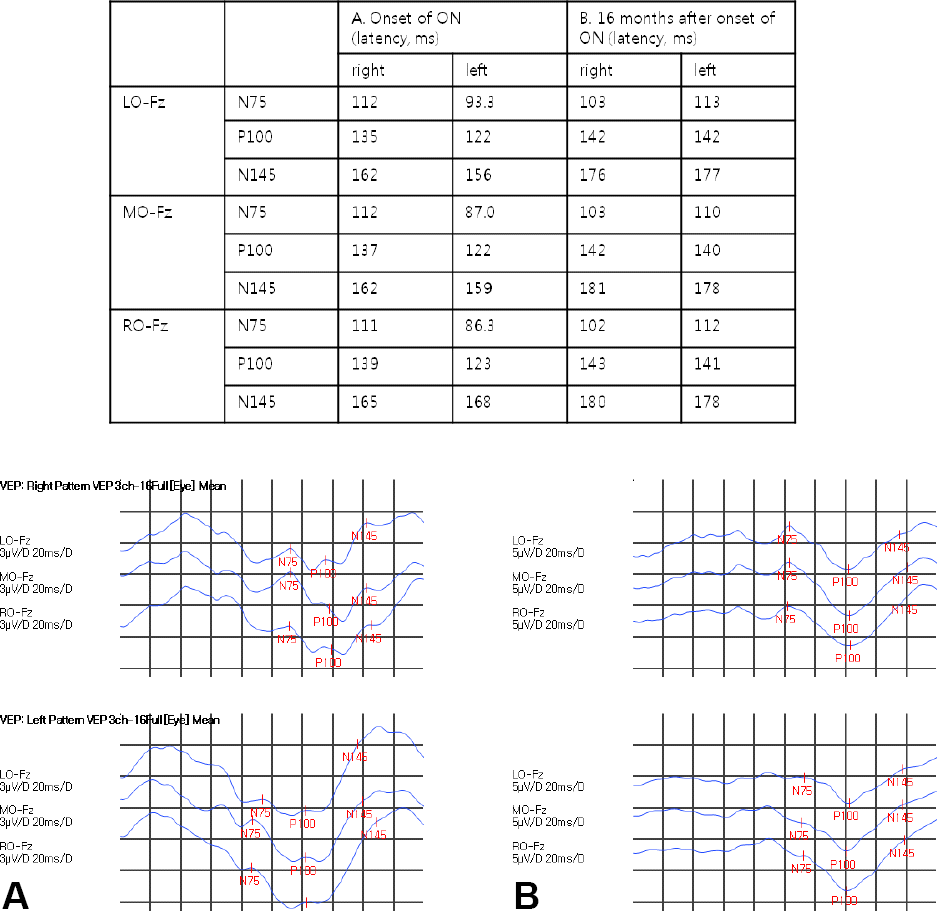 | Figure 2.Pattern shift visual evoked potential of patient. The graph showed “W” shaped P100 wave formation and bilateral prolonged P100 latency at onset of optic neuritis (A), and normal wave formation and prolonged P 100 latency bilaterally after 16 months (B). LO; left occipital, Fz; fontal zero, MO; midline occipital, RO; right occipital, ON; optic neuritis. |
Table 1.
All tests were performed in the right side.
SNAP amplitude (µV), CMAP amplitude (mV).
Lat; latency, Amp; amplitude, CV; conduction velocity, MS f-w; median sensory finger-wrist, MS w-e; median sensory wrist-elbow, US f-w; ulnar sensory finger-wrist, US w-e; ulnar sensory wrist-elbow, SS; sural sensory, SPS; superficial peroneal sensory, MM-W; median motor wrist, MM-E; median motor elbow, UM-W; ulnar motor wrist, UM-E; ulnar motor elbow, CPM-A; common peroneal motor ankle, CPM-F; common peroneal motor fibular head, PTM-A; posterior tibial motor ankle, PTM-K; posterior tibial motor knee, M-F; median F-wave, U-F; ulnar F-wave, CP-F; commo peroneal F-wave, PT-F; posterior tibial F-wave, H; H-reflex, NR; no response.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download