Abstract
Objective
The purpose of this study is to demonstrate clinical characteristics of atraumatic intracranial abscesses according to analyze the medical records and imaging studies of patients.
Methods
This study is performed with retrospective reviews of medical records of 15 patients which were admitted under the diagnosis as atraumatic intracranial abscess from 2004 to 2009.
Results
The infection entities were 2 epidural abscess, 1 subdural abscess, and 13 brain abscesses. Among them, 8 cases were bacterial infections, 6 unknown organisms, and 1 toxoplasmosis. 14 patients were managed with surgical and medical treatments. 1 patient was treated with medication only. Generally, the outcome was good and no mortality was recorded. According to the results of this study, the preponderance of smoking and alcoholics of intracranial abscesses were suggested.
Conclusion
To diagnose intracranial abscess accurately, more careful listening to the patient's history including smoking, alcohol consumption, and disease is necessarily required. The prognosis of the intracranial abscess would be good if accurate results for pathogens, appropriate usage of antibioticis, and suitable surgical method were done.
Figures and Tables
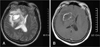 | FIGURE 1Preoperative MRI findings. T2 weighted image (A) shows high signal intensity mass around low signal intensity rim and peripheral edema. Enhanced T1 weighted image (B) shows low signal intensity mass with well-enhanced rim. |
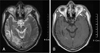 | FIGURE 2Preoperative MRI shows the ill defined high signal intensity lesion on T2 weighted image (A) and multiple small enhanced masses on enhanced T1 weighted image (B). |
References
1. Agarwal AK, Garg R, Simon M. Ring enhancing lesion on CT scan: metastases or a brain abscess? Emerg Med J. 2007; 24:706.

3. Bagaitkar J, Demuth DR, Scott DA. Tobacco use increases susceptibility to bacterial infection. Tob Induc Dis. 2008; 4:12.

4. Barlas O, Sencer A, Erkan K, Eraksoy H, Sencer S, Bayindir C. Stereotactic surgery in the management of brain abscess. Surg Neurol. 1999; 52:404–410. discussion 411.

5. Black P, Graybill JR, Charache P. Penetration of brain abscess by systemically administered antibiotics. J Neurosurg. 1973; 38:705–709.

6. Black PM, Levine BW, Picard EH, Nirmel K. Asymmetrical hydrocephalus following ventriculitis from rupture of a thalamic abscess. Surg Neurol. 1983; 19:524–527.
7. Brewer NS, MacCarty CS, Wellman WE. Brain abscess: a review of recent experience. Ann Intern Med. 1975; 82:571–576.

8. Cansever T, Izgi N, Civelek E, Aydoseli A, Kiris T, Sencer A. Retrospective analysis of changes in diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of brain abscess for a period of thirty-three-years. In : 13th World Congress of Neurological Surgery; June 19-24, 2005; Marrakesh. Nyon Vaud, Switzerland: World Federation of Neurosurgical Societies;2005. (Abstract).
9. Carpenter J, Stapleton S, Holliman R. Retrospective analysis of 49 cases of brain abscess and review of the literature. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2007; 26:1–11.

10. Chun CH, Johnson JD, Hofstetter M, Raff MJ. Brain abscess. A study of 45 consecutive cases. Medicine (Baltimore). 1986; 65:415–431.
11. Desprechins B, Stadnik T, Koerts G, Shabana W, Breucq C, Osteaux M. Use of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in differential diagnosis between intracerebral necrotic tumors and cerebral abscesses. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999; 20:1252–1257.
13. Everett ED, Strausbaugh LJ. Antimicrobial agents and the central nervous system. Neurosurgery. 1980; 6:691–714.

14. Gillet GR, Garner JE, Bremner DA. Antimicrobial management of intracranial abscess. Aust N Z J Surg. 1984; 54:253–255.

15. Goodkin HP, Harper MB, Pomeroy SL. Intracerebral abscess in children: historical trends at Children's Hospital Boston. Pediatrics. 2004; 113:1765–1770.

16. Gordts F, Clement PA, Destryker A, Desprechins B, Kaufman L. Prevalence of sinusitis signs on MRI in a non-ENT pediatric population. Rhinology. 1997; 35:154–157.
17. Gortvai P, De Louvois J, Hurley R. The bacteriology and chemotherapy of acute pyogenic brain abscess. Br J Neurosurg. 1987; 1:189–203.

18. Greenberg MS. Handbook of Neurosurgery. ed 5. New York: Thieme;2001. p. 217–223.
19. Guzman R, Barth A, Lövblad KO, El-Koussy M, Weis J, Schroth G, et al. Use of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in differentiating purulent brain processes from cystic brain tumors. J Neurosurg. 2002; 97:1101–1107.

20. Haimes AB, Zimmerman RD, Morgello S, Weingarten K, Becker RD, Jennis R, et al. MR imaging of brain abscesses. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1989; 152:1073–1085.

21. Hakan T, Ceran N, Erdem I, Berkman MZ, Göktaş P. Bacterial brain abscesses: an evaluation of 96 cases. J Infect. 2006; 52:359–366.

22. Hirschberg H, Bosnes V. C-reactive protein levels in the differential diagnosis of brain abscesses. J Neurosurg. 1987; 67:358–360.

23. Iannotti CA, Hall GS, Procop GW, Tuohy MJ, Staugaitis SM, Weil RJ. Solitary Nocardia farcinica brain abscess in an immunocompetent adult mimicking metastatic brain tumor: rapid diagnosis by pyrosequencing and successful treatment. Surg Neurol. 2009; 72:74–79. discussion 79.

24. Jamjoom AB. Short course antimicrobial therapy in intracranial abscess. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1996; 138:835–839.

25. Kao PT, Tseng HK, Liu CP, Su SC, Lee CM. Brain abscess: clinical analysis of 53 cases. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2003; 36:129–136.
26. Lee TH, Chang WN, Su TM, Chang HW, Lui CC, Ho JT, et al. Clinical features and predictive factors of intraventricular rupture in patients who have bacterial brain abscesses. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2007; 78:303–309.

27. Le Moal G, Landron C, Grollier G, Bataille B, Roblot F, Nassans P, et al. Characteristics of brain abscess with isolation of anaerobic bacteria. Scand J Infect Dis. 2003; 35:318–321.

28. Lescop J, Brinquin L, Schill H, Soulié D, Sarrazin JL, Cordoliani YS. [Diffuse toxoplasmic encephalitis in a non-immunosuppressed patient.]. J Radiol. 1995; 76:21–24.
29. Longatti P, Perin A, Ettorre F, Fiorindi A, Baratto V. Endoscopic treatment of brain abscesses. Childs Nerv Syst. 2006; 22:1447–1450.

30. Lu CH, Chang WN, Lui CC. Strategies for the management of bacterial brain abscess. J Clin Neurosci. 2006; 13:979–985.

32. Mafee MF, Tran BH, Chapa AR. Imaging of rhinosinusitis and its complications: plain film, CT, and MRI. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2006; 30:165–186.

33. Mamelak AN, Mampalam TJ, Obana WG, Rosenblum ML. Improved management of multiple brain abscesses: a combined surgical and medical approach. Neurosurgery. 1995; 36:76–85. discussion 85-86.

34. Mampalam TJ, Rosenblum ML. Trends in the management of bacterial brain abscesses: a review of 102 cases over 17 years. Neurosurgery. 1988; 23:451–458.

35. Mandell BJ, Dolin R. Mandell, Douglas and Bennett's principles and practice of infectious disease. 6th ed. New York: Churchill Livingstone;2005. p. 2924–2931.
37. Naito M, Hirakawa H, Yamashita A, Ohara N, Shoji M, Yukitake H, et al. Determination of the genome sequence of Porphyromonas gingivalis strain ATCC 33277 and genomic comparison with strain W83 revealed extensive genome rearrangements in P. gingivalis. DNA Res. 2008; 15:215–225.

38. Ng PY, Seow WT, Ong PL. Brain abscesses: review of 30 cases treated with surgery. Aust N Z J Surg. 1995; 65:664–666.

39. Nunez DA. Aetiological role of otolaryngological disease in paediatric intracranial abscess. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1992; 37:80–82.
40. Nunez DA, Browning GG. Risks of developing an otogenic intracranial abscess. J Laryngol Otol. 1990; 104:468–472.

41. Osenbach RK, Loftus CM. Diagnosis and management of brain abscess. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 1992; 3:403–420.

42. Pit S, Jamal F, Cheah FK. Microbiology of cerebral abscess: a four-year study in Malaysia. J Trop Med Hyg. 1993; 96:191–196.
43. Quartey GR, Johnston JA, Rozdilsky B. Decadron in the treatment of cerebral abscess. An experimental study. J Neurosurg. 1976; 45:301–310.
44. Qureshi HU, Habib AA, Siddiqui AA, Mozaffar T, Sarwari AR. Predictors of mortality in brain abscess. J Pak Med Assoc. 2002; 52:111–116.
45. Roche M, Humphreys H, Smyth E, Phillips J, Cunney R, McNamara E, et al. A twelve-year review of central nervous system bacterial abscesses; presentation and aetiology. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2003; 9:803–809.

46. Rosenblum ML, Mampalam TJ, Pons VG. Controversies in the management of brain abscesses. Clin Neurosurg. 1986; 33:603–632.
47. Salzman C, Tuazon CU. Value of the ring-enhancing sign in differentiating intracerebral hematomas and brain abscesses. Arch Intern Med. 1987; 147:951–952.

48. Schroeder KA, McKeever PE, Schaberg DR, Hoff JT. Effect of dexamethasone on experimental brain abscess. J Neurosurg. 1987; 66:264–269.

49. Seydoux C, Francioli P. Bacterial brain abscesses: factors influencing mortality and sequelae. Clin Infect Dis. 1992; 15:394–401.

50. Sharma BS, Gupta SK, Khosla VK. Current concepts in the management of pyogenic brain abscess. Neurol India. 2000; 48:105–111.
51. Sharma BS, Khosla VK, Kak VK, Gupta VK, Tewari MK, Mathuriya SN, et al. Multiple pyogenic brain abscesses. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1995; 133:36–43.

52. Silva LA, Vieira RS, Serafini LN, Carlotti CG Jr, Figueiredo JF. [Toxoplasmosis of the central nervous system in a patient without immunosupression: case report.]. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2001; 34:487–490.
55. Stephanov S, Joubert MJ. Large brain abscesses treated by aspiration alone. Surg Neurol. 1982; 17:338–340.

56. Takeshita M, Kagawa M, Izawa M, Takakura K. Current treatment strategies and factors influencing outcome in patients with bacterial brain abscess. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1998; 140:1263–1270.

57. Tseng JH, Tseng MY. Brain abscess in 142 patients: factors influencing outcome and mortality. Surg Neurol. 2006; 65:557–562. discussion 562.

58. Vander Top EA, Wyatt TA, Gentry-Nielsen MJ. Smoke exposure exacerbates an ethanol-induced defect in mucociliary clearance of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005; 29:882–887.

59. Wise BL, Gleason CA. CT-directed stereotactic surgery in the management of brain abscess. Ann Neurol. 1979; 6:457.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print






 XML Download
XML Download