Abstract
We report a case of organized intracerebral hematoma caused by head injury and osteoplastic craniotomy for the hematoma removal. An organizing intracerebral hematoma is relatively rare complication. A 64-year-old male had had a history of explosive head injury and osteoplastic craniotomy and removal of the traumatic intracerebral hematoma. He complained of headache intermittently. Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance (MR) imaging of the brain revealed a heterogeneous round mass in the left frontal lobe and a metallic foreign body with artifact in the parietal lobe. We performed osteoplastic craniotomy and removal of the mass. The lesion was located in the left frontal lobe and removed totally. Histologic examination showed an encapsulated organized hematoma with reactive gliosis. We achieved good results.
Figures and Tables
 | FIGURE 1Plain skull X-rays showing an osteoplastic craniotomy in the left frontal region (A) and a metallic foreign body in the vertex (B). |
 | FIGURE 2Computed tomography scans revealing 4×3×2 cm mass (A) showing no contrast-enhancement (B) in the left frontal lobe with a metallic foreign body in the parietal lobe (C). |
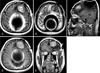 | FIGURE 3Magnetic resonance images revealing 4×3×2 cm mass showing no gadolinium-enhancement in the left frontal lobe and artifact in the parietal lobe. A: Axial T1-weighted MR image. B: T2-weighted MR image. C: Sagittal T1-weighted MR image. D: Gadolinium-enhanced axial T1-weighted MR image. E: Coronal T1-weighted MR image. |
References
1. Afra D. Ossification of subdural hematoma. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg. 1961; 18:393–397.
2. Boskey AL. Ali SY, editor. Phospholipids and calcification: an overview. Cell mediated calcification and matrix vesicles. Proceedings of the IV International Conference on Matrix Vesicles, Cambridge. 15 July 1985; Amsterdam: Excerpta Medica;1986. p. 175–179.
3. Dolinskas CA, Bilaniuk LT, Zimmerman RA, Kuhl DE. Computed tomography of intracerebral hematomas. I. Transmission CT observations on hematoma resolution. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1977; 129:681–688.

4. Enzmann DR, Britt RH, Lyons BE, Buxton JL, Wilson DA. Natural history of experimental intracerebral hemorrhage: sonography, computed tomography and neuropathology. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1981; (6):517–526.
5. Fiumara E, Gamacorta M, D'Angelo V, Ferrara M, Corona C. Chronic encapsulated intracerebral hematoma: pathogenesis and diagnostic considerations. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1989; 52:1296–1299.
6. Hirsh LF, Spector HB, Bogdanoff BM. Chronic encapsulated intracerebral hematoma. Neurosurgery. 1981; 9:169–172.

7. Laster DW, Moody DM, Ball MR. Resolving intracerebral hematoma: alteration of the "ring sign" with steroids. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1978; 130:935–939.

8. Lee YY, Moser R, Bruner JM, Van Tassel P. Organized intracerebral hematoma with acute hemorrhage: CT patterns and pathologic correlations. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1986; 147:111–118.

9. Lin SZ, Shih CJ, Wang YC, Tsai SH. Intracerebral hematoma simulating a new growth. Surg Neurol. 1984; 21:459–464.

10. Majno G, Joris I, editors. Cells, Tissues, and Disesase: Principles of General Pathology. Cambridge, MA: Blackwell Science;1996. p. 229–246.
11. Pozzati E, Giuliani G, Gaist G, Piazza G, Vergoni G. Chronic expanding intracerebral hematoma. J Neurosurg. 1986; 65:611–614.

12. Reid JD, Kommareddi S, Lankerani M, Park MC. Chronic expanding hematomas. A clinicopathologic entity. JAMA. 1980; 244:2441–2442.

13. Roda JM, Carceller F, Pérez-Higueras A, Morales C. Encapsulated intracerebral hematomas: a defined entity. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1993; 78:829–833.
14. Tsuruta W, Tsuboi K, Nose T. Serial neuroimaging of encapsulated chronic intracerebral hematoma with repeated hemorrhage. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2003; 43:439–442.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download