Abstract
Interferon-alpha (IFN-α) is an important therapeutic agent for hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, but has various side effects including thyroiditis. We report a case of interferon-induced non-autoimmune hypothyroidism followed by autoimmune-medicated Graves' disease. A 59-year-old woman was diagnosed with chronic active hepatitis C; she had been treated with IFN-α and ribavirin for 24 weeks. Before starting the IFN-α, her thyroid function was normal and she was negative for autoantibodies. Severe hypothyroidism developed 5 weeks after halting the IFN-α, with the Graves' disease phase arising at 32 weeks. For accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment of thyroid dysfunction during treatment with IFN-α, we need to understand and consider rare cases of multiphasic disorder involving both non-autoimmune and autoimmune thyroiditis induced by IFN-α.
Go to : 
References
1. Mao XR, Zhang LT, Chen H, Xiao P, Zhang YC. Possible factors affecting thyroid dysfunction in hepatitis C virusinfected untreated patients. Exp Ther Med. 2014; 8(1):133–40.

2. Mandac JC, Chaudhry S, Sherman KE, Tomer Y. The clinical and physiological spectrum of interferon-alpha induced thyroiditis: toward a new classification. Hepatology. 2006; 43(4):661–72.

3. Tran HA. The swinging thyroid in hepatitis C infection and interferon therapy. QJM. 2010; 103(3):187–91.

4. Tomer Y, Menconi F. Interferon induced thyroiditis. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009; 23(6):703–12.

5. Barut Ş, Günal Ö. Thyroid disorders associated with hepatitis C or interferon based therapies. J Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013; 3(3):147–9.
6. Jadali Z. Autoimmune thyroid disorders in hepatitis C virus infection: effect of interferon therapy. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 17(1):69–75.

7. Caraccio N, Cuccato S, Pratesi F, Dardano A, Ursino S, Chimenti D, et al. Effect of type I interferon(s) on cell viability and apoptosis in primary human thyrocyte cultures. Thyroid. 2009; 19(2):149–55.

8. Akeno N, Smith EP, Stefan M, Huber AK, Zhang W, Keddache M, et al. IFN-alpha mediates the development of autoimmunity both by direct tissue toxicity and through immune cell recruitment mechanisms. J Immunol. 2011; 186(8):4693–706.
9. Kim BK, Choi YS, Park YH, Lee SU. Interferon-alphainduced destructive thyroiditis followed by Graves' disease in a patient with chronic hepatitis C: a case report. J Korean Med Sci. 2011; 26(12):1638–41.

10. Bohbot NL, Young J, Orgiazzi J, Buffet C, Francois M, Bernard-Chabert B, et al. Interferon-alpha-induced hyperthyroidism: a three-stage evolution from silent thyroiditis towards Graves' disease. Eur J Endocrinol. 2006; 154(3):367–72.
11. Savvas SP, Papakostas N, Giannaris M, Malaktari S, Koskinas J, Archimandritis AJ. Interferon alpha-induced hashimoto thyroiditis followed by transient graves disease in a patient with chronic HCV infection. South Med J. 2010; 103(6):585–8.

12. Parmar S, Platanias LC. Interferons: mechanisms of action and clinical applications. Curr Opin Oncol. 2003; 15(6):431–9.

13. Roti E, Minelli R, Giuberti T, Marchelli S, Schianchi C, Gardini E, et al. Multiple changes in thyroid function in patients with chronic active HCV hepatitis treated with recombinant interferon-alpha. Am J Med. 1996; 101(5):482–7.

14. Farrar JD, Murphy KM. Type I interferons and T helper development. Immunol Today. 2000; 21(10):484–9.

15. Watanabe U, Hashimoto E, Hisamitsu T, Obata H, Hayashi N. The risk factor for development of thyroid disease during interferon-alpha therapy for chronic hepatitis C. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994; 89(3):399–403.
16. Preziati D, La Rosa L, Covini G, Marcelli R, Rescalli S, Persani L, et al. Autoimmunity and thyroid function in patients with chronic active hepatitis treated with recombinant interferon alpha-2a. Eur J Endocrinol. 1995; 132(5):587–93.

17. Carella C, Mazziotti G, Morisco F, Manganella G, Rotondi M, Tuccillo C, et al. Long-term outcome of interferon-alpha-induced thyroid autoimmunity and prognostic influence of thyroid autoantibody pattern at the end of treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001; 86(5):1925–9.
18. Wong V, Fu AX, George J, Cheung NW. Thyrotoxicosis induced by alpha-interferon therapy in chronic viral hepatitis. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2002; 56(6):793–8.

19. Lisker-Melman M, Di Bisceglie AM, Usala SJ, Weintraub B, Murray LM, Hoofnagle JH. Development of thyroid disease during therapy of chronic viral hepatitis with interferon alfa. Gastroenterology. 1992; 102(6):2155–60.

20. Carella C, Mazziotti G, Amato G, Braverman LE, Roti E. Clinical review 169: Interferon-alpha-related thyroid disease: pathophysiological, epidemiological, and clinical aspects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004; 89(8):3656–61.
Go to : 
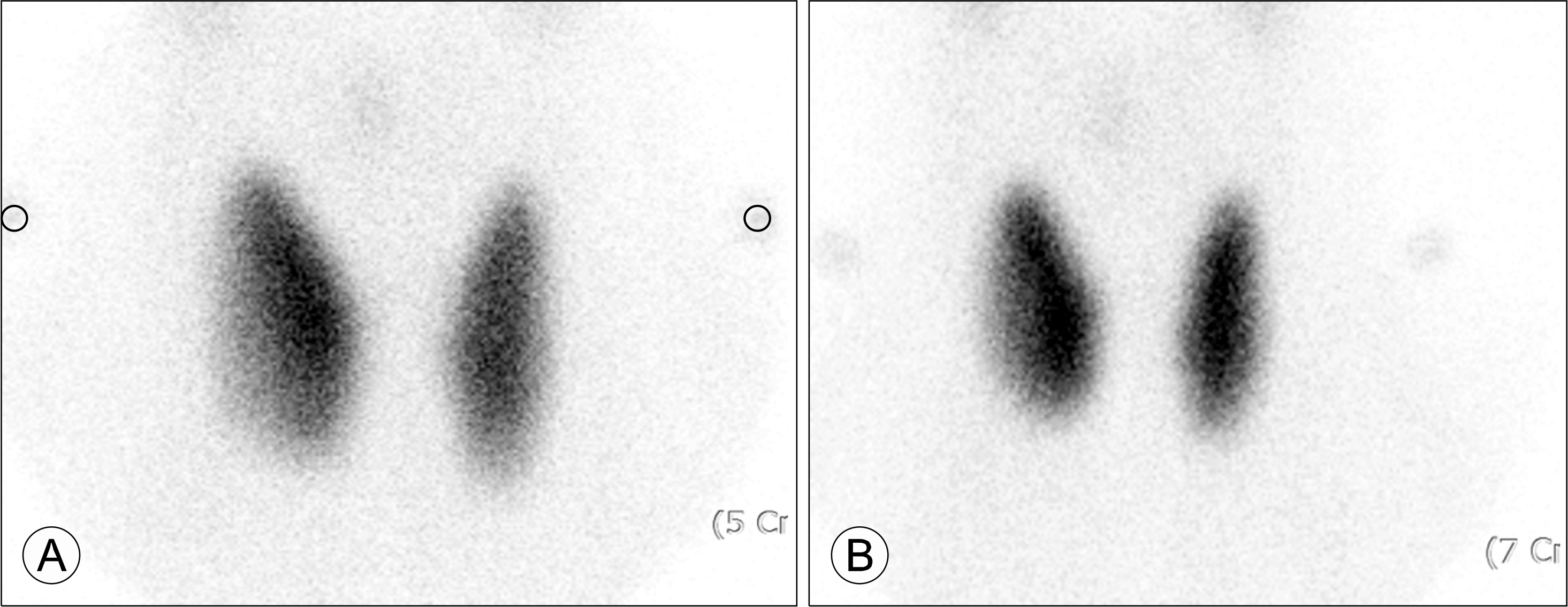 | Fig. 1.Tc-99m scintigraphy in the thyrotoxic period. (A) After taking levothyroxine for hypothyroidism for 7 weeks. (B) Eight weeks after disconti-nuing levothyroxine with con-firmed TSH receptor antibody positivity. |
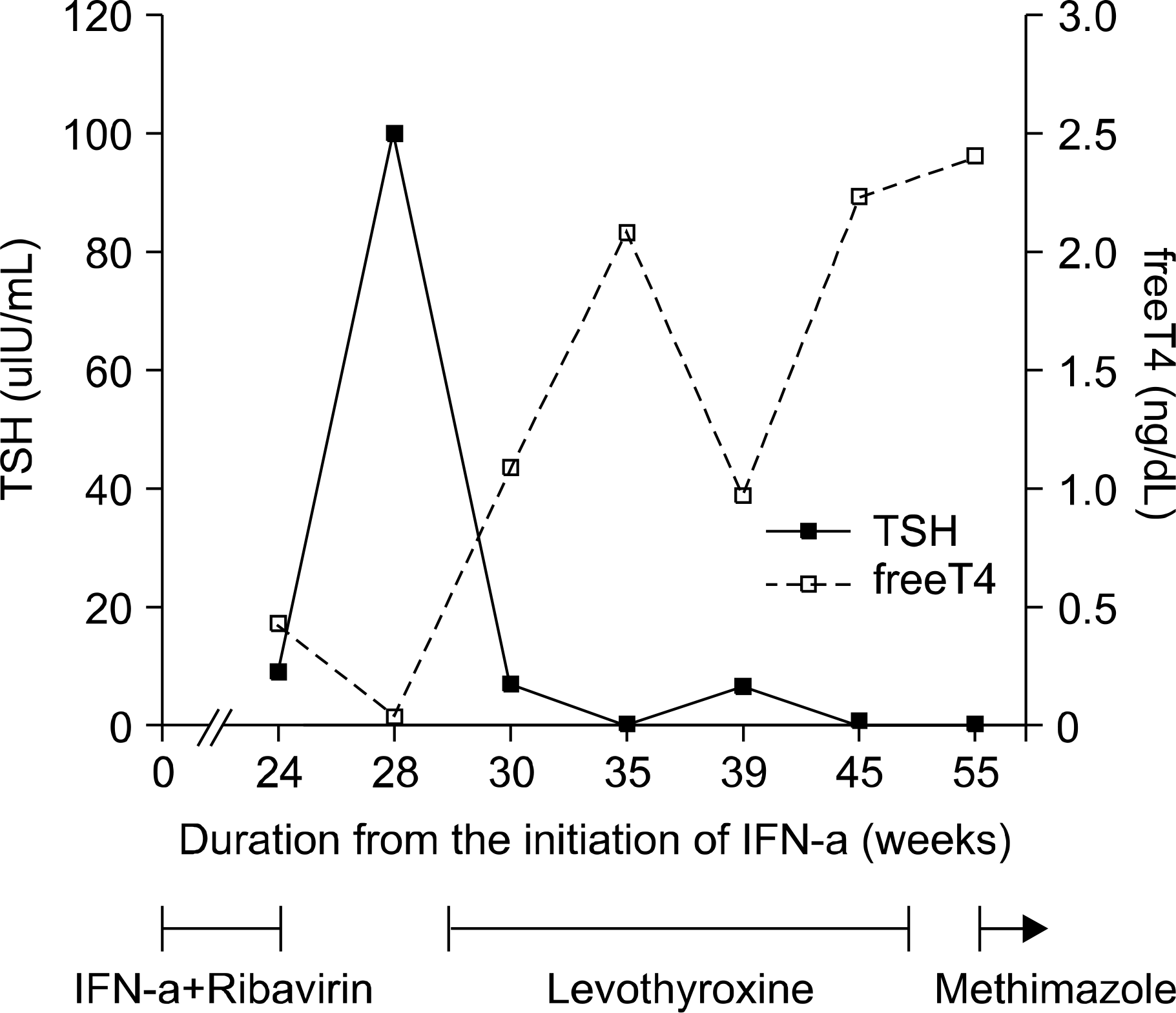 | Fig. 2.The clinical course of thyroid function in the HCV- infected patient on IFN-α therapy: the biphasic pattern of thyroid function after initiation of IFN-α therapy. |
Table 1.
Summaries of multi-phasic thyroiditis in five cases




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download