Abstract
Figures and Tables
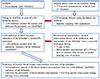 | Figure 1Overall Study Flow Diagram.
*Abbreviations: PK, pharmacokinetics; MAP, Maximum a posteriori; OAPKM, Original Alcohol PK model; BAPPKP, Alcohol Population PK Parameter from bootstrapping; MAPIPKP, PK Parameter estimated from MAP Bayesian Method.
|
Table 1
Pharmacokinetic parameter estimates of alcohol concentration (%) after drinking alcohol (32 mg) in 24 healthy male volunteers

Abbreviations: IIV, inter-individual variability; CV, coefficient of variation; Ka, absorption rate constant; V, volume of distribution; Vmax, maximum alcohol elimination rate; Km, alcohol concentration at the half of Vmax; CI, confidence interval, †V and Vmax are typical values in subjects weighing 70 kg, since they are expressed in the form of V=V(70)*(WT/70), and Vmax=Vmax(70)*(WT/70), respectively, where V(70) and Vmax(70) are typical values for individuals weighing 70 kg. ††ε represents the standard deviation.
Table 2
Maximum a posteriori (MAP) Bayesian Individual alcohol pharmacokinetic parameters of the defendant

| Parameter | Median | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|
| Ka, 1/hour | 2.50 | 2.08 ~ 5.88 |
| V, L | 143.09 | 112.00 ~ 416.06 |
| Vmax, %/hour | 604.30 | 0.70 ~ 10965700000.00 |
| Km, % | 14.31 | 0.00 ~ 210444250.00 |
Abbreviations: Ka, absorption rate constant; V, volume of distribution; Vmax, maximum alcohol elimination rate; Km, alcohol concentration at the half of Vmax; CI, confidence interval.
*The pharmacokinetic parameters of the defendant were estimated by performing 1,000 Bayesian estimations, based on the bootstrap pharmacokinetic parameters, which were obtained from 1,000 different bootstrap samples from the original pharmacokinetic data, the defendant's statement that he drank four cups of soju, and blood alcohol concentration (%) estimated by the breath alcohol test.
Table 3
Estimated blood alcohol concentrations over time in the defendant





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download