Abstract
Acknowledgements
Notes
References
Figure 1
Study design; treatment A, atorvastatin 40 mg once daily for seven days; treatment B, ezetimibe 10 mg once daily for seven days; treatment C, co-administration of atorvastatin 40 mg and ezetimibe 10 mg once daily for seven days.
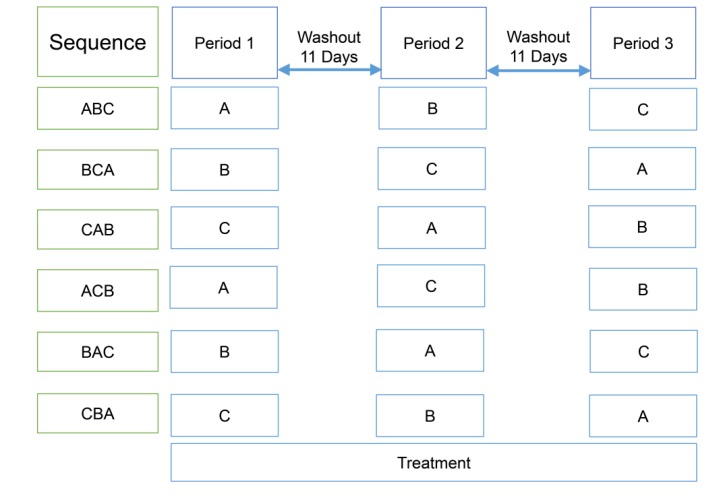
Figure 2
Plasma concentration-time profiles of atorvastatin with or without ezetimibe at steady state plotted using (a) linear and (b) log-linear scales, and of 2-hydroxyatorvastatin (c) linear and (d) log-linear scales.
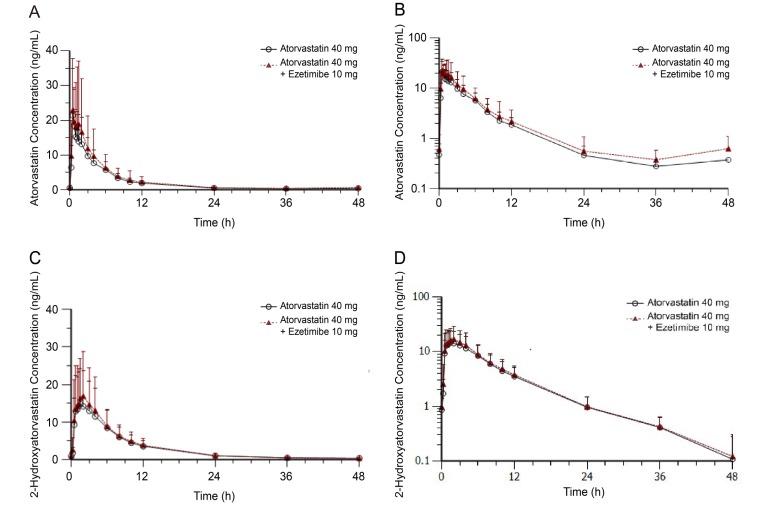
Figure 3
Plasma concentration-time profiles of total ezetimibe with or without atorvastatin at steady state plotted using (a) linear and (b) log-linear scales, and of free ezetimibe (c) linear and (d) log-linear scales.
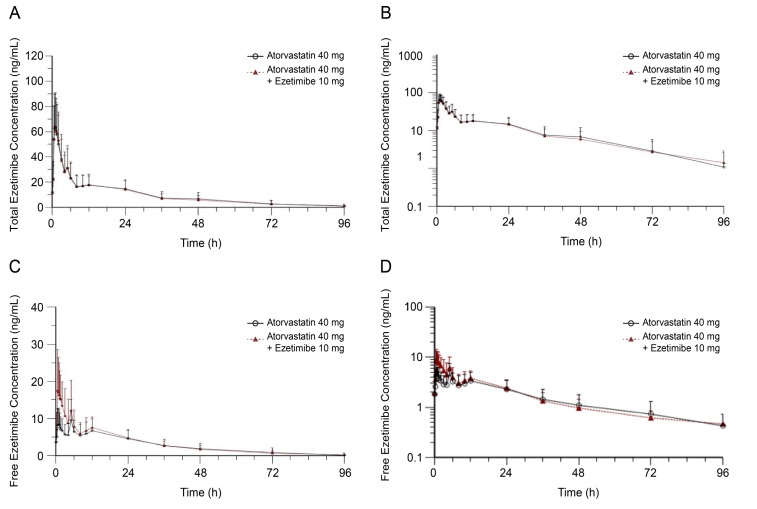
Table 1
Demographic characteristics of each treatment sequence
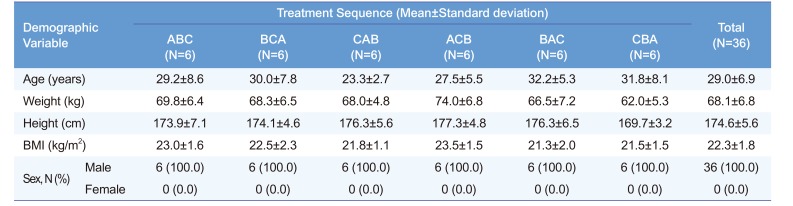
Table 2
Pharmacokinetic parameters of atorvastatin and 2-hydroxyatorvastatin
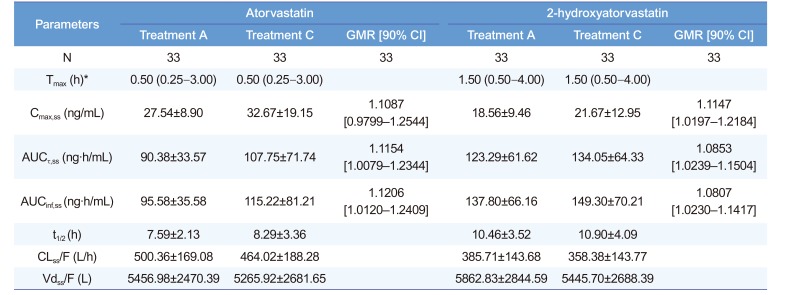
*Median (min–max). GMR, geometric mean ratio; CI, confidence interval. Treatment A, atorvastatin 40 mg once daily for seven days; treatment C, co-administration of atorvastatin 40 mg and ezetimibe 10 mg once daily for seven days. Tmax, time to reach maximum plasma concentration; Cmax,ss, maximum plasma concentration at steady state; AUCτ,ss, area under the plasma concentration-time curve within a dosing interval at steady state; AUCinf,ss, area under the plasma concentration-time curve from dosing time extrapolated to infinity at steady state; t1/2, elimination half-life; CLss/F, apparent clearance; Vdss/F, apparent volume of distribution.
Table 3
Pharmacokinetic parameters of total ezetimibe and free ezetimibe
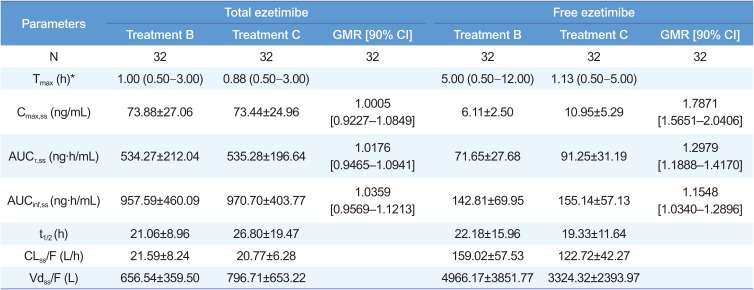
*Median (min–max). GMR, geometric mean ratio; CI, confidence interval. Treatment B, ezetimibe 10 mg once daily for seven days; treatment C, co-administration of atorvastatin 40 mg and ezetimibe 10 mg once daily for seven days; Tmax, time to reach maximum plasma concentration; Cmax,ss, maximum plasma concentration at steady state; AUCτ,ss, area under the plasma concentration-time curve within a dosing interval at steady state; AUCinf,ss, area under the plasma concentration-time curve from dosing time extrapolated to infinity at steady state; t1/2, elimination half-life; CLss/F, apparent clearance; Vdss/F, apparent volume of distribution.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download