Abstract
This study was to clarify population pharmacokinetics (PK) of sildenafil and its metabolite, N-desmethyl sildenafil (NDS) in Korean healthy male population using a pooled data from multiple clinical trials in consideration of inter-institution and inter-laboratory difference. A population PK analysis was performed with data of 243 healthy volunteers from five single-center (4 centers) comparative PK trials. The dataset included 7,376 sildenafil and NDS concentration (3,688 for each analyte) observed during 24 hours after the single dose of original sildenafil (either 50 mg or 100 mg of Viagra®). The plasma concentration was assayed in two laboratories. Various model structure was tested and the final model was evaluated using visual predictive checks. Demographic and clinical variables were assessed as potential covariates for PK parameters. A one-compartment first-order elimination model with proportional error was selected for the dispositional characteristics of sildenafil, and two-compartment model was chosen for NDS. Three transit compartments with Erlang-type absorption for fast absorption pathway and one compartment for slow absorption pathway constructed overall absorption model. The first-pass effect was rejected since it does not improve the model. The difference of NDS level by the bioanalysis laboratory was selected as the only covariate. Even though a direct comparison was difficult, the general trend in PK of sildenafil and NDS for Korean healthy male was considered similar to that of the other populations reported previously. It is recommended that the laboratory effect should be explored and evaluated when dataset is built using results from several laboratories.
Go to : 
References
1. Braun M, Wassmer G, Klotz T, Reifenrath B, Mathers M, Engelmann U. Epidemiology of erectile dysfunction: results of the “Cologne Male Survey”. Int J Impot Res. 2000; 12:305–311. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijir.3900622.

2. Laumann EO, Paik A, Rosen RC. Sexual dysfunction in the United States: prevalence and predictors. JAMA. 1999; 281:537–545. doi: 10.1001/jama. 281.6.537.
3. Lewis RW, Fugl-Meyer KS, Bosch R, Fugl-Meyer AR, Laumann EO, Lizza E, et al. Epidemiology/risk factors of sexual dysfunction. J Sex Med. 2004; 1:35–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2004.10106.x.

4. Burnett AL. Erectile dysfunction. J Urol. 2006; 175::. 25S–31S. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347 (05)00309-5.

5. Goldstein I, Lue TF, Padma-Nathan H, Rosen RC, Steers WD, Wicker PA. Oral sildenafil in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Sildenafil Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1998; 338:1397–1404. doi: 10.1056/NEJM1998051 43382001.
6. Dean RC, Lue TF. Physiology of penile erection and pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction. Urol Clin North Am. 2005; 32:379–395. doi: 10.1016/j. ucl.2005.08.007.

7. Melman A, Gingell JC. The epidemiology and pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction. J Urol. 1999; 161:5–11. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347 (01)62045-7.

8. Salonia A, Rigatti P, Montorsi F. Sildenafil in erectile dysfunction: a critical review. Curr Med Res Opin. 2003; 19:241–262. doi: 10.1185/030079903125 001839.

9. Montague DK, Barada JH, Belker AM, Levine LA, Nadig PW, Roehrborn CG, et al. Clinical guidelines panel on erectile dysfunction: summary report on the treatment of organic erectile dysfunction. J Urol. 1996; 156:2007–2011.

10. Ignarro LJ, Napoli C, Loscalzo J. Nitric oxide donors and cardiovascular agents modulating the bioactivity of nitric oxide: an overview. Circ Res. 2002; 90:21–28. doi: 10.1161/hh0102.102330.
11. Muirhead GJ, Rance DJ, Walker DK, Wastall P. Comparative human pharmacokinetics and metabolism of single-dose oral and intravenous sildenafil. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2002; 53::. 13S–20S. doi: 10.1046/j.0306-5251.2001. 00028.x.

12. Nichols DJ, Muirhead GJ, Harness JA. Pharmacokinetics of sildenafil after single oral doses in healthy male subjects: absolute bioavailability, food effects and dose proportionality. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2002; 53::. 5S–12S. doi: 10.1046/j.0306-5251.2001.00027.x.

13. Benmebarek M, Devaud C, Gex-Fabry M, Powell Golay K, Brogli C, Baumann P, et al. Effects of grapefruit juice on the pharmacokinetics of the enantiomers of methadone. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2004; 76:55–63. doi: 10. 1016/j.clpt.2004.03.007.
14. Wilner K, Laboy L, LeBel M. The effects of cimetidine and antacid on the pharmacokinetic profile of sildenafil citrate in healthy male volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2002; 53::. 31S–36S. doi: 10.1046/j.0306-5251.2001.000 30.x.

15. Al-Ghazawi MA, Tutunji MS, Aburuz SM. The effects of pummelo juice on pharmacokinetics of sildenafil in healthy adult male Jordanian volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2010; 66:159–163. doi: 10.1007/s00228-009-0738-0.

16. Pfizer. VIAGRA (sildenafil citrate) label. 2015.http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2015/020895s045lbl.pdf/AccessedMay24. 2016.
17. Walker DK, Ackland MJ, James GC, Muirhead GJ, Rance DJ, Wastall P, et al. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of sildenafil in mouse, rat, rabbit, dog and man. Xenobiotica. 1999; 29:297–310.

18. Liew KB, Tan YT, Peh KK. Effect of polymer, plasticizer and filler on orally disintegrating film. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2014; 40:110–119. doi: 10.3109/03639045.2012.749889.

19. Al-Ghazawi M, Tutunji M, AbuRuz S. Simultaneous determination of sildenafil and N-desmethyl sildenafil in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography method using electrochemical detection with application to a pharmacokinetic study. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2007; 43:613–618. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2006.07.028.

20. Beal SL. Ways to fit a PK model with some data below the quantification Limit. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2001; 28:481–504.
21. Hyland R, Roe EG, Jones BC, Smith DA. Identification of the cytochrome P450 enzymes involved in the N-demethylation of sildenafil. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2001; 51:239–248. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.2001.00318.x.
Go to : 
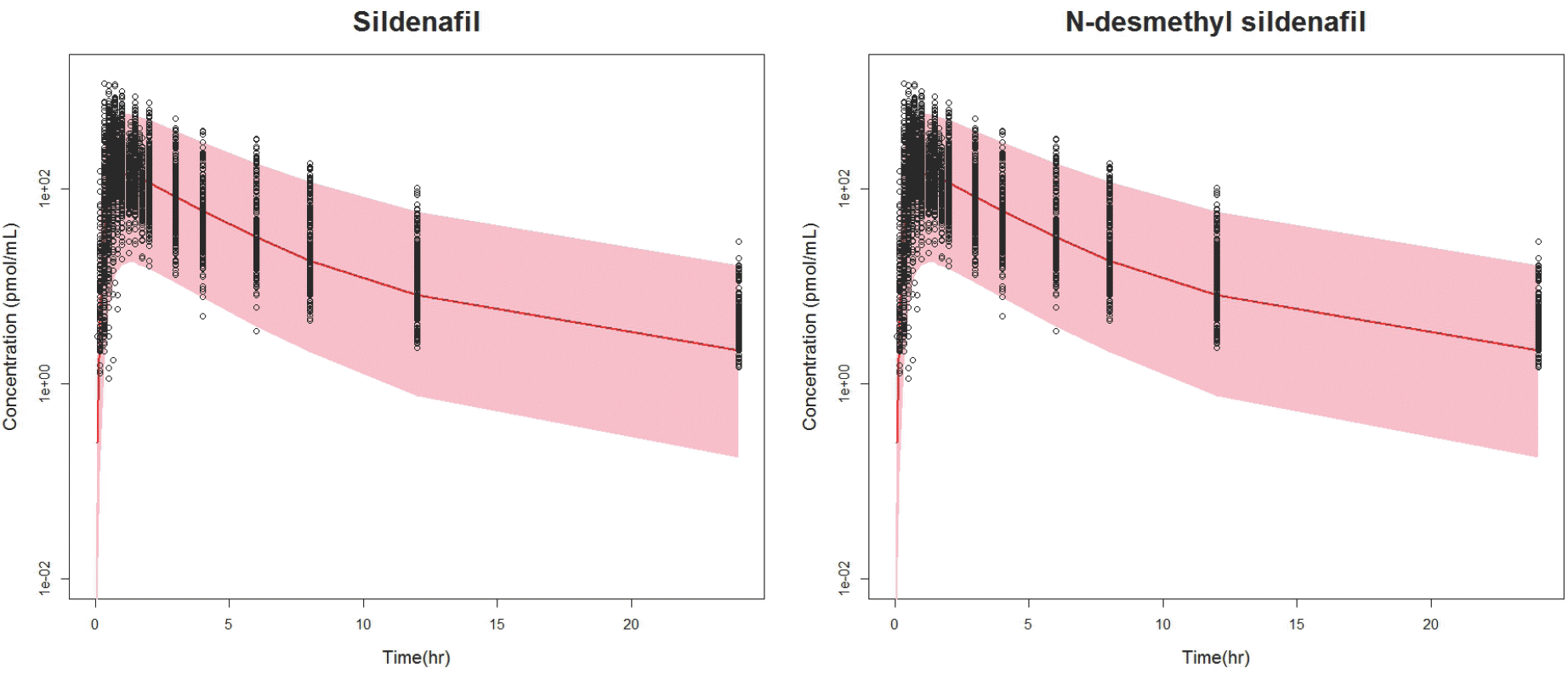 | Figure 2.Visual predictive check. Solid line: prediction median, Colored band: 90% prediction interval. |
Table 1.
The five clinical trial protocols and their properties
Table 2.
Final sildenafil and NDS parameter estimates
| Parameters | Description | Estimates | % RSEa |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed effects | |||
| Ka,1 (h−1) | Rate constant of rapid absorption | 9.38 | 1.663 |
| Ka,2 (h−1) | Rate constant of slow absorption | 0.119 | 1.118 |
| CL/F (L/h) | Apparent clearance of sildenafil | 37.1 | 2.106 |
| V5/F (L) | Apparent volume of sildenafil central compartment | 174 | 1.644 |
| V6/F (L) | Apparent volume of NDS central compartment | 14.2 | 5.282 |
| K60 (h−1) | Elimination rate constant of NDS | 11.3 | 3.531 |
| V7/F (L) | Apparent volume of NDS peripheral compartment | 444 | 7.658 |
| QM/F (L/h) | Inter-compartmental clearance of NDS | 40.9 | 5.515 |
| LVF | Inter-laboratory variability factor on NDS concentration | –0.347 | –2.634 |
| Random effects | |||
| ωKa,1 | Between-subject variability of Ka,1 | 0.301 | 9.701 |
| ωKa,2 | Between-subject variability of Ka,2 | NE | – |
| ωCL/F | Between-subject variability of CL/F | 0.137 | 12.993 |
| ωV5/F | Between-subject variability of V5/F | 0.137 | 13.645 |
| ωV6/F | Between-subject variability of V6/F | 0.194 | 7.01 |
| ωk60 | Between-subject variability of K60 | NE | – |
| ωV7/F | Between-subject variability of V7/F | 0.0369 | 98.92 |
| ωQM/F | Between-subject variability of QM/F | 0.184 | 21.63 |
| Residual errorb | |||
| σadditive,1 | Additive error for sildenafil | NE | – |
| σprop,1 | Proportional error for sildenafil | 0.441 | – |
| σadditive,2 | Additive error for NDS | NE | – |
| σprop,2 | Proportional error for NDS | 0.515 | 1.464 |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download