Abstract
Donepezil is a centrally acting, reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor that is widely used for treating Alzheimer's disease. This study aimed to compare the pharmacokinetics of Bastia®, a test tablet formulation of donepezil hydrochloride 10 mg, with those of Aricept®, the reference tablet formulation of donepezil hydrochloride 10 mg, in healthy Korean male volunteers. A randomized, single-dose, two-way crossover study was conducted in 32 subjects. Subjects received a single dose of either test or reference compound and the alternate drug after a 4-week washout period. Serial blood samples for pharmacokinetic analysis were collected prior to dosing and periodically for 288 h after dosing for measurement of the plasma concentrations of donepezil. A non-compartmental method was used to estimate the pharmacokinetic parameters. The maximum concentration (Cmax) and the area under the concentration-time curve from time zero to the time of the last quantifiable concentration (AUC288h) for the two formulations were compared to evaluate bioequivalence. The Cmax of the test and reference drugs were 27.58±7.46 and 26.35±6.51 μg/L (mean±SD), respectively, while AUC288h was 1080.14±229.77 and 1043.07±242.28 μg·h/L (mean±SD), respectively. The geometric mean ratios (90% confidence interval) of the Cmax and AUC288h of the two tablets were 1.043 (0.990–1.099) and 1.039 (1.013–1.065). In conclusion, the newly formulated tablet of donepezil hydrochloride 10 mg is bioequivalent to the currently marketed 10 mg tablet.
Go to : 
References
1. Rogers SL, Doody RS, Mohs RC, Friedhoff LT. Donepezil improves cognition and global function in alzheimer disease: a 15-week, double-blind, placebocontrolled study. Arch Intern Med. 1998; 158:1021–1031.
2. Shintani EY, Uchida KM. Donepezil: an anticholinesterase inhibitor for Alzheimer's disease. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 1997; 54:2805–2810.

3. Rogers SL, Friedhoff LT. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile of donepezil HCl following single oral doses. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1998; 46:S1–S6.

4. Tiseo PJ, Foley K, Friedhoff LT. An evaluation of the pharmacokinetics of donepezil HCl in patients with moderately to severely impaired renal function. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1998; 46:S56–S60.

5. Rojanasthien N, Aunmuang S, Hanprasertpong N, Roongapinun S, Teeka-chunhatean S. Bioequivalence study of donepezil hydrochloride tablets in healthy male volunteers. ISRN Pharmacol. 2012; 2012:527679. doi: 10.5402/2012/527679.

6. Rogers SL, Farlow MR, Doody RS, Mohs R, Friedhoff LT. A 24-week, double-blind, placebocontrolled trial of donepezil in patients with Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1998; 50:136–145.

7. Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. http://www.mfds.go.kr/index.do?mid=1042&cmd=v&seq=2775. Accessed 4 June. 2015.
Go to : 
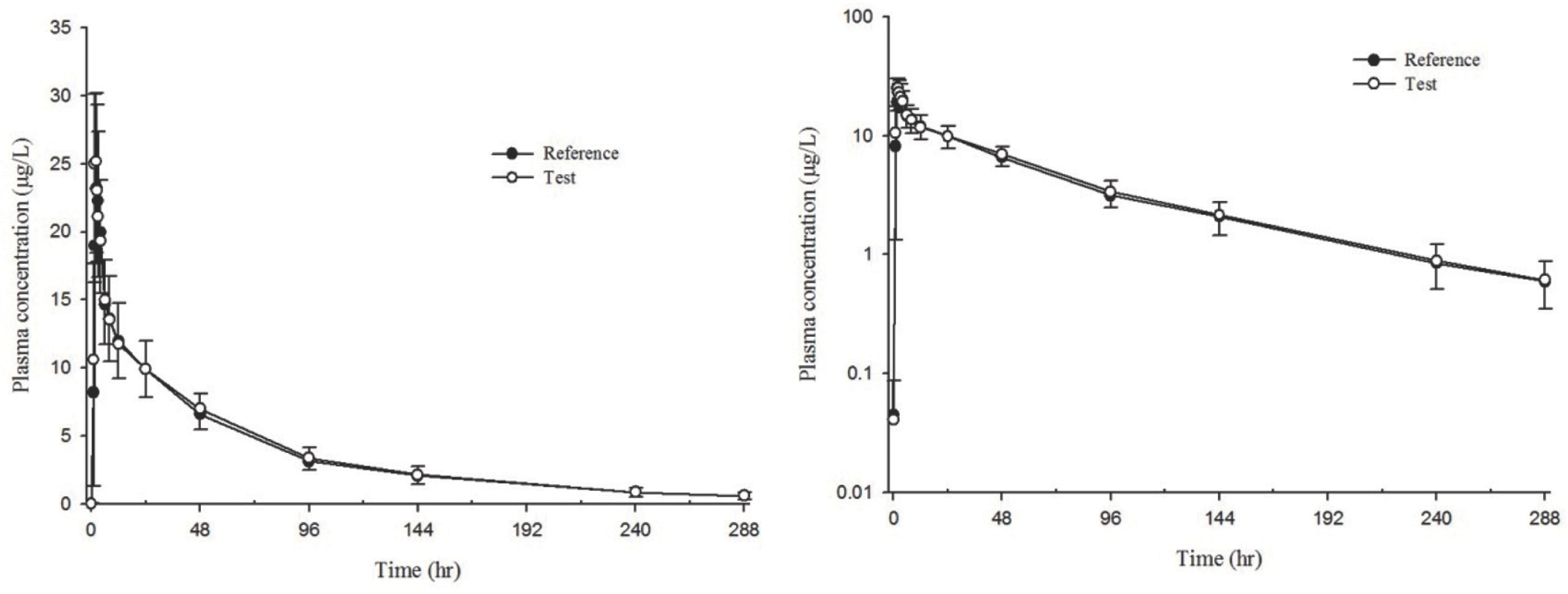 | Figure 1.Mean plasma concentration-time profiles of donepezil after single oral administration of reference formulation (filled circles) and test formulation (open circles). Bars represent standard deviations. (Left, linear; right, log-linear) |
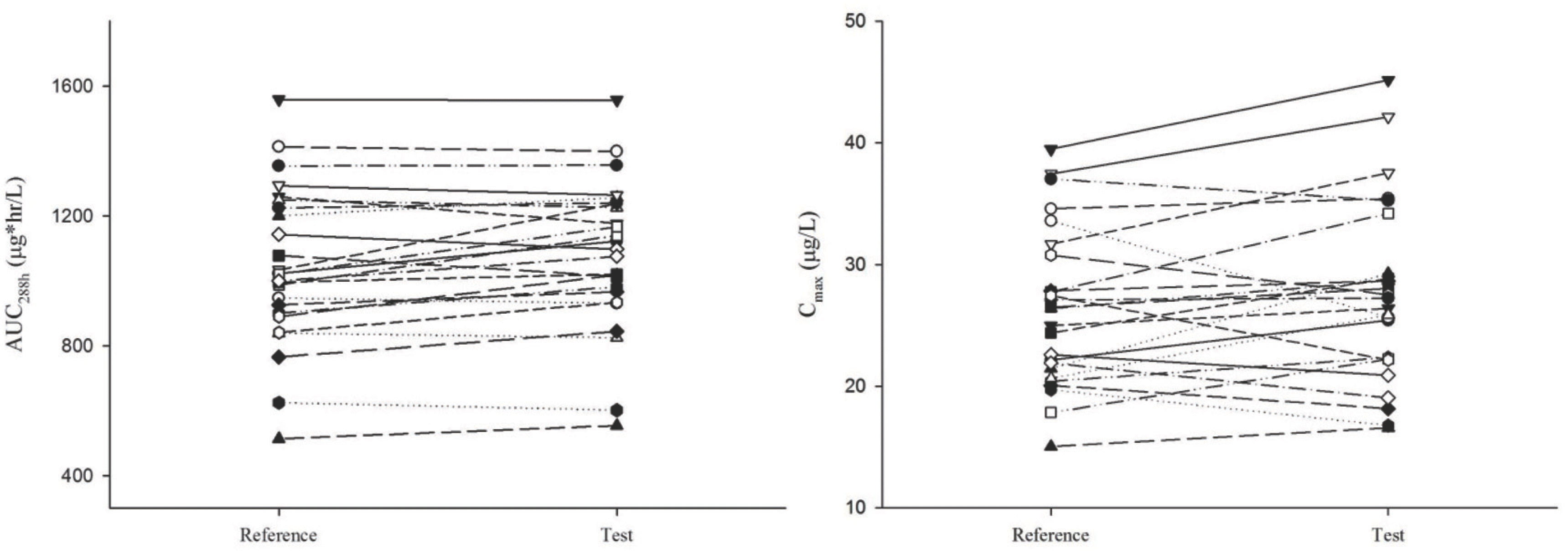 | Figure 2.Individual subject's Cmax and AUC288h values for donepezil reference formulation and test formulation (Left: AUC288h, Right: Cmax) |
Table 1.
Pharmacokinetic parameters of donepezil administered as the reference drug and test formulation
| Parameters | Reference (N=25) | Test (N=25) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean±SD | CV(%) | Mean±SD | CV(%) | Geometric mean ratio (90% CI)b | |
| tmax (h)a | 2.0 (1.0–4.0) | 2.0 (1.5–3.0) | |||
| Cmax (μg/L) | 26.35±6.51 | 24.71 | 27.58±7.46 | 27.04 | 1.043 (0.990–1.099) |
| AUC144h (μg·h/L) | 867.37±188.69 | 21.75 | 897.97±180.10 | 20.06 | 1.035 (1.010–1.062) |
| AUC240h (μg·h/L) | 1008.30±230.20 | 22.83 | 1044.24±218.32 | 20.91 | 1.039 (1.013–1.064) |
| AUC288h (μg·h/L) | 1043.07±242.28 | 23.23 | 1080.14±229.77 | 21.27 | 1.039 (1.013–1.065) |
| AUCinf (μg·h/L) | 1108.44±268.52 | 24.23 | 1143.71±254.17 | 22.22 | 1.035 (1.009–1.061) |
| AUCextra144ha (%) | 20.37 (13.97–29.33) | 21.98 (13.46–30.86) | |||
| AUCextra240h a (%) | 8.38 (4.80–15.25) | 8.59 (4.51–13.53) | |||
| AUCextra288ha (%) | 5.26 (2.73–10.88) | 5.30 (2.55–8.59) | |||
| Half-life (h) | 72.81±11.78 | 16.18 | 70.4±10.08 | 14.31 | |
| CL/F (L/h) | 9.65±2.87 | 29.77 | 9.27±2.63 | 28.42 | |
All values, except for AUCextra144h, AUCextra240h and AUCextra288h, are presented as the arithmetic mean±standard deviation and coefficient of variation (%). tmax, time to peak concentration; Cmax, peak plasma concentration; AUCt, area under the plasma concentration-time curve from 0 to t h; AUCextrat(%), % extrapolated AUCt which was calculated as [(AUCinf-AUCt) / AUCinf]; CL/F, apparent clearance.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download