Abstract
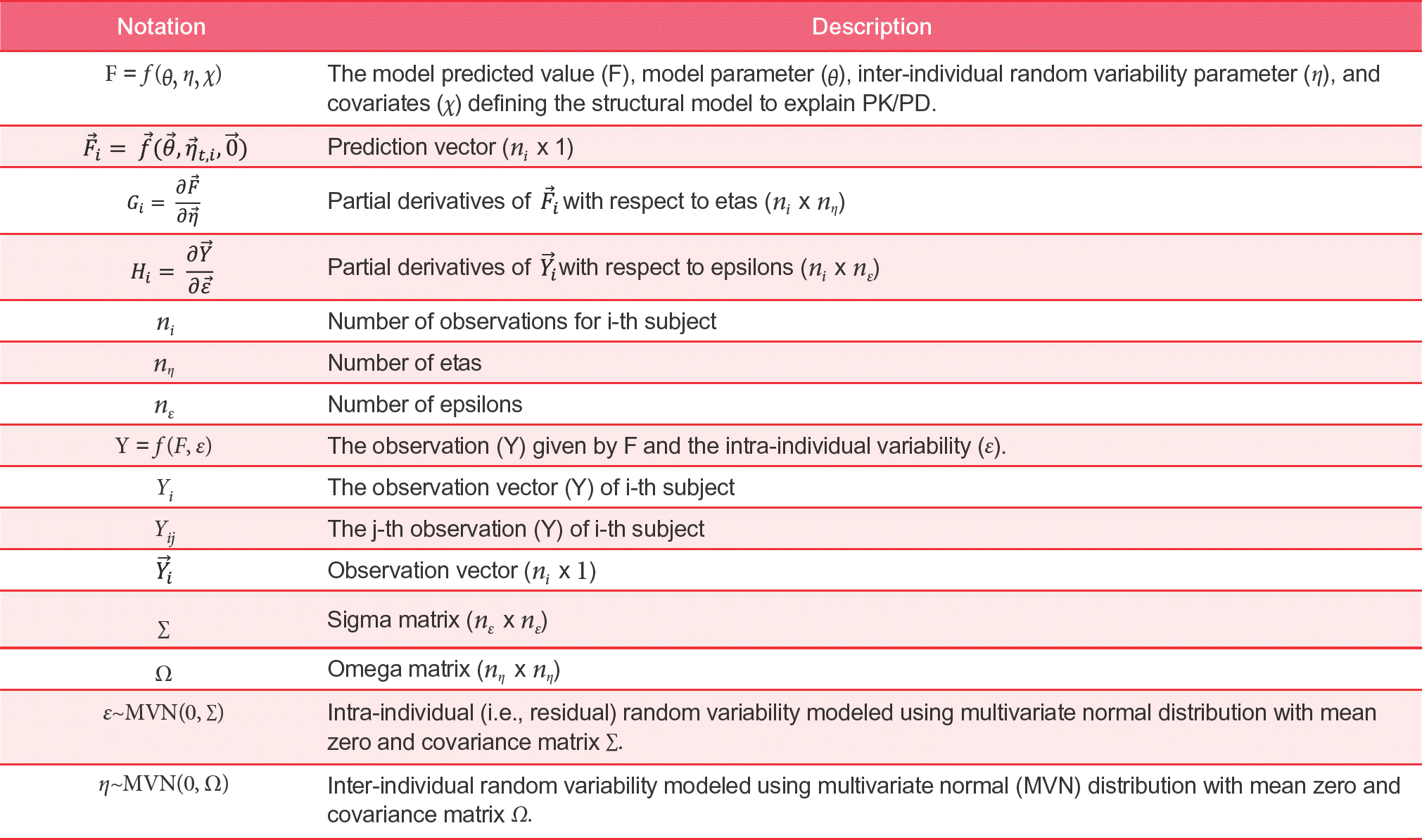
NONMEM® is the most-widely used nonlinear mixed effects modelling tool introduced into population PK/PD analysis. Even though thousands of pharmaceutical scientists utilize NONMEM® routinely for their data analysis, the various estimation methods implemented in NONMEM® remain a mystery for most users due to the complex statistical and mathematical derivations underlying the algorithm used in NONMEM®. In this tutorial, we demonstrated how to directly obtain the objective function value and post hoc η for the first order approximation method by the use of R. We hope that this tutorial helps pharmacometricians understand the underlying estimation process of nonlinear mixed effects modelling.
Go to : 
References
1. Sheiner LB, Beal SL. Evaluation of methods for estimating population pharmacokinetics parameters. I. Michaelis-Menten model: routine clinical pharmacokinetic data. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1980; 8:553–571.
2. Sheiner LB, Beal SL. Evaluation of methods for estimating population pharmacokinetic parameters. II. Biexponential model and experimental pharmacokinetic data. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1981; 9:635–651.

3. Sheiner LB, Beal SL. Evaluation of methods for estimating population pharmacokinetic parameters. III. Monoexponential model: routine clinical pharmacokinetic data. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1983; 11:303–319.

4. Beal S, Sheiner L, Boeckmann A, Bauer R. NONMEM user's guides. Elli-cott city, MD, USA,. 1989–2009.
5. Wang Y. Derivation of various NONMEM estimation methods. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2007; 34:575–593.

6. Kang D, Bae KS, Houk BE, Savic RM, Karlsson MO. Standard Error of Empirical Bayes Estimate in NONMEM® VI. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012; 16:97–106. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2012.16.2.97.

8. Plan EL, Maloney A, Mentre F, Karlsson MO, Bertrand J. Performance comparison of various maximum likelihood nonlinear mixed-effects estimation methods for dose-response models. AAPS J. 2012; 14:420–432. doi: 10.1208/s12248-012-9349-2.

9. Fisher D, Shafer S. Fisher/Shafer NONMEM Workshop Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Analysis with NONMEM. Het Pand, Ghent, Belgium. 2007.
10. Peck CC, Beal SL, Sheiner LB, Nichols AI. Extended least squares nonlinear regression: a possible solution to the "choice of weights" problem in analysis of individual pharmacokinetic data. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1984; 12:545–558.

Go to : 




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download