INTRODUCTION
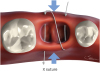 | Figure 1X suture or conventional X suture. The needle passes through over the extraction socket twice as if performing a continuous suture. A large crossed X is created over the socket after suturing. The blue arrows indicate the pulling vectors created by the X suture.
X suture, crossed mattress suture.
|
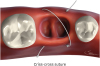 | Figure 2Criss-cross suture or crossed horizontal external suture. The needle engages the buccal and lingual flaps in the same direction (mesial to distal or distal to mesial), then a knot is created. A large crossed X is created over the socket, as in the X suture.
X suture, crossed mattress suture.
|
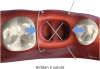 | Figure 3Hidden X suture. The needle enters the buccal flap and passes to the opposite side in a diagonal direction, then it passes again from the buccal to the lingual side, also in a diagonal direction. A crossed X is created under the flap, unlike the X suture or criss-cross suture. The blue arrows indicate the vectors created by the hidden X suture.
X suture, crossed mattress suture.
|
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study population and design
Inclusion criteria
Patients' age between 18 years old and 65 years old
Presence of a single periodontally compromised molar in the mandible or the maxilla requiring extraction and expected to be suitable for replacement by a dental implant
Residual extraction sockets with less than 50% bone loss in all dimensions
Ability to fully understand the nature of the proposed operation and ability to sign an Ethics Committee-approved informed consent form
Exclusion criteria
Uncontrolled or untreated periodontal disease
History of systemic diseases that would contraindicate surgical treatment
Allergy to collagen and bone substitute
Requirement of antibiotic prophylaxis
Heavy smoking (>10 cigarettes per day)
Pregnancy or lactation
Inability to consent to participation in the study and/or to accept the proposed treatment plan
Experimental groups
Table 1
Demographic information of the enrolled patients

Group 1 (open healing and hidden X suture; test)
Suture techniques
Hidden X suture procedure
X suture procedure
Outcomes
Surgical procedure
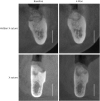
 | Figure 4The clinical process from baseline to 4 months after ARP.
ARP, alveolar ridge preservation; X suture, crossed mattress suture; DBBM-C, demineralized bovine bone matrix mixed with 10% collagen; DL-CM, double-layered collagen membrane; S-O, stitch-out.
|
Re-entry procedure
CBCT analysis
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Table 2
Change in KT width from the extraction to 4 months

| Parameters | Hidden X suture (mm; n=7) | X suture (mm; n=7) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline to post-suture | 0.25±0.66 (0.0) | −1.56±0.90 (−1.5) | 0.003a) |
| Baseline to 4 mon | −1.05±1.07 (−1.0) | −2.83±1.26 (−2.5) | 0.007a) |
Table 3
Horizontal changes of the alveolar ridge

Table 4
Vertical changes in the alveolar ridge





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download