1. Anselme K, Bigerelle M, Noel B, Dufresne E, Judas D, Iost A, et al. Qualitative and quantitative study of human osteoblast adhesion on materials with various surface roughnesses. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000; 49:155–166.

2. Lausmaa J. Surface spectroscopic characterization of titanium implant materials. J Electron Spectros Relat Phenomena. 1996; 81:343–361.

3. Albrektsson T. Direct bone anchorage of dental implants. J Prosthet Dent. 1983; 50:255–261.

4. Lim YJ, Oshida Y, Andres CJ, Barco MT. Surface characterizations of variously treated titanium materials. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2001; 16:333–342.
5. Taborelli M, Jobin M, François P, Vaudaux P, Tonetti M, Szmukler-Moncler S, et al. Influence of surface treatments developed for oral implants on the physical and biological properties of titanium. (I) Surface characterization. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1997; 8:208–216.

6. Wennerberg A, Albrektsson T. Effects of titanium surface topography on bone integration: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009; 20:Suppl 4. 172–184.

7. Cooper LF. A role for surface topography in creating and maintaining bone at titanium endosseous implants. J Prosthet Dent. 2000; 84:522–534.

8. Pilliar RM. Overview of surface variability of metallic endosseous dental implants: textured and porous surface-structured designs. Implant Dent. 1998; 7:305–314.
9. Kilpadi DV, Lemons JE. Surface energy characterization of unalloyed titanium implants. J Biomed Mater Res. 1994; 28:1419–1425.

10. Wang R, Hashimoto K, Fujishima A, Chikuni M, Kojima E, Kitamura A, et al. Light-induced amphiphilic surfaces. Nature. 1997; 388:431–432.

11. Wennerberg A, Albrektsson T. Suggested guidelines for the topographic evaluation of implant surfaces. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2000; 15:331–344.
12. Bico J, Thiele U, Quéré D. Wetting of textured surfaces. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp. 2002; 206:41–46.

13. Rupp F, Scheideler L, Eichler M, Geis-Gerstorfer J. Wetting behavior of dental implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2011; 26:1256–1266.
14. Rupp F, Scheideler L, Olshanska N, de Wild M, Wieland M, Geis-Gerstorfer J. Enhancing surface free energy and hydrophilicity through chemical modification of microstructured titanium implant surfaces. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2006; 76:323–334.

15. Rupp F, Scheideler L, Rehbein D, Axmann D, Geis-Gerstorfer J. Roughness induced dynamic changes of wettability of acid etched titanium implant modifications. Biomaterials. 2004; 25:1429–1438.

16. Textor M, Sittig C, Frauchiger V, Tosatti S, Brunette DM. Properties and biological significance of natural oxide films on titanium and its alloys. In : Brunette DM, Tengvall P, Textor M, Thomsen P, editors. Titanium in medicine: material science, surface science, engineering, biological responses, and medical applications. Berlin: Springer;2001. p. 171–230.
17. Buser D, Broggini N, Wieland M, Schenk RK, Denzer AJ, Cochran DL, et al. Enhanced bone apposition to a chemically modified SLA titanium surface. J Dent Res. 2004; 83:529–533.

18. Junker R, Dimakis A, Thoneick M, Jansen JA. Effects of implant surface coatings and composition on bone integration: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009; 20:Suppl 4. 185–206.

19. Schwarz F, Ferrari D, Herten M, Mihatovic I, Wieland M, Sager M, et al. Effects of surface hydrophilicity and microtopography on early stages of soft and hard tissue integration at non-submerged titanium implants: an immunohistochemical study in dogs. J Periodontol. 2007; 78:2171–2184.

20. Choi JY, Lee HJ, Jang JU, Yeo IS. Comparison between bioactive fluoride modified and bioinert anodically oxidized implant surfaces in early bone response using rabbit tibia model. Implant Dent. 2012; 21:124–128.

21. Wennerberg A, Albrektsson T. On implant surfaces: a review of current knowledge and opinions. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2010; 25:63–74.
22. Iwai-Yoshida M, Shibata Y, Wurihan , Suzuki D, Fujisawa N, Tanimoto Y, et al. Antioxidant and osteogenic properties of anodically oxidized titanium. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2012; 13:230–236.

23. Le Guehennec L, Lopez-Heredia MA, Enkel B, Weiss P, Amouriq Y, Layrolle P. Osteoblastic cell behaviour on different titanium implant surfaces. Acta Biomater. 2008; 4:535–543.

24. Schuler RF, Janakievski J, Hacker BM, O'Neal RB, Roberts FA. Effect of implant surface and grafting on implants placed into simulated extraction sockets: a histologic study in dogs. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2010; 25:893–900.
25. Ferguson SJ, Broggini N, Wieland M, de Wild M, Rupp F, Geis-Gerstorfer J, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of the interfacial strength of a chemically modified sandblasted and acid-etched titanium surface. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2006; 78:291–297.

26. Wall I, Donos N, Carlqvist K, Jones F, Brett P. Modified titanium surfaces promote accelerated osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stromal cells in vitro. Bone. 2009; 45:17–26.

27. Hong J, Kurt S, Thor A. A hydrophilic dental implant surface exhibits thrombogenic properties in vitro. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2013; 15:105–112.

28. Yeo IS, Han JS, Yang JH. Biomechanical and histomorphometric study of dental implants with different surface characteristics. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2008; 87:303–311.

29. Donath K, Breuner G. A method for the study of undecalcified bones and teeth with attached soft tissues. The Säge-Schliff (sawing and grinding) technique. J Oral Pathol. 1982; 11:318–326.

30. Roberts WE, Smith RK, Zilberman Y, Mozsary PG, Smith RS. Osseous adaptation to continuous loading of rigid endosseous implants. Am J Orthod. 1984; 86:95–111.

31. Steigenga J, Al-Shammari K, Misch C, Nociti FH Jr, Wang HL. Effects of implant thread geometry on percentage of osseointegration and resistance to reverse torque in the tibia of rabbits. J Periodontol. 2004; 75:1233–1241.

32. Albrektsson T, Wennerberg A. Oral implant surfaces: Part 2--review focusing on clinical knowledge of different surfaces. Int J Prosthodont. 2004; 17:544–564.
33. Schwarz F, Herten M, Sager M, Wieland M, Dard M, Becker J. Bone regeneration in dehiscence-type defects at chemically modified (SLActive) and conventional SLA titanium implants: a pilot study in dogs. J Clin Periodontol. 2007; 34:78–86.

34. Gottlow J, Barkarmo S, Sennerby L. An experimental comparison of two different clinically used implant designs and surfaces. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2012; 14:Suppl 1. e204–e212.

35. Abrahamsson I, Berglundh T, Linder E, Lang NP, Lindhe J. Early bone formation adjacent to rough and turned endosseous implant surfaces. An experimental study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2004; 15:381–392.

36. Berglundh T, Abrahamsson I, Lang NP, Lindhe J. De novo alveolar bone formation adjacent to endosseous implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2003; 14:251–262.

37. Schwarz F, Herten M, Sager M, Wieland M, Dard M, Becker J. Histological and immunohistochemical analysis of initial and early osseous integration at chemically modified and conventional SLA titanium implants: preliminary results of a pilot study in dogs. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2007; 18:481–488.

38. Schmid J, Wallkamm B, Hämmerle CH, Gogolewski S, Lang NP. The significance of angiogenesis in guided bone regeneration. A case report of a rabbit experiment. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1997; 8:244–248.

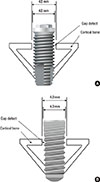
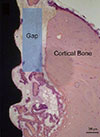






 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download