INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals
Study design
Experimental materials
Experimental mini-implants
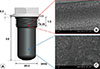 | Figure 1Custom-made mini-implants and micrographs of their surfaces with and without a recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein (rhBMP)-2 coating.Custom-made mini-implants and micrographs of their surfaces with and without a recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein (rhBMP)-2 coating. (A) Schematic of the mini-implant (length, 6.0 mm; diameter, 3.0 mm), which had a sandblasted, large grain, acid-etched surface and included a 1.5-mm threaded portion in the coronal area for fixation and a 4.5-mm cylindrical portion that was coated with rhBMP-2. (B) Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) scan of the uncoated surface in the threaded area. (C) SEM scan of the rhBMP-2-coated surface in the cylindrical area.
|
rhBMP-2 coating on mini-implants
Surgical procedure
Radiographic analysis: micro-computed tomography
Histologic and histomorphometric analyses
 | Figure 2Parameters for the linear and areal measurements.The rectangle with the blue border indicates the area of interest (AOI). The subarea bordered by a dotted line indicates the total augmented area (TA). The orange dotted line dividing the AOI indicates the Schneiderian membrane. NBA, new bone area; PH, protruding height; NBH, new bone height; CBT, cortical bone thickness; EH, exposed height.
|
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Clinical observations
Radiographic analysis: micro-CT
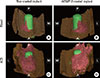 | Figure 3Three-dimensionally reconstructed images of representative micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) views. Newly formed bone appears red, the mini-implant fixture appears green, and the nasal bone appears brown, with the internal surface of the implant facing upwards. (A, B) The newly formed bone had a pyramidal shape in the BN and BC groups. (C, D) The newly formed bone had a trapezoidal shape in the AN and AC groups.(A) The BN group, (B) the BC group, (C) the AN group, (D) the AC group. BC, blood-filled and coated implant; BN, blood-filled and non-coated implant; AC, absorbable collagen sponge and coated implant; AN, absorbable collagen sponge and non-coated implant.
ACS, absorbable collagen sponge; L, lateral; M, medial; A, anterior; P, posterior.
|
Histologic observations
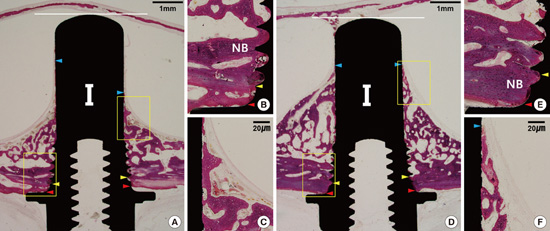
 | Figure 5Histologic images of representative sites after eight weeks of healing in the blood-filled group.(A): BN group. Bone formation in a pyramidal shape was observed. The red arrowhead indicates the outer boundary of the cortical bone layer, the yellow arrowhead indicates the inner boundary of the cortical bone layer, the blue arrowhead indicates the apical margin of new bone height (NBH), and the white horizontal line indicates the most apical line meeting the fixture. (B) The coronal part adjacent to the top area of the implant. (C) The apical part around the end of the newly formed bone. A well-maintained Schneiderian membrane was observed. (D) The BC group. (E) The coronal part adjacent to the top area of the implant. (F) The apical part around the end of the newly formed bone. NB, new bone.
|
 | Figure 6Histologic images of representative sites after eight weeks of healing in the ACS-grafted group.(A) The AN group. (B) The coronal part adjacent to the top area of the implant. (C) The apical part around the end of the newly formed bone. A well-maintained Schneiderian membrane was observed. Detached newly formed bone was seen on the apical margin of the new bone height (NBH). Newly formed bone had a relatively low density. (D) The AC group. (E) The coronal part adjacent to the top area of the implant. (F) The apical part around the end of the newly formed bone. A high bone-to-implant contact ratio (BIC) was observed. NB, new bone.
|
Histomorphometric analysis
Table 1
Linear measurements in the histometric analysis. The data are mean± standard deviation values (in millimeters) for averaged measurements on the medial and lateral sides.

 | Figure 7Mean values of bone-to-implant contact (BIC), total augmented area (TA), newly formed bone area (NBA) and fibrovascular tissue area (FVA) in the area of interest in the histometric analysis (n=6, respectively).(A) BIC, (B) TA, (C) NBA, (D) FVA.
*, significant difference, P<0.05
|




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download